Comtech Completes Acquisition of UHP Networks

Comtech Telecommunications Corp. (“Comtech”) (NASDAQ: CMTL), a global leader in the advanced secure wireless communications market, announced today that it has closed the acquisition of UHP Networks Inc. (“UHP”), a leading provider of innovative and disruptive satellite ground station technology solutions. Founded in 2011, UHP is based in Canada and has developed revolutionary technology that is transforming the growing Very Small Aperture Terminal (“VSAT”) market.
UHP’s unique time divisional multiple access (“TDMA”) technology used in its VSAT platforms has software defined network functionality that offers bestinclass support for very large networks. With over 3 billion people globally who are not connected to any wireless services, the UHP acquisition allows Comtech’s customers to costeffectively provide service to endusers with the quality and reassurance of the Comtech brand and service offerings.
All UHP employees are expected to join Comtech, including Vagan Shakhgildian, the President of UHP, who will also assume the role of Senior Vice President of Network Products, leading Comtech’s efforts to expand the presence of both HEIGHTS™ and UHP’s solutions in the mobile backhaul, maritime, enterprise and defense/government markets, which all have a growing need for highspeed satellitebased networks.

The initial upfront payment of approximately $24.0 million was paid in shares of Comtech common stock. An additional payment of $5.0 million (payable in cash and/or common stock at Comtech’s option) is due upon certain conditions being met, all of which are expected to occur within the next 12 months. The purchase agreement also provides for an earnout payment of up to an additional $9.0 million (payable in cash and/or common stock at Comtech’s option) if certain agreed upon sales milestones are reached over an eighteenmonth period. Approximately 1.0 million shares of Comtech’s common stock were issued at closing in respect of the initial payment and escrow arrangements under the terms of the purchase agreement.
Comtech is not purchasing UHP’s sister company headquartered in Moscow; however, Comtech will be able to immediately market and sell UHP products to customers in that region. Except for five months of incremental amortization of intangible assets that is expected to approximate $1.0 million, the acquisition will not materially impact Comtech’s fiscal 2021 consolidated net sales or Adjusted EBITDA guidance previously issued on December 9, 2020.

Fred Kornberg, Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer of Comtech said, “The acquisition of UHP fits perfectly with our strategy of offering the most robust and advanced wireless communications solutions for our global customers. We are delighted to acquire UHP and expect use of its incredible technology to expand globally for many years to come.”
Spaceflight Inc. Signs Multiple Launch Agreements to Start 2021
Spaceflight Inc. has started the year by signing several significant launch agreements with a wide range of organizations including growing constellations needing routine and reliable launch schedules, smaller payloads requiring affordable buslike options to popular orbits, firms needing regulatory and logistical guidance, as well as those seeking a personalized taxi service from loading dock to final orbital destination.

Organizations that recently signed launch deals with Spaceflight include Lynk, Astro Digital, Kleos, BlackSky, Umbra, Orbit Fab and several, undisclosed, U.S. government payloads.
In November 2020, Spaceflight supported the successful launch of the Kleos Scouting Mission satellites (KSM1) and is now helping Kleos Space prepare for the launch of its second cluster of satellites in mid2021. The second cluster — KSF1 Polar Vigilance Mission satellites will launch into a 500 kilometer SSO aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9, under a rideshare contract with Spaceflight Inc. Kleos’ satellites will detect and geolocate maritime radio frequency transmissions to provide global activitybased information, enhancing the intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities of governments and commercial entities.
Most recently, Spaceflight coordinated its first fully dedicated PSLV mission, successfully deploying its largest customer satellite to date, Amazonia1, a nearly 700kilogram Earth observation satellite. The company also successfully deployed 14 spacecraft from its first nextgen OTV (SherpaFX) on the recordbreaking SpaceX Falcon 9 Transporter1 launch in January.
In the coming months, Spaceflight is managing two dedicated rideshare missions on Rocket Lab Electron vehicles and a deployment from the International Space Station for several U.S government spacecraft. The company is preparing several ESPAclass OTVs complete with electric and chemical propulsion for missions later this year along with many traditional rideshare missions for a total of approximately 10 launches in 2021.
Spaceflight has also signed an exclusive business development agreement with Mitsui Bussan Aerospace Co., Ltd., the leading aerospace trading company in Japan. The new alliance enables Mitsui Bussan Aerospace to expand its services to now offer Spaceflight’s global rideshare and integration services in the APAC region, capitalizing on its regional and cultural expertise.
Celebrating 10 years of providing launch services, Spaceflight has launched nearly 350 satellites across 37 missions on eight different launch vehicles, including the Falcon 9, Electron, PSLV, and Vega. It has orchestrated several industry firsts, including the first fully dedicated rideshare with 64 smallsats about the historic SSOA mission and the firstever rideshare mission to GTO with a lunar lander.

“While the pandemic initially stalled many launch deals, we’ve really seen a tremendous resurgence in organizations coming to us to handle their very diverse launch needs,” said Grant Bonin, Senior Vice President of Business Development at Spaceflight, Inc. “In addition to traditional, costeffective rideshare options, we’re also offering proven OTV solutions to satisfy a variety of orbital needs including GTO and beyond, many new dedicated launches, as well as expertise in many of the often overlooked but critical services like licensing, integration and logistics. We’re committed to ensuring the first mile of our customers’ launch is as wellexecuted as the last because both are equally critical to success.”

“Spaceflight Inc. played an important role in the success of Kleos’ first satellite mission and proved to be a proactive and flexible partner, which is essential to the success of the new space industry,” said Andy Bowyer, Kleos Space CEO. “They went above and beyond the call of duty to get our scouting satellites launched in the middle of a pandemic. We are grateful to have Spaceflight's expertise and experience at our disposal as we prepare for the launch of our second cluster."
Ursa Space Systems Names Nicole Robinson As The Firm’s President

Ursa Space Systems (Ursa Space) has appointed Nicole Robinson as the firm’s President. With support and direction from this new leadership role, Ursa Space plans to expand its product offerings for both commercial and government customers.
Nicole brings more than 15 years of satellite industry expertise, leadership skills, and business development experience to her role as President at Ursa Space. Previously at global satellite operator SES, she served as Senior Vice President of Global Government and is currently the President of the largest professional space industry association, SSPI.
Alongside current CEO and CoFounder, Adam Maher, Robinson will continue expanding Ursa Space’s commercial and government business relationships on a global scale.
Maher will remain CEO, with plans to devote more time to thought leadership, satellite community and partnership building as well as creating unique opportunities for the company.
In 2020, Ursa Space successfully expanded its commercial offerings across a number of market verticals and has plans to further grow its product lines in 2021.
“At a time referred to as the ‘golden age’ of SAR satellites, it’s clear we’re embarking on the ‘platinum age’ of data analytics, at the head of which are the brilliant men and women of Ursa Space,” Robinson said. “I am thrilled to join Ursa Space at this important inflection point for the industry and our customers; it’s an honor to join such innovators.”
OQ Technology To Manage + Operate The MACSAT Mission For ESA
OQ Technology recently signed a 2 million euros contract with the European Space Agency as part of the Luxembourg National Space program (“LuxIMPULSE”) for the onorbit pathfinder mission (MACSAT). The contract aims to foster Luxembourg and European space partnerships and involves the development of a 6U smallsat, an advanced flight payload and user terminals and their software stack.

OQ Technology will manage and operate the mission, procurement of the satellite, and also continue development and testing in lab and onorbit of satellitebased, narrowband, IoT software and algorithms (the wireless technology proposed for 5G machine communication), while EmTroniX (Luxembourg based company) will be responsible for the payload hardware and user hardware.
OQ Technology is the prime contractor and is currently in talks with candidate satellite manufacturers that would be announced soon.

OQ Technology will also install a ground station in Luxembourg to run its spacecraft flight operations from its control center in Leudelange (LU). The mission is planned for launch in 2021/2022 and will be a flagship for demonstrating advanced 5G IoT services in strategic satellite frequencies and for different endcustomers.
OQ Technology has been on the quest of providing global IoT and machine communication through satellites. What makes OQ’s offering different from others is that their technology follows the global 3GPP standard of cellular communication with a large ecosystem which allows to reduce the cost of ownership for end users as they can use the same cellular hardware with satellites instead of buying a proprietary expensive satellite modem.

The technology is also highly secure and scalable making millions of devices capable of connecting to the satellite network. OQ Technology has developed under this program (contrast to buying black box foreign IP) essential software layers of the cellular base station payload on the satellite giving them control over the performance of the system to ensure high quality of service for endusers.
“The MACSAT project represents stateofthe art development and first in the world agile nanosatellite mission dedicated to 5G technology in low earth orbit. Thanks to the technical management of the European Space Agency and businessoriented support of Luxembourg Space Agency we have advanced in a short time Narrowband IoT technology on all levels (space and ground) to be a new and attractive solution in the world of satellite communication, we are very grateful to the teams involved and happy to kick off 2021 with this collaboration,” said Omar Qaise, Founder and CEO, OQ Technology.
Kymeta’s Global Satellite Network To Be Optimized By Capanet Communications
Capanet Communications has announced that Kymeta Corporation has selected the firm’s network operations management software to optimize its global satellite network.

Kymeta will leverage the Capanet Ops Suite platform under a multiyear deal to provide critical insights into its network performance. The cloudbased software solution integrates seamlessly with the Kymeta network to provide a holistic view of network utilization, distribution, and remote usage.
The Capanet Ops Suite offers a robust network analysis engine and reporting framework that provides the network operation team realtime information to make datadriven decisions on network provisioning and configuration. The solution offers Kymeta the visibility it needs to optimize the network and reduce network costs making satellite connectivity more affordable for everyone.

Kymeta’s communications solutions are built specifically for mobility and designed to meet the needs of global defense, government, public safety, and commercial customers. In addition to delivering the world’s only commercially available, electronically steered, flat panel antenna with no moving parts, the Kymeta™ u8, the company also offers Kymeta™ Broadband, a global satellite network tailored to extremely small aperture antennas.
The integration of Capanet’s Ops Suite will enable optimal efficiency in operating the network, maximizing available bandwidth and ensuring Kymeta customers experience bestinclass quality of service.
“We are excited to add the Capanet Ops Suite to our platform of network monitoring and customer support tools,” said Victor Jimenez, Director of Network Operations at Kymeta. “The level of visibility into network performance and utilization the Ops Suite provides will help us optimize network engineering and spending, forecast future capacity needs, and ensure top quality of service availability for Kymeta™ Broadband
L3Harris To Develop Ground System Command + Control for NOAA’s Space Weather Follow On Observatory

In February of 2021, L3Harris was selected to develop and deploy the ground system command and control (C2) for NOAA’s environmental satellite program, Space Weather Follow On (SWFO).
The SWFO program is comprised of two projects: CCOR on the GOES U spacecraft and the Space Weather FollowOn L1 mission (SWFOL1).
L3Harris will perform up to two years of operations support for the SWFO observatory as part of this contract. The SWFO mission will use the ground system for NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental SatellitesR (GOESR). L3Harris’ Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) is the primary payload onboard GOESR and the company designed and built the scalable ground system for the satellite.
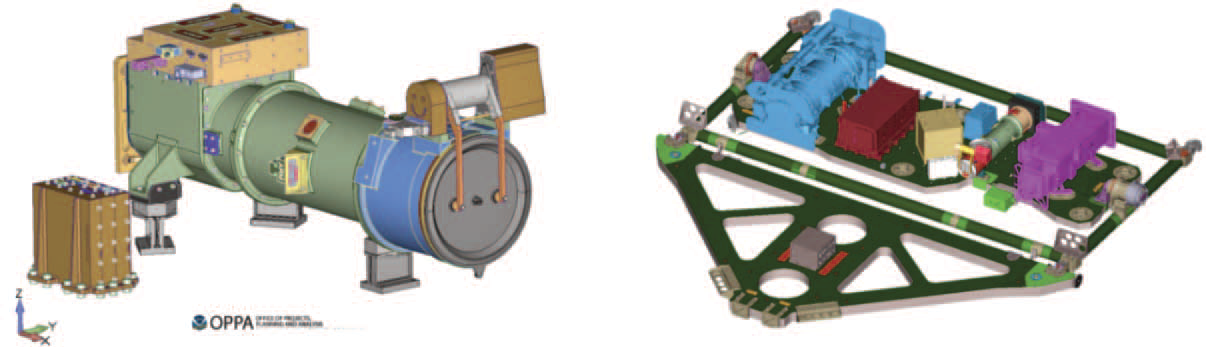
Left: A CAD rendering of the CCOR instrument.
Right: A CAD rendering of the CCOR instrument’s placement
on the GOESU satellite. Imagery is courtesy of NOAA.
The SWFO spacecraft will collect space weather data, such as continuous data from coronal mass ejections and solar flares, that can damage spacecraft and disrupt electrical power grid and communications and will provide an advanced warning for such events.
Scheduled to launch in 2025, the SWFO mission is planned as a ride share with the NASA Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe.

Photo of the L3Harris CrIS instrument,
courtesy of the company.
Plus, in related news, L3Harris delivered the Crosstrack Infrared Sounder (CrIS) instrument for NOAA’s Joint Polar Satellite System2 (JPSS2) in January of 2021. The advanced CrIS instrument provides detailed, threedimensional temperature and moisture data from both the Suomi National Polarorbiting Partnership and JPSS/NOAA satellites. JPSS2 is the second of NOAA’s latest generation of U.S. polarorbiting, nongeosynchronous, environmental satellites.
More information on NOAA’s SWFO mission is available at this direct link…
“The Space Weather Follow On (SWFO) Command and Control contract awarded to L3Harris Technologies confirms NOAA’s ongoing confidence in us to deliver a missionrelevant capability which meets their needs,” said Rob Mitrevski, Vice President and General Manager, Spectral Solutions, Space and Airborne Systems, L3Harris. “L3Harris initially designed the GOESR ground system as an Enterprise Solution scalable to efficiently add new missions, such as SWFO, and deliver critical data to a variety of end users.”

Photo of the L3Harris ABI, courtesy of the company. 
Artistic rendition of the GOESR satellite on orbit


