UK’s space industry test facility plans
The UK is taking their space industry plans to the next step with contracts worth £19 million for the first of the major facilities — the National Satellite Test Facility (NSTF), which is to be built and operated by STFC’s RAL Space on behalf of the UK government.
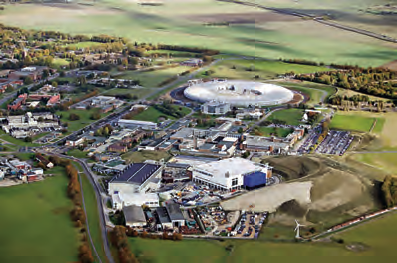
The Harwell Space Cluster. UK.
The contracts are the first steps in meeting the UK space industry’s need for a set of co-located world-class facilities for environmental testing of space payloads and satellites.
The three successful contractors will supply the large space test chamber, vibration facility and the combined electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and antenna measurement system.
Satellite test facilities at this scale, in one location do not currently exist in the UK.
Once operational in 2021, the NSTF will provide the space sector across the UK with all the major testing facilities they need under one roof, without incurring expensive international shipping costs.
The NSTF will expand and complement the existing RAL Space facilities at the heart of the Harwell Space Cluster.
This major national infrastructure will support the UK’s space sector as it seeks to capitalize on the estimated 3,500 to 10,000 satellites that are due to be launched by 2025.
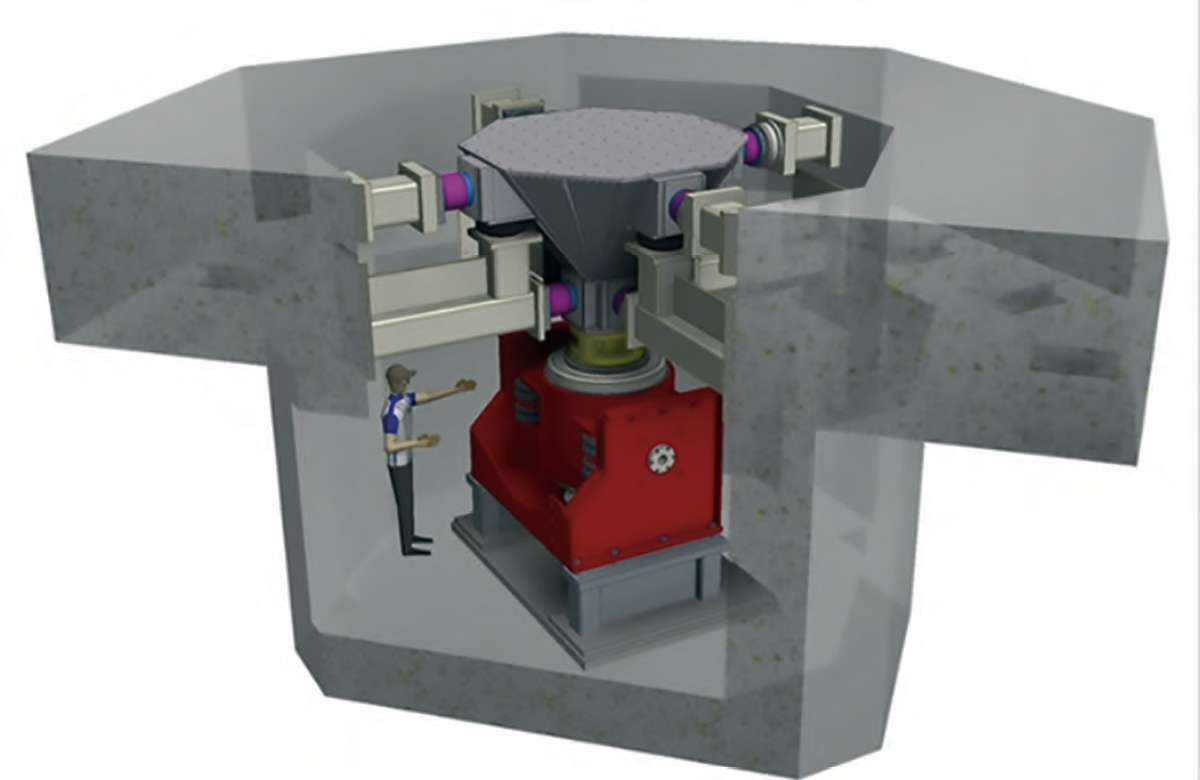

Artistic impression of the Large Space Test Chamber.
Image is courtesy of NVT Group.
Artistic impression of the vibration facility, vertical system.
Image is courtesy of NVT Group.
Sean Stewart, NSTF Project Manager, RAL Space said, “Alongside the existing RAL Space assembly, integration and validation facilities, the NSTF will put all the test equipment needed by industry and academia in one place and accessible to everyone. Awarding these contracts is one of the early and hugely significant milestones towards building the NSTF.”
The large space test chamber will be built by Angelantoni Test Technologies and delivered in six large loads to be assembled on site at the NSTF.
With an internal, usable size of 7 meters in diameter by 12 meters long, the chamber will be the largest of its kind in the UK and among the giants of Europe.
It has a temperature range of 95K to 400K, providing the conditions needed to test a variety of complex science missions as well as commercial satellites for Earth orbit.
The Astroscale and Catapult companies hope for involvement in this opportunity. Astroscale Ltd., the UK branch of Astroscale Pte Ltd. (Astroscale), is leading a £4 million grant from the UK Government to help establish a National In-Orbit Servicing Control Facility at the Satellite Applications Catapult in Harwell, Oxfordshire. The National In-Orbit Servicing Control Facility will support advanced robotics activities in the hostile environment of space, specifically enabling the provision of a commercial service for de-orbiting smallsats.
The new facility will initially control Astroscale’s pioneering ELSA-d mission, the first project to demonstrate the core rendezvous, capture and de-orbit technologies used by the ELSA (End-of-Life Service by Astroscale) program.
ELSA-d is comprised of two satellites, the ‘Chaser’ and the ‘Target’. The ‘Chaser’ is equipped with optical sensing instruments and a capture mechanism which will attach to a Docking Plate on the ‘Target’ satellite. The Chaser and Target will then de-orbit together, burning up as they re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere.
Upwards of 15,000 satellites are expected to be launched over the next 10 years, including into orbits that are already highly populated.
There are growing concerns that a collision between uncontrolled space debris and an active satellite could cause global commercial and security risks and lead to a cascading debris effect making these orbits unsustainable.
This issue was highlighted in August 2017 when the governments of Japan and the UK signed a memorandum of understanding to strengthen collaboration on mitigating space debris.
As part of the operational system, the new Centre will use highly advanced algorithms developed from state-of-the-art European Space Agency (ESA) software and technologies used in the recent pioneering Rosetta mission.
The grant has been awarded through the Government’s Industrial Strategy Challenge Fund, which supports innovative businesses that address important industrial and societal challenges.
astroscale.com/
sa.catapult.org.uk/
www.harwellcampus.com/space-cluster/
Hiber + KSAT are grounded
Dutch company Hiber and Norwegian KSAT have announced a new, long-term partnership to create a state-of-the-art and reliable ground station infrastructure for Hiber’s Low Power Global Area Network (LPGAN), named Hiberband.

Artistic rendition of a Hiber smallsat.

The first two satellites of the Hiberband constellation (Hiber One and Hiber Two) will be launched in the last quarter of this year.
The new ground station network starts with a redundant network with two stations; one on top of Hiber’s Research and Development Centre in Delft, the Netherlands, and one on Svalbard in Norway.
The ground stations use motorized 4.5 meter Cobham S-band antennas that will receive the data messages from Hiber’s satellites.
Both stations also have UHF-VHF antennas for the constellation Telemetry, Tracking and Command (TT&C) and are connected to the Hiber Mission Control Centre in Delft.
Both antenna systems are extremely robust and built to last for the coming decade.
KSAT’s Svalbard Ground Station is uniquely located at 78 degrees North, close to the North Pole, which optimizes contact time for communication with the Hiber satellites that fly in a polar orbit.
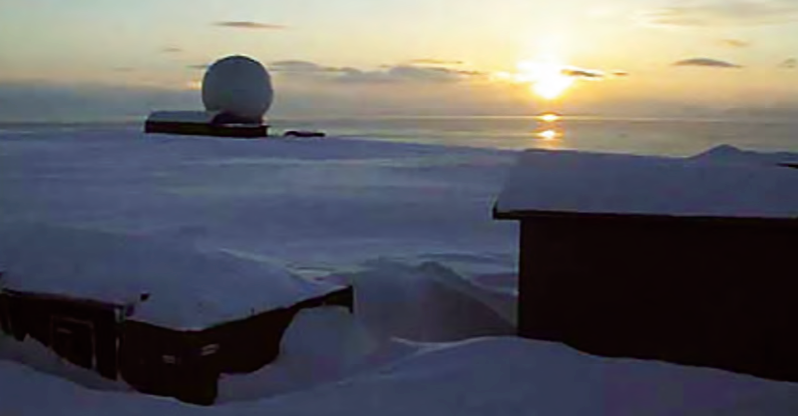 KSAT’s Svalbard ground station.
KSAT’s Svalbard ground station.
KSAT has introduced KSATLite, a global integrated ground network optimized for smallsats and smallsat constellations. Building on the foundation of expertise that KSAT has acquired through 50 years of ground station service operations, KSATLite is able to leverage many of the key strengths of the existing infrastructure.
hiber.global/
www.ksat.no/
Boeing lands Millennium Space
Boeing [NYSE: BA] will acquire Millennium Space Systems, a provider of agile, flight-proven smallsat solutions, under an acquisition agreement that will expand Boeing’s satellite and space portfolio, talent and capabilities.
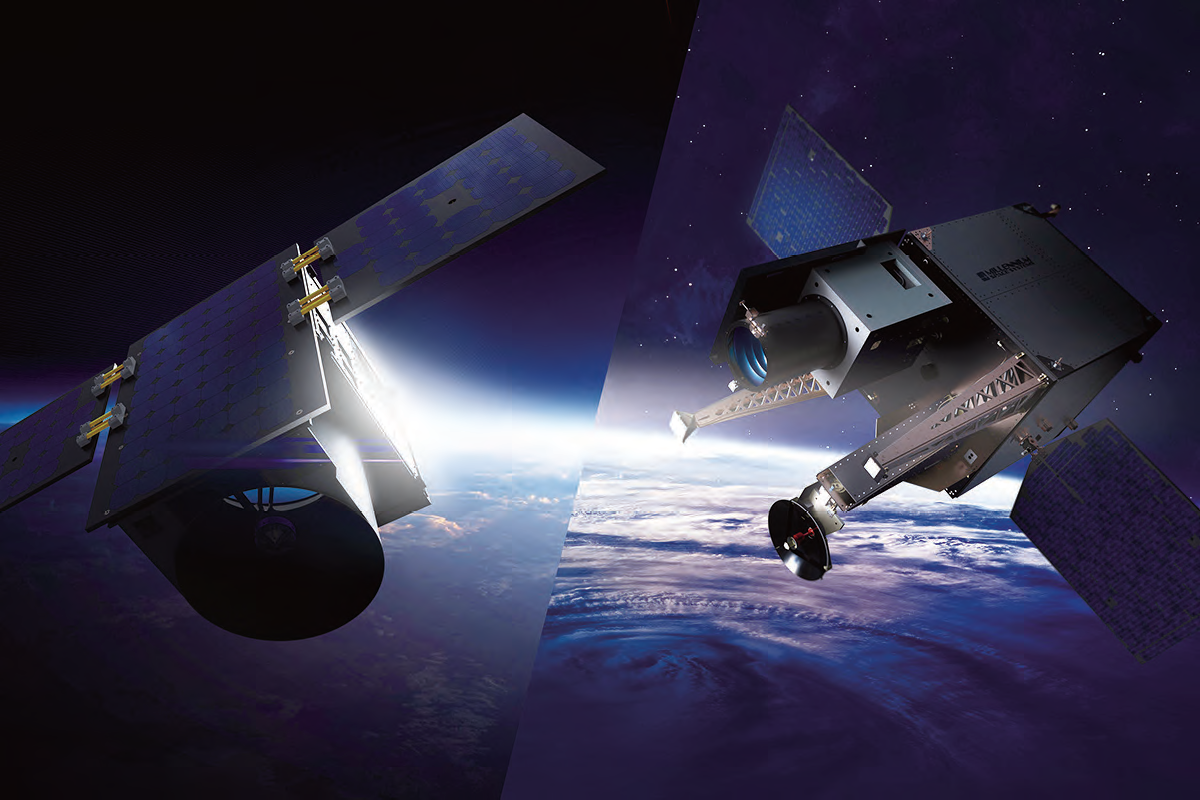

Millennium Space Systems two satellite platforms:
ALTAIR™, which is constellation optimized, 10 to
200 kg., and AQUILA™, offering precision pointing,
200 to 2000 kg. Images are courtesy of Millennium
Space Systems.
Millennium Space Systems was founded in 2001 and is based in El Segundo, California. With approximately 260 employees, the company has developed high-performance satellites for exacting missions ranging from 50 to more than 6,000 kg.
The acquisition, which is subject to customary conditions, is expected to close by the end of third quarter 2018. Once finalized, Millennium Space Systems will become a Boeing subsidiary, operating under its current business model and reporting to Mark Cherry, VP and GM of Phantom Works.
The terms of the agreement were not disclosed. The transaction will have no impact on Boeing’s 2018 financial guidance or the company’s commitment to returning approximately 100 percent of free cash flow to shareholders.
Stan Dubyn, the CEO of Millennium Space Systems, said that he is proud of the talented and dedicated team the company has built at Millennium Space Systems over the past 17 years. By combining the firm’s tools, talent, technologies and culture, they’ll be able to do even more incredible things as part of Boeing.
Leanne Caret, the President and CEO of Boeing Defense, Space and Security, added that Millennium Space Systems’ expertise in vertically-integrated smallsat solutions perfectly complements Boeing’s existing satellite portfolio and will allow the company to meet the needs of a diverse customer set. Boeing looks forward to incorporating Millennium Space Systems’ end-to-end mission solution capabilities into the service offerings in satellite operations and data solutions.
www.boeing.com
www.millennium-space.com
Comtech EF Data’s China contract
Comtech EF Data has won a tender by a major Mobile Network Operator (MNO) in China to replace the older generation of lower efficiency modems to provide more reliable services at a much lower OPEX.
 Comtech EF Data’s CDM-625A satellite modem. DoubleTalk
Comtech EF Data’s CDM-625A satellite modem. DoubleTalk
Carrier-in-Carriers is based on the company’s patented “Adaptive Cancellation” technology that allows transmit and receive carriers
of a duplex link to share the same transponder bandwidth.
This latest order for $1.9 million, specified Comtech EF Data’s CDM-625A Advanced Satellite Modems, Up & Down Frequency Converters and the CX-U Series RAN Optimization by their subsidiary, Memotec.
According to the company, the purchase highlights the customer’s long-standing confidence in the Comtech mobile backhaul solution.
For more than 10 years, the MNO has used Comtech’s infrastructure equipment to support 1000+ sites that are serving China’s rural communities and disaster recovery efforts.
By leveraging Comtech EF Data’s bandwidth efficient satellite modems and Memotec’s 2G traffic optimization solutions, the MNO has been extremely successful in lowering the total cost of ownership (TCO) of backhauling traffic over satellite.
Some of the leveraged features include industry best VersaFEC-2 Forward Error Correction, the DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier bandwidth compression, lower rolloffs, and 2G TDM optimization.
Fred Kornberg, President and CEO of Comtech Telecommunications Corporation, said the company is pleased that this customer has — once again — selected the firm’s mobile backhaul solution, demonstrating their strong faith in Comtech EF Data products and the China-based sales and support staff.
He added that this equipment will provide the performance that enables MNOs to operate at their highest level of performance and allows them to truly monetize investments, to drive down OPEX and to increase profitability.
www.comtechefdata.com
Space Force to become real...
The U.S. Defense Department will establish a sixth branch of the armed forces, the U.S. Department of the Space Force, by 2020, Vice President Mike Pence announced.

In a speech at the Pentagon, the Vice President also announced plans to establish a new combatant command — U.S. Space Command — as well as a Space Operations Force and a new joint organization called the Space Development Agency. The announcement follows a seven-week review by DoD, directed by President Donald J. Trump, of “the process necessary to establish a space force as the sixth branch of the armed forces.”
“In his inaugural address to the nation, President Trump declared that the United States stands ‘at the birth of a new millennium, ready to unlock the mysteries of space,’” Pence said.
Space Force
Just as advances in aviation technology drove the emergence of air as a new battlefield in the 20th century, advances in space technology have made it clear that space is the new battlefield for the 21st century, the vice president said. The U.S. will meet the emerging threats on this new battlefield, he said, and carry on the cause of liberty and peace into the next great frontier.
“The time has come to establish the United States Space Force,” Pence said.
The new branch will be separate from, but equal to, the five other branches, he said.
“To be clear: the Space Force will not be built from scratch, because the men and women who run and protect our nation’s space programs today are already the best in the world,” the vice president said. “Across this department and our intelligence agencies, there are literally tens of thousands of military personnel, civilians and contractors operating and supporting our space systems -- and together, they are the eyes and ears of America’s warfighters around the globe,” he added.
Peace Through Strength
Actions by U.S. adversaries make it clear that space is already a warfighting domain, the vice president said.
“For many years, nations from Russia and China to North Korea and Iran have pursued weapons to jam, blind and disable our navigation and communications satellites via electronic attacks from the ground,” Pence said. “But recently, our adversaries have been working to bring new weapons of war into space itself.”
In 2007, China launched a missile that tracked and destroyed one of its own satellites, the vice president said. And Russia is working on an airborne laser to disrupt space-based systems, he added.
“Both nations are also investing heavily in what are known as hypersonic missiles designed to fly up to 5 miles per second at such low altitudes that they could potentially evade detection by our missile defense radars,” Pence said. “In fact, China claimed to have made its first successful test of a hypersonic vehicle just last week.”
In every domain, America will always seek peace, the vice president said. “But history proves that peace only comes through strength,” he added. “And in the realm of outer space, the United States Space Force will be that strength.”
Action Steps
A report to be released shortly represents a critical step toward establishing the Space Force, Pence said. It identifies several actions that DoD will take as the nation evolves its space capabilities, “and they are built on the lessons of the past,” Pence said.
First, the report calls for the creation of the U.S. Space Command, a new unified combatant command for space.
“This new command … will establish unified command and control for our Space Force operations, ensure integration across the military, and develop the space warfighting doctrine, tactics, techniques, and procedures of the future,” he said.
Second, the report calls for the establishment of a Space Operations Force — an elite group of joint warfighters, specializing in the domain of space, who will form the backbone of the nation’s newest armed service. This force will draw from across the military to provide space expertise in times of crisis and conflict, Pence said.
“Third, the report calls for a new joint organization — the Space Development Agency — that will ensure the men and women of the Space Force have the cutting-edge warfighting capabilities that they need and deserve,” he said.

Finally, the report calls for clear lines of responsibility and accountability to manage the process of establishing and growing the Space Force, including the appointment of an assistant secretary of defense for space, the vice president said.
“Creating a new branch of the military is not a simple process,” Pence noted. “It will require collaboration, diligence and, above all, leadership. As challenges arise and deadlines approach, there must be someone in charge who can execute, hold others accountable, and be responsible for the results.”
Ultimately, Congress must establish the new department, the vice president said. “Next February, in the president’s budget, we will call on the Congress to marshal the resources we need to stand up the Space Force, and before the end of next year, our administration will work with the congress to enact the statutory authority for the space force in the National Defense Authorization Act,” he said.
www.defense.gov/
It’s about time...
Orolia’s respected atomic clock solutions have been selected for the Galileo Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS).

Under contracts totaling 26M euros, Orolia will deliver the most stable, accurate timing solutions available to date building on Orolia’s reputation of providing the most precise timing technology for satellite programs.
The quadruple clock redundancy designed into each satellite ensures that even if a failure occurs, overall system performance will not be compromised.
Each satellite will carry two Rubidium atomic clocks and two passive Hydrogen Masers. Under these contracts, Orolia will supply its Spectratime Rubidium Atomic Frequency Standard and its Passive Hydrogen Masers physics package for an additional 12 Galileo satellites.
These new satellites will reinforce Orolia’s world leadership position in the number of active atomic clocks in space, including more than 100 in the Galileo system.
Orolia CEO Jean-Yves Courtois stated that they’re honored to continue supporting the European Commission with precise timing for Galileo. These new contracts further emphasize Orolia’s position as the world’s leading provider of resilient positioning, timing and navigation (PNT) solutions.
In addition to serving as Europe’s independent PNT source, Galileo can also serve as a secondary signal source for systems such as GPS, GLONASS or BeiDou in the event of service disruption. Galileo delivers the highest accuracy of any GNSS system in operation today.
The quadruple clock redundancy designed into each satellite ensures that even if a failure occurs, overall system performance will not
be compromised.
More than 150 Orolia Spectratime atomic clocks are flying to support Galileo, IRNSS, BeiDou, GAIA and other missions, some for more than ten years. Orolia provides the expertise necessary to design solutions for highly reliable space applications.
Orolia designs and manufactures a full range of high-performance, low cost GNSS synchronized crystal solutions, Rubidium and Maser sources, smart integrated GNSS reference clocks, rugged PNT devices, GNSS simulation and clock testing systems that support applications including defense, government, space, maritime, enterprise networks, aviation and telecommunications.
Also, in response to the growing threat of GPS/GNSS interference in military operations, Orolia presented their Assured Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) Solutions at the Eurosatory exhibition that occurred earlier this year.
In addition to showcasing their proven technology solutions, Orolia also distributed their latest whitepaper, “A Holistic Approach to Trusted, Resilient PNT,” which presents innovative strategies and opportunities to protect against GPS/GNSS spoofing and jamming in military environments.
The world’s leading provider of Resilient PNT solutions, Orolia is also a European leader in delivering trusted technology solutions for critical programs such as the European GNSS system Galileo, and the European Commission’s Horizon 2020 HELIOS project for next generation air, land, and sea search and rescue technology.
Orolia recently announced a 26 million euros contract to support new Galileo satellites and introduced their GADSS ELT commercial aircraft emergency tracking beacon as part of the HELIOS project at the Paris Air Show last year.
On the global stage, Orolia has also recently received a $34 million contract from the U.S. military to provide personnel recovery devices to covertly locate and help rescue warfighters who are lost, captured or in distress.
“At Orolia, we’re committed to delivering innovative, yet practical technology solutions to meet Europe’s most critical defense and security needs,” said Orolia CEO Jean-Yves Courtois. “We provide timing and location data you can trust, and our solutions are often the first line of defense in protecting critical intelligence, navigation and communications systems.”
Military forces require continuous access to trusted PNT resources anytime, anywhere. Yet vulnerabilities give adversaries the opportunity to deny access to, or even falsify, navigation and timing data. Orolia delivers Assured PNT capabilities for warfighters to detect, mitigate and help prevent threats such as interference, jamming and spoofing.
Orolia’s solutions are flexible, scalable and configurable based on required features, performance and budget considerations.
Their complete, end-to-end solutions include GNSS jamming and spoofing detection, alternative sources of robust, encrypted satellite-based PNT data, and military personnel recovery systems.
www.orolia.com/





