SES launches SES Open Orbits™ IFC Network
SES has reached agreements-in-principle with several regional satellite network operators to launch the SES Open Orbits™ Inflight Connectivity (IFC) Network to enable seamless connectivity services to airlines around the world.

This fully interoperable Ka-band platform will combine the GEO and MEO satellite networks of SES; NEO Space Group (NSG), a subsidiary of Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund (PIF); AeroSat Link (ASL), a subsidiary of China Satcom; and Hughes Communications India (HCI).
SES Open Orbits™ aims to enable satellite operators with regional satellite coverage to be able to participate in a worldwide IFC service offering to airlines. SES Open Orbits™ will support an open architecture network where traffic can be intelligently steered from one interoperable Ka-band network to another for a seamless connected airline passenger experience across the satellites of multiple parties.
The global inflight connectivity network will use multi-orbit and multi-waveform capacity offered by regional connectivity service partners and SES to deliver resilient services, such as quality video, data, and communications offerings like those offered on the ground.
As SES is a Managed Service Provider (MSP) of Airbus’s HBCplus program, SES Open Orbits™ network will also be easily accessible through SES to airlines who are part of that program. SES, through Safran Passenger Innovations, is also working on offering SES Open Orbits™ on Boeing aircraft through the Boeing TSA process.
“By spearheading the creation of SES Open Orbits™ using an open architecture that supports multiple orbits and multiple waveforms, SES is enabling more satellite operators and inflight service providers to participate in the global market for inflight connectivity.,” said Elias Zaccack, Global Head of Aviation for SES. “SES Open Orbits™ is the future of inflight connectivity – the solution airlines must have to differentiate and future proof their IFC services. It will allow airlines to roam seamlessly across multiple satellites and orbits to deliver the best quality inflight connectivity services.”
“NSG is excited to be among the first global partners to join the SES Open Orbits inflight connectivity network,” said Philippe Carette, Head of Aerospace Segment of PIF. “Through the combination of our satellite network across Europe, Africa, and the Middle East and SES Open Orbits, we are setting new expectations across the inflight connectivity market, delivering a superior performance that goes well above and beyond traditional industry standards.”
“Connecting flights over, in and out of China, and throughout the Asia-Pacific region is extremely important to most major airlines around the world. China Satcom is extremely pleased to partner with SES to help bring a whole new level of inflight connectivity by leveraging our Ka-band network,” said Yufei Shen, Vice President at China Satcom.
Shivaji Chatterjee, CEO, President and MD of HCI, said, “Our high throughput network on GSAT-20 satellite over India will launch soon and will play a key role in the global SES Open Orbits™ aero network. We will also bring our deep experience in providing end-to-end connectivity services in multiple verticals to our partnership with SES to help ensure the best possible passenger experience to airlines using this exciting, first-of-its- ind inflight connectivity network.”
SKY Perfect JSAT selects Thales Alenia Space to build the JSAT-31 satellite
SKY Perfect JSAT and Thales Alenia Space, the joint venture between Thales (67%) and Leonardo (33%), have signed a contract to build JSAT-31, a new generation of software-defined satellite based on the Space INSPIRE (INstant SPace In-orbit REconfiguration) platform by Thales Alenia Space.

SKY Perfect JSAT’s newest satellite will rely on Space INSPIRE, a highly flexible and fully software-defined solution that offers instant on-orbit adjustment to broadband connectivity demand, while maximizing the effective use of the satellite resources.
SKY Perfect JSAT will leverage the satellite’s extreme flexibility to offer enhanced communications services all along JSAT-31’s lifespan on-orbit.
Operating both in Ka- and Ku-bands, JSAT-31 High Throughput Satellite (HTS) will offer high speed broadband services over Japan, South-East Asia, Australia, New Zealand and Pacific islands. JSAT-31 will have the largest capacity in the history of SKY Perfect JSAT satellites and is expected to launch in 2027. JSAT- 31, which is the 31st satellite procured by SKY Perfect JSAT counting from JCSAT-1, is the first satellite ordered from Thales Alenia Space. Additionally, starting with this JSAT-31, SKY Perfect JSAT will be calling their new satellites “JSAT” instead of “JCSAT” and “Superbird”.
As the prime contractor, Thales Alenia Space is responsible for the design, manufacturing, tests and on-ground delivery of the satellite as well as for the ground segment and associated services.

“SKY Perfect JSAT is aiming to enhance our overall offering by developing innovative, next-generation satellite communications services that embody ‘high speed, high capacity, high reliability, user-friendliness, and competitive pricing.’ The new JSAT-31 will play a key role in our infrastructure with its 50Gbps-class capacity and flexibility as a software- defined satellite,” said SKY Perfect JSAT President and CEO, Eiichi Yonekura. “Amidst significant market shifts, including the entry of new players, JSAT-31 will enable us to meet advanced customer needs and cater to the demands of growing markets, particularly in the expanding global and mobile sectors.“
“Understanding the significance and importance of this project to SKY Perfect JSAT, I wanted to sincerely thank our new customer for putting its trust in our company along with French and European Space agencies, CNES and ESA, for supporting our new Space INSPIRE product line,” said Thales Alenia Space CEO, Hervé Derrey. “SKY Perfect JSAT will benefit from a state-of-the-art telecommunications satellite that provides both a very high performance and a full flexibility in orbit. JSAT-31 is the first telecommunications satellite awarded to Thales Alenia Space in Japan and the first Space INSPIRE satellite in Asia.”
Rocket Lab launches first of two NASA climate change satellites
“Today we successfully launched the first of two back-to-back launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) climate change-focused mission.”

After a slight delay at T-12 minutes due to ‘ground winds,’ Rocket Lab USA, Inc. (Nasdaq: RKLB), a provider in launch services and space systems, launched the first of two, back-to-back launches, for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) climate change-focused mission.
‘Ready, Aim, PREFIRE’ lifted-off from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand at 7:41 pm NZST on May 25th, 2024 (photo above captured from the Rocket Lab video stream of the launch).
The launch deployed the first of two satellites for the PREFIRE mission to a 525km circular LEO.
Now that the first satellite has been successfully deployed, the second will follow on another dedicated Electron launch in just a few days. The launch date for the next mission, ‘PREFIRE and Ice’ will be confirmed within the next few days.
Rocket Lab’s ability to launch dedicated missions to precise orbits on demand is critical to the success of PREFIRE. The mission requires two separate satellites to follow similar trajectories but along different paths to overlap with each other every few hours near the Arctic and Antarctica and capture accurate heat loss measurements.
Both PREFIRE satellites are equipped with a device called a thermopile, similar to sensors found in household thermostats, to measure heat loss at far-infrared wavelengths which have never been systematically measured before. This data collected by the PREFIRE mission will help to improve climate and ice models and provide better predictions of how the planet’s sea level and weather are likely to change in the future.
Rocket Lab founder and CEO, Peter Beck, said, “Missions like PREFIRE demonstrate the unique benefit of Electron – dedicated launch for small satellites to precise orbits on precise schedules. We’ve demonstrated this back-to- back launch capability for NASA once before with the TROPICS mission and we’re excited to deliver it once again for PREFIRE. Climate change- focused missions like this are essential to understanding and safeguarding the future of our planet. It’s a privilege to support them on Electron.”
This successful mission was Rocket Lab’s 48th Electron launch overall and their sixth launch of 2024.
SpaceX completes bi-coastal ‘two in one’ launches
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 completed the ESA JAXA EarthCARE (Earth Cloud Aerosol and Radiation Explorer) mission launch on Tuesday, May 28 at 3:10 p.m. PDT to LEO from Space Launch Complex 4 East (SLC-4E) at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
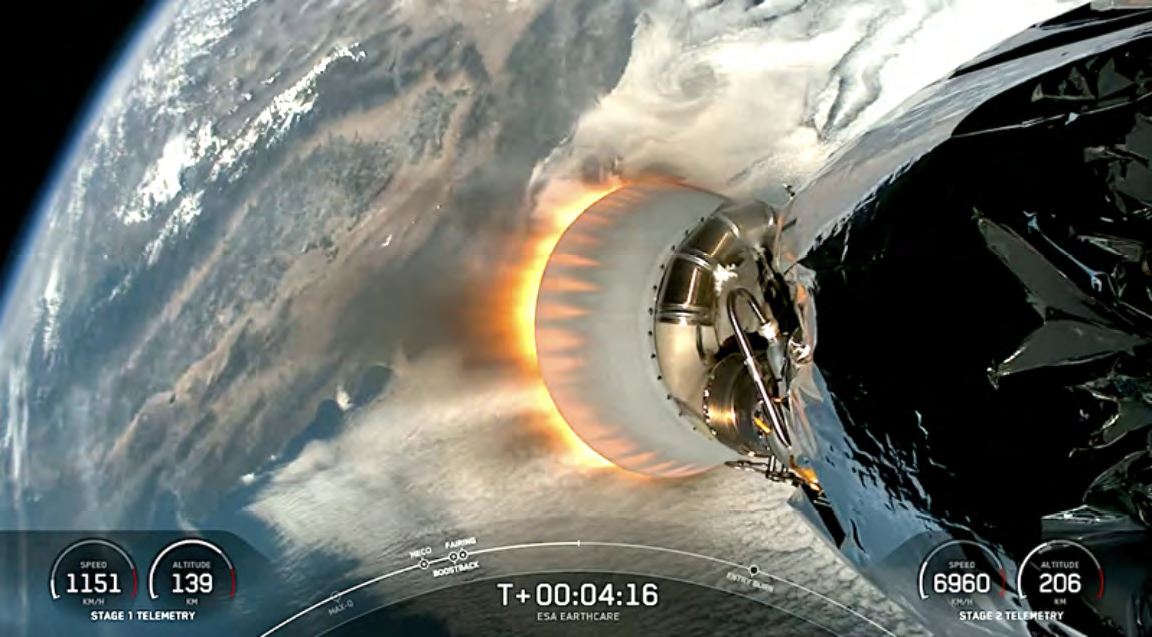

Developed as a cooperation between ESA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), EarthCARE will examine the roll that clouds and aerosols play in reflecting solar radiation back into space and also in trapping infrared radiation emitted from Earth’s surface.
EarthCARE, the most complex of all of ESA’s Earth Explorer missions, will quantify and reduce the uncertainty about the role that clouds and aerosols play in heating and cooling Earth’s atmosphere – contributing to our better understanding of climate change.
Using a suite of different instruments on one satellite, EarthCARE will be able to take different types of measurements that will complement each other, allowing scientists to build a better understanding of how clouds and atmospheric aerosols interact with solar radiation and how this affects the planet’s radiation balance — the difference between the energy that the Earth gains from the Sun and what it radiates into space.
This was SpaceX’s second launch of the day after sending a group of the company’s Starlink internet satellites to orbit from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on the same day.
A live webcast of this mission is available for replay on X @SpaceX.
This is the seventh flight for the Falcon 9 first stage booster supporting this mission, which previously launched Crew-7, CRS-29, PACE, Transporter-10, and two Starlink missions. After stage separation, the first stage landed on Landing Zone 4 (LZ-4) at Vandenberg Space Force Base.
Intelsat Multi-Orbit IFC Coming to Japan Airlines
Intelsat has been selected by Japan Airlines to provide multi-orbit, inflight connectivity (IFC) service on more than 20 Boeing 737 MAX aircraft to be delivered in the coming years.

The airline will become one of the first in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region to offer reliable, multi-orbit service using Intelsat’s new electronically steered array (ESA) antenna (pictured below, courtesy of Intelsat).
The new service will be installed by Boeing in the factory, making JAL one of the first airlines to take delivery of a Boeing aircraft with ESA inflight service ready for immediate passenger use. The first linefit aircraft is expected to be delivered in 2026.
The Intelsat ESA is less than seven centimeters tall and interoperates on both Intelsat’s family of geo-stationary satellites and its partner’s constellation of LEO satellites.

In addition to JAL’s Boeing 737s and 767s flying with 2Ku service, JAL’s subsidiary airline, J-AIR Co., Ltd.. is currently installing Intelsat’s 2Ku system on the carrier’s fleet of Embraer E190 aircraft. As recently announced, J-AIR will complete installation of the 2Ku system on 14 E190s in the coming months. When completed, J-AIR will be the first regional airline in Japan to offer inflight entertainment and connectivity services.
“Japan Airlines’ passengers will soon benefit from multi-orbit connectivity that will provide the same fast and dependable internet access they enjoy at home, thanks to wide coverage and low latency,” said Dave Bijur, Senior Vice President for Commercial Aviation. “JAL was Intelsat’s first non-U.S. commercial aviation customer, and we look forward to continuing to support JAL’s market-leading inflight connectivity service in Japan where their guests enjoy free service.”
Hisdesat’s SpainSat NG II enters the final construction phase
The communications module (CM) of Hisdesat’s SpainSat NG II secure telecommunications satellite is entering the final stretch of the construction process.

After 12 months of work in the clean room of Thales Alenia Space España, the company in charge of integrating the military Ka-band and UHF communications payloads, the CM of SpainSat NG II is ready to leave in the next days for the Airbus facilities (Toulouse) and continue there with the assembly, integration and testing (AIT) activities for the entire satellite.
The SPAINSAT NG program, owned and operated by Hisdesat, comprises two satellites — SpainSat NG I and II — which will be located in different geostationary positions to operate in X-, military Ka- and UHF bands. The capabilities and technologies incorporated in SpainSat NG place it among the most advanced in the world, including the following:
• Its active Xband antennas, in reception and transmission, pioneers in the European aerospace sector, and which will provide 16 communications beams each, with electronic configuration and orientation, developed by Airbus Defense & Space System in Spain.
• They have a transparent digital processor which, together with the antennas, allows the payload to be defined by software in almost real time, so that it really is a software-defined satellite.
• In addition, they will be equipped with the latest systems for protection against interference and cyber-attacks (anti-jamming), and will be reinforced against nuclear phenomena at high altitude.
In the development and execution of this project, it is worth highlighting the participation of Spanish industry, which has reached 45% of the workload. The Spanish divisions of Airbus Defence & Space and Thales Alenia Space have led the execution and construction process of the satellites.
The SPAINSAT NG program is the result of public-private collaboration between the Ministry of Defence and Hisdesat.The project is also financed by the Ministry of Industry and Tourism and the collaboration of the ESA (European Space Agency) financed by the Spanish Centre for the Development of Industrial Technology (CDTI) of the Ministry of Science and Innovation within the framework of the Pacis3 program.
“This is the first time that all the payloads of a telecommunications satellite have been integrated in Spain,’ said Basilio Garrido, Hisdesat’s director of operations and programs. “These are cutting- edge technologies that make these communications satellites the most advanced in Europe. These satellites will serve the Spanish Government and Armed Forces from 2025, as well as friendly governments and international organisations such as NATO. SpainSat NG I is scheduled to be launched at the end of this year, while its twin will be launche into orbit in the third quarter of 2025, in both cases with Space X.”