Evaluation Underway by Shenzhen Airlines of Inmarsat SB-S via Cobham AVIATOR 300D
Shenzhen Airlines is launching their in-flight evaluation of SwiftBroadband-Safety (SB-S), Inmarsat’s next-generation, IP-based broadband service for the flight deck.

Cobham’s AVIATOR 300D
The SB-S platform, which will be installed on Shenzhen’s Airbus 320 aircraft using Cobham avionics’ AVIATOR 300D hardware, will deliver powerful and flexible in-flight communications and secure, real-time, in-air information to enhance Shenzhen’s safety, security and operational capabilities — both in the air and on the ground.
The Shenzhen partnership is part of a joint venture between Inmarsat, Beijing Marine Communication & Navigation Company, Ltd. (MCN) and Aviation Data Communication Corporation (ADCC) to provide aviation safety services to the rapidly growing Chinese market. Under this partnership, MCN and ADCC will deliver satellite voice, ACARS (Aircraft Communications Addressing & Reporting System) and data services. MCN will serve as project manager for Shenzhen’s SB-S evaluation process.
In addition to compliance with the Civil Aviation Authority of China (CAAC) mandates CCAR 121 and AC-121, Shenzhen Airlines will focus its evaluation on three core SB-S SATCOM capabilities, including:
Satellite Voice (satvoice Communications — Two-channel satellite-based services that enable faster and high-quality voice communication between the flight deck crew and its designated contacts on the ground, including air traffic controllers and airline operations personnel.
Integral Global Flight Tracking — This enhanced, live tracking feature pinpoints an aircraft’s location through regular transmission of position reports. SB-S flight tracking enables the airline and Air Traffic Control (ATC) to know where the aircraft is and to understand its status in real time, which is essential for both safety and delivery of fuel-efficient flight.
ACARS Over IP — Traditionally used to communicate with both the Airline Operations Centre and ATC, this short-text capability over IP is a prerequisite for FANS 1/A compliance in remote oceanic areas.
Shenzhen Airlines also will be able to take advantage of other SB-S platform features, including real-time electronic flight bag applications, such as networked graphical weather and, ultimately, flight data streaming (“Black Box in the Cloud”). And, in addition to providing critical flight safety solutions, its high-speed communications capabilities also allow SB-S to deliver operational savings to airlines in the form of reduced fuel costs, improved efficiency and enhanced security. A recent study by Helios showed that satellite communications has already delivered US$3 billion in benefits to airlines to date (see link below).
Through its SB-S evaluation, Shenzhen Airlines is preparing for China’s explosive growth in passenger demand, which, according the International Air Transport Association (IATA)*, is expected to more than double over the next 20 years. IATA also predicts that China will displace the United States as the world’s largest aviation market around 2024*.
Much of this demand will be for international travel and Shenzhen is anticipating this demand by employing next generation satellite connectivity, which allows aircraft to travel in oceanic areas and across remote continental areas where terrestrial networks are not established. These satellite-based capabilities will allow Shenzhen to offer passengers a vastly wider range of service destinations that, until now, could not be realized due to the decades-old limitations of traditional, ground-based communications.
Cheng-Yu Tang, General Manager, China Cobham SATCOM, reported that Shenzhen’s decision to evaluate SB-S demonstrates that one of the China’s largest airlines has full confidence in the performance of the Cobham AVIATOR 300D system and the Inmarsat SB-S platform. This evaluation also supports the company’s development of communication technologies to meet the future needs of the aviation community.
Captain Shao Bin, Vice President of Operations for Shenzhen Airlines, noted that as China’s skies become more crowded and advanced flight-tracking capabilities become a necessity in the region’s airspace, Shenzhen wants to be at the forefront of this exciting next chapter of aviation history and is looking forward to evaluating SwiftBroadband-Safety as a pioneering, satellite-based connectivity solution that will enable Shenzhen to offer enhanced safety, increased capacity and more efficient operations to our passengers – both in China and beyond.
Captain Mary McMillan, Vice President of Safety and Operational Services at Inmarsat’s Aviation business unit, added that as China continues its path toward becoming the world’s largest passenger aviation nation, Shenzhen is making an important move to ensure it is ready to not only expand its domestic service offerings but also meet Chinese passengers’ growing demand for international travel. As the trusted provider of aviation safety and operational services, Inmarsat’s work with Shenzhen and company partners will help the company to understand how SB-S can optimize their flight deck and aircraft operations as they enter this new era in Chinese aviation.
*Source: IATA 20-year Passenger Forecast (Oct. 18, 2016)
shenzhenair.com/
www.inmarsat.com/aviation/complete-aviation-connectivity/swiftbroadband-safety/
www.cobham.com/
Speedcast Becomes Tampnet’s First Partner for Gulf of Mexico Service
Speedcast International Limited (ASX: SDA) has signed a reseller agreement with Tampnet for 4G/LTE services in the Gulf of Mexico — this agreement marks Speedcast as the first service provider to partner with Tampnet for its high capacity offshore network in the region.

Tampnet announced in March that it had reached 25 percent of its planned coverage for the Gulf of Mexico.
Upon completion at the end of 2018, Tampnet will have a low latency, high capacity fiber and microwave network made up of more than 60 base stations that they estimate will cover 98 percent of all manned offshore assets.
Tampnet currently owns a similarly designed offshore low-latency network in the North Sea which has been in operation since 2001. Offshore LTE has been available in the North Sea since 2013.
Tampnet’s new Gulf of Mexico network comes at a time when the oil and gas industry is looking to advancements in communications to help better support the operations of offshore platforms, increase safety measures and improve crew morale.
Additionally, the network is being designed to provide ample fiber-based LTE coverage for deep-water exploration activities which represents a first for the Gulf of Mexico.
The LTE network will be supported by the largest high-capacity, low-latency backhaul network in the Gulf of Mexico — based on state-of-the-art, carrier-grade microwave equipment and the only offshore fiber network in the Gulf of Mexico, making the LTE network and services offering truly unique.
Speedcast will leverage Tampnet’s Gulf of Mexico high-capacity network as part of its connectivity portfolio to support current and future services.
www.speedcast.com
A First for China... Cargo Spacecraft Launched
China has launched the nation’s first cargo spacecraft, Tianzhou-1, into space — this is a crucial step for the country as they plan to build a space station by 2022.

The Tianzhou 1 cargo craft launched aboard a Long March 7 rocket Thursday. Credit: Xinhua
Lifted by a Long March-7 Y2 carrier rocket, Tianzhou-1 roared into the air from the Wenchang Space Launch Center in south China’s Hainan Province on April 20.
In space, the cargo ship will dock with the orbiting Tiangong-2 space lab, provide fuel and other supplies and conduct space experiments before falling back to Earth.
China aims to build a permanent space station that is expected to orbit for at least 10 years and the debut of the cargo ship is important as the spacecraft will act as a courier to help maintain the space station.
Without a cargo transportation system, the station would run out of power and basic necessities, causing it to return to Earth before the designated time.
China becomes the third country in addition to Russia and the United States to master the technique of refueling in space.
“The Tianzhou-1 mission includes the breakthrough of in-orbit refueling and other key technologies needed to build a space station, laying a foundation for future space station operations,” said Bai Mingsheng, chief designer of the cargo ship.
The cargo ship is 10.6 meters long and has a maximum diameter of 3.35 meters. Its maximum takeoff weight is 13.5 tonnes, enabling it to carry over 6 tonnes of supplies.
Tianzhou-1 is larger and heavier than Tiangong-2, which is 10.4 meters in length and has a maximum diameter of 3.35 meters, weighing 8.6 tonnes.
Bai said that supplies loaded on the cargo spacecraft are nearly as heavy as the ship’s own weight, exceeding the loading capacity of Russian cargo ships in active service.
Tianzhou-1 will dock with Tiangong-2 three times, said Bai. After the first docking, aerospace engineers will test the controlling ability of the cargo spacecraft over the two spacecraft.
The second docking will be conducted from a different direction, which aims to test the ability of the cargo ship to dock with the space station from different directions.
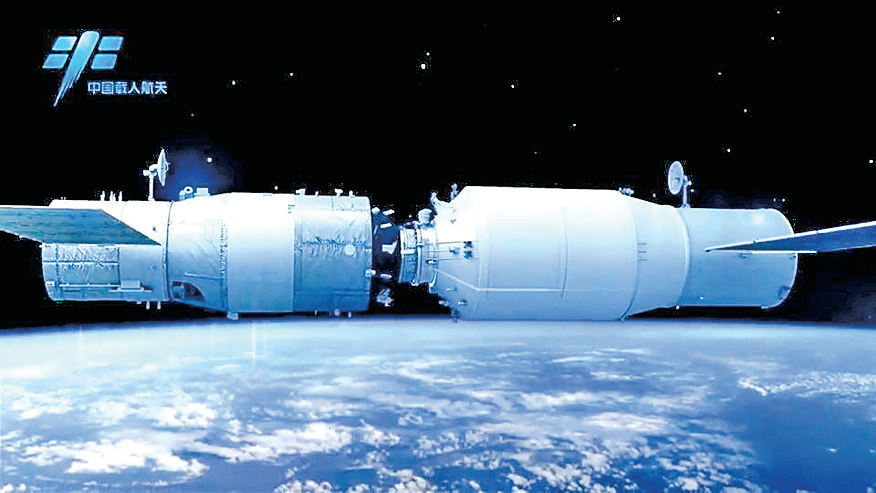

China’s Tianzhou-1 cargo spacecraft. Image is courtesy of Xinhua.
In the last docking, Tianzhou-1 will use fast-docking technology. Previously, it took China about two days to dock, while fast docking will take about six hours, according to Bai.
Refueling is conducted during docking, a process that is much more complicated than refueling vehicles on land.
The refueling procedure will take 29 steps and will last for several days each time.
MEASAT’s Video Neighborhood Continues to Grow
MEASAT Satellite Systems Sdn. Bhd. (“MEASAT”) announced that Encompass Digital Media (“Encompass”) is expanding their presence on MEASAT’s leading 91.5 degrees E video neighborhood.

Eight (8) more channels are now available from the company’s satellite at the 91.5 degrees East slot::
• HITS HD
• KIX360 SD
• Zee Sine SD
• beIN SPORTS 1
• beIN SPORTS 2
• beIN SPORTS 3 (beIN Asia Pacific’s Indonesia feeds)
• WAKUWAKU JAPAN SEA HD
• WAKUWAKU JAPAN Taiwan HD
These channels are distributed to TV platforms in more than 100 countries across APAC.
Deepakjit Singh, Chief Innovation Officer, Encompass stated that Encompass is delighted to increase their video line-up in MEASAT’s 91.5 degrees E video hotslot. With satellite still the preferred means for linear TV distribution for emerging markets, MEASAT and Encompass are working together to expand in this segment. He added that they look forward to continue growing with MEASAT in the years to come.
Yau Chyong Lim, Chief Operating Officer, MEASAT added that by strengthening their partnership, MEASAT and Encompass continue to increase compelling content for Asia Pacific audiences. Video continues to be MEASAT’s core focus and they will continue to grow this segment in cooperation with partners, content providers and channel operators.
The 91.5 degrees E prime video hot slot is home to the MEASAT-3, MEASAT-3a and MEASAT-3b satellites, forming the region’s strongest video neighborhood. From 91.5 degrees E, MEASAT supports broadcasters and DTH operators to distribute UHD, HD and SD channels to audiences across Asia, Australia, East Africa and South Eastern Europe.
www.measat.com/
Launch Date in India for SSG’s Smallsats
Nanosatellite telecommunications provider Sky and Space Global (ASX: SAS) has successfully integrated their ‘Three Diamonds’ smallsats into the launch pod of Innovative Space Logistics BV in the Netherlands.

Sky & Space Global’s smallsats are set to disrupt the telco space by enabling the provision of less expensive voice, data and instant messaging services to areas in South and Central America, and Africa and Asia. Airliners and shipping companies in the coverage area will also be serviced.
The Three Diamonds will now be transported from the premises of Innovative Space Logistics BV in the Netherlands to India ahead of the upcoming launch, which is scheduled for late May.
These nanosatellites will be launched from the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
The PSLV launch system has had 37 successful launches so far and its most recent PSLV–C37 was marked by the successful deployment of a record 104 satellites in sun-synchronous orbit.
The integration of the nanosatellites follows the successful completion of the testing of SAS’s Ground and Space Communication systems and software in early April and represents another major milestone in the journey to the commercial launch in May.
This news follows the company announcement on April 6 that their Three Diamonds nanosatellites launch window has been confirmed for late May of this year.
www.skyandspace.global/
India’s ISRO Planning a J-V for Launch Vehicle Manufacturing
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has plans to forge a joint venture with an industrial consortium to build rockets, this according to the Indian infosite, Daily News & Analysis.
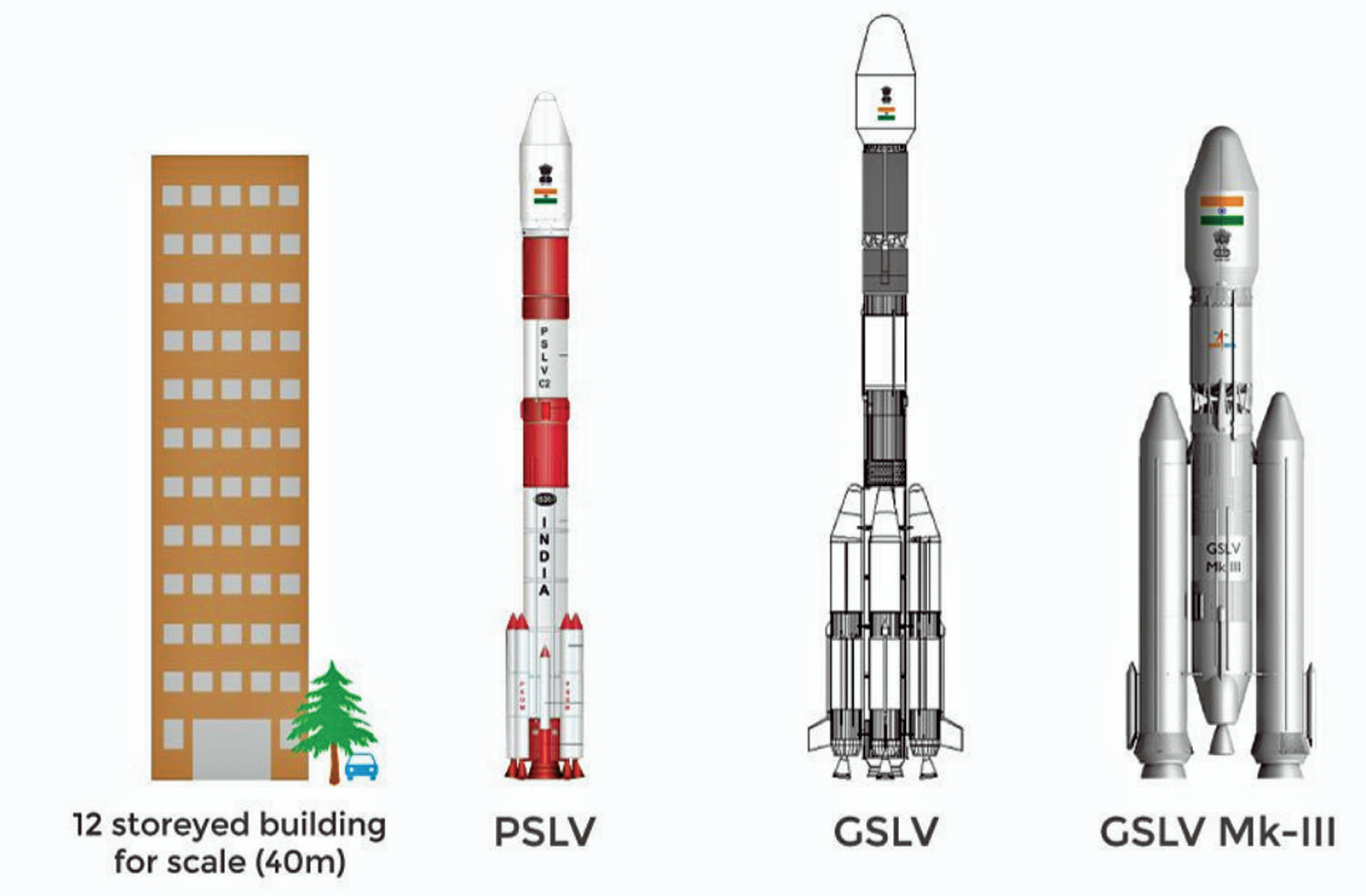
Infographic depicting the agency’s current launcher family. The image is courtesy of ISRO
The ISRO plans to forge a joint venture with an industrial consortium to build rockets.
“We are (currently) using significant amount of things from the industry. If you take launch vehicles (space rockets), 80 per cent of our work, we do with the industry (which are making space-related equipment) today,” the agency’s Chairman A S Kiran Kumar said in an interview.
The space agency is looking to form a joint venture with an industry consortium (to build polar satellite launch vehicle or PSLV), with the first launch planned for 2020-21 under this proposed entity.
Kumar added, “We are now going through the process of establishing those mechanisms and getting the necessary approvals.”
According to the ISRO Chairman, the consortium would have less than half-a-dozen companies from the industry, which would, however, have many sub-contractors working with them.
In the area of satellites, the ISRO has given a contract to a company for assembly, integration and testing of spacecraft. “We are getting many of the sub-systems done through the industry across the country,” he said.
Asked if he sees the ISRO as a pure R&D player outsourcing all other work to the industry, Kiran Kumar said, “It should be an ideal thing to happen in the long run because if the industry is able to do what is required, then definitely it’s a better opportunity for us (ISRO). The ISRO recognizes the contributions of the industry in meeting the demands of national needs of the space systems. The participation of the industry in the realization of space systems such as spacecraft, launch vehicles, establishment and operations of ground systems and facilities and implementation of application programs have been steadily growing.”