Rohde & Schwarz expands testing equipment portfolio to support Telesat Lightspeed
State-of-the-art signal generators, spectrum and signal analyzers are key measuring tools to ensure optimal performance of next-generation Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite networks—Rohde & Schwarz advanced measuring technology plays a key role in modeling and evaluating performance of the Telesat Lightspeed integrated space and terrestrial network.
Rohde & Schwarz has enhanced the company’s measurement options across its testing equipment portfolio to meet the unique requirements of advanced, next-generation satellite networks.

Rohde & Schwarz’s equipment portfolio is
playing a pivotal role in the progression of
the latest satellite generation development.
Image is courtesy of Telesat.Telesat (Nasdaq and TSX: TSAT), one of the world’s largest and most innovative satellite operators, has been leveraging Rohde & Schwarz’s advanced testing equipment to optimize service link design of its Telesat Lightspeed LEO network. Telesat Lightspeed aims to revolutionize global satellite connectivity by providing ubiquitous, affordable, high-capacity links at fiber-like speeds, with global service anticipated by the end of 2027.
Telesat uses the Rohde & Schwarz signal generator R&S SMW and spectrum and signal analyzer R&S FSW to qualify and verify new RF chipsets and satellite modems across multiple vendors. The instruments are employed for testing receiver chipsets, as well as comprehensive evaluation and verification of modem performance for multiple waveforms, notably DVB-S2X and DVB-RCS2. These unique test capabilities ensure the integrity and reliability of highest data throughput rates of the Telesat Lightspeed constellation.
EUTELSAT OneWeb + E-SAT sign a distribution partnership agreement
Under this partnership, E-Sat will be selling a full suite of LEO connectivity solutions powered by Eutelsat’s OneWeb constellation to Maritime and Enterprise customers across Europe These high-speed, low-latency offerings, made possible by Eutelsat’s OneWeb LEO constellation, will extend existing E-Sat service portfolio, and enable low-latency connectivity solutions to reach customers out of traditional coverage on land and offshore.


Combining Eutelsat OneWeb’s resilient, secure, high-performance connectivity with E-Sat’s commitment to end-to-end service excellence will ensure that customers receive the best satellite connectivity experience coupled with the best customer service experience.
For instance, OneWeb offers new specific market opportunities for maritime users requiring quality services with fast connection speeds and low latency of OneWeb LEO satellites with easy to install hardware and costs savings plans.
“We are very enthusiastic to enter into this partnership with Eutelsat OneWeb. This promising collaboration will enable us to offer to our land and maritime customers high-speed, low-latency connectivity solutions with value added services. For more than 25years we have been offering the very best of satellite technology to our customers and we look forward continuing this with OneWeb,” said Sophie Proniewski, E-SAT CEO.
“We are delighted to add E-Sat to our list of trusted distributors in a further step in expanding the reach of our OneWeb constellation’s high-performance connectivity solutions in Europe. By adding OneWeb to its suite of offers, we are confident E-Sat will be able to leverage secure, low-latency satellite technology to deliver enhanced service to its enterprise and mobility customers,” said Pascal Fallet, EUTELSAT Group VP Connectivity Europe.
Partisia, Squareroot8 + NuSpace forge alliance for quantum-secure SATCOM
Partisia, Squareroot8 and NuSpace have signed a Memorandum of Understanding to advance the future of secure communications—by integrating a Quantum Random Number Generator (QRNG), placed in a satellite in space, with advanced cryptography, this partnership aims to deliver a fully quantum-proof solution for using satellite to provide encrypted correlated randomness to perform Multi-Party Computation (MPC). QRNG can create highly secure random keys. A satellite equipped with a QRNG generates a random key and securely sends it to two parties, allowing them to communicate privately using post-quantum cryptography. This setup ensures a quantum-safe encryption method.

Beyond secure communication, the satellite can also preprocess data for Multiparty Computation (MPC). MPC calculations often require specific secret values that must remain private. Instead of generating these values during computation, we can precompute random values and store intermediate results.
Later, when real inputs arrive, the preprocessed data speeds up the final calculation. By leveraging QRNG-equipped satellites, a trusted, quantum-secure environment for faster and safer cryptographic computations can be created.
Ppreprocessing is the initial stage of data processing, where raw data is prepared for analysis. It improves efficiency, accuracy, and security in various applications, including cryptography and machine learning.
This process is often time-consuming and costly. However, imagine a secure, quantum-proof machine that generates preprocessed “false” numbers. When real data needs to be processed, these false numbers can be combined with the real ones for faster calculations, reducing processing time by up to 80%.
“By integrating quantum-safe cryptography with QRNG-equipped satellites, this partnership delivers a revolutionary solution for secure communication and multiparty computation—ensuring privacy, efficiency, and quantum-proof security for the future of data processing,” said Mark Medum Bundgaard, Chief Product Officer at Partisia.
“Preprocessing with QRNG-equipped satellites transforms secure computation by drastically reducing processing time, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring quantum-safe security—leveraging space as the ultimate trusted environment for data privacy and cryptographic advances,” said Dr. Goh Koon Tong, Chief Technologist & Co-Founder from Squareroot8 Technologies.
NASA trains for Orion water recovery ahead of Artemis II launch
Preparations for NASA’s next Artemis flight recently took to the seas as a joint NASA and Department of Defense team, led by NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program, spent a week aboard USS Somerset off the coast of California practicing procedures for recovering the Artemis II spacecraft and crew.
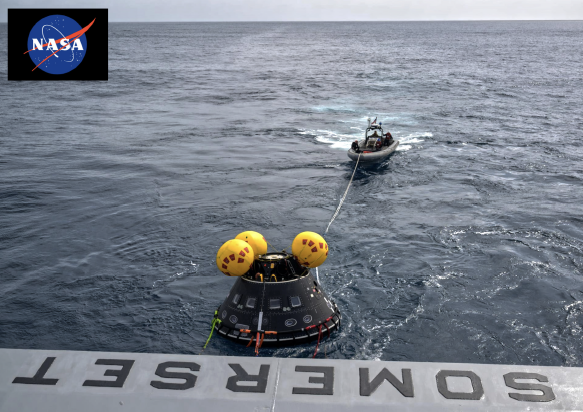

The Crew Module Test Article (CMTA), a full scale
mockup of the Orion spacecraft, is seen in the
Pacific Ocean as teams practice Artemis recovery operations during Underway Recovery Test-12
onboard USS Somerset off the coast of California.
Photo credit NASA/Bill Ingall
Following successful completion of Underway Recovery Test-12 (URT-12) on Monday, NASA’s Landing and Recovery team and their Defense Department counterparts are certified to recover the Orion spacecraft as part of the upcoming Artemis II test flight that will send NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, and Christina Koch, as well as CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen, on a 10-day journey around the Moon. This will be NASA’s first crewed mission to the Moon under the Artemis program,” said Lili Villarreal, the landing and recovery director for Artemis II. “A lot of practice led up to this week’s event, and seeing everything come together at sea gives me great confidence that the air, water, ground, and medical support teams are ready to safely recover the spacecraft and the crew for this historic mission.”
Once Orion reenters Earth’s atmosphere, the capsule will keep the crew safe as it slows from nearly 25,000 mph to about 325 mph. Then its system of 11 parachutes will deploy in a precise sequence to slow the capsule and crew to a relatively gentle 20 mph for splashdown off the coast of California.
From the time it enters Earth’s atmosphere, the Artemis II spacecraft will fly 1,775 nautical miles to its landing spot in the Pacific Ocean. This direct approach allows NASA to control the amount of time the spacecraft will spend in extremely high temperature ranges.
The Artemis II astronauts trained during URT-11 in February of 2024, when they donned Orion Crew Survival System suits and practiced a range of recovery operations at sea using the Crew Module Test Article, a stand -in for their spacecraft.
For the 12th training exercise, NASA astronauts Deniz Burnham and Andre Douglas, along with ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Luca Parmitano, did the same, moving from the simulated crew module to USS Somerset, with helicopters, a team of Navy divers in small boats, NASA’s open water lead—a technical expert and lead design engineer for all open water operations—as well as Navy and NASA medical teams rehearsing different recovery scenarios.
Allowing astronauts to participate when they are not directly involved in a mission gives them valuable experience by exposing them to a lot of different scenarios,” said Glover, who will pilot Artemis II. “Learning about different systems and working with ground control teams also broadens their skillsets and prepares them for future roles. It also allows astronauts like me who are assigned to the mission to experience other roles—in this case, I am serving in the role of Joe Acaba, Chief of the Astronaut Office.”
As the astronauts arrive safely at the ship for medical checkouts, recovery teams focus on returning the spacecraft and its auxiliary ground support hardware to the amphibious transport dock.
Navy divers attach a connection collar to the spacecraft and an additional line to a pneumatic winch inside USS Somerset’s well deck, allowing joint NASA and Navy teams to tow Orion toward the ship.
A team of sailors and NASA recovery personnel inside the ship manually pull some of the lines to help align Orion with its stand, which will secure the spacecraft for its trip to the shore.
Following a safe and precise recovery, sailors will drain the well deck of water, and the ship will make its way back to Naval Base San Diego.
Article author: Allison Tankersley, Public Affairs Specialist, NASA
HyImpulse unveils HyMOVE OTV
HyImpulse Technologies GmbH has unveiled HyMOVE, the company’s Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV) that is designed to serve the rapidly expanding small satellite market—expected to grow to $30 billion globally by 2030.

HyMOVE is designed to enhance the capabilities of small satellite missions, delivering tailored in-space logistics for orbital missions. To mark this launch, HyImpulse has launched a partnership with Spacemanic Ltd., a leading nanosatellite provider, for as many as 10 missions over the next decade.
Powered by HyMOVE’s hybrid propulsion system, these services will enable Spacemanic to deploy and manage payloads with precision and efficiency across various orbital configurations. Developed under the Bavarian Spaceflight Funding Program, HyMOVE will conclude ground testing in 2025 and commence commercial operations in 2029.
With HyMOVE, HyImpulse is strengthening Europe’s capability for independent access to space. As demand for nanosatellites and flexible orbital services increases, the partnership with Spacemanic demonstrates how collaboration can advance Europe’s position in the global space sector.
GomSpace joins ESA’s RAMSES mission to study near-Earth asteroid using advanced cubesat technology
GomSpace has joined ESA’s RAMSES mission to study a near-Earth asteroid using advanced cubesat technology
GomSpace is participating in the Rapid Apophis Mission for Space Safety (RAMSES), an innovative initiative led by the European Space Agency (ESA)—the contract value is 900,000 euros.
This mission aims at studying the near-Earth asteroid 99942 Apophis during its exceptionally close approach to Earth in April of 2029. The company participates in phase A/B of the RAMSES mission with a 12 month contract.
The RAMSES mission will consist of a main spacecraft complemented by two CubeSats. This collaborative approach mirrors the ESA HERA mission and further enhances Europe’s capabilities in space exploration and planetary defense.
The The HERA/Juventas mission was launched in October of 2024, with the prime role of GomSpace for the Juventas CubeSat spacecraft.
The deployment of CubeSats will maximize the scientific return of the RAMSES mission, providing detailed observations of Apophis before, during, and after its Earth flyby. These studies will significantly enhance our understanding of asteroid behaviors and contribute to our preparedness for potential planetary defense scenarios.
GomSpace, leveraging its expertise from the HERA/Juventas program, has been contracted to provide system engineering support for CubeSat 2, led by Emxys of Spain.
The collaboration underscores GomSpace’s capacity to engage in and successfully realize deep-space missions. Additionally, this experience builds upon previous endeavors and showcases GomSpace’s commitment to advancing scientific exploration in the field of planetary defense.
This historic cubesat encounter with asteroid Apophis represents a defining moment in our journey beyond Earth,” said Edgar Millic, Senior Director Strategic Business Growth and Managing Director, GomSpace Luxembourg. “By building on our proven deep space experience, we are setting the stage for future missions that will deepen our understanding of the solar system and extend humanity’s reach.”