Planet Labs plans to launch 36 SuperDove smallsats with SpaceX
Planet Labs PBC plans to launch 36 of their SuperDove satellites, Flock 4y, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket no earlier than Tuesday, January 3, 2023, at 9:56 a.m., ET (14:56 UTC).
Flock 4y is planned to launch on SpaceX’s Transporter-6 mission from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (SFS), Florida.
These 36 SuperDoves will replenish Planet’s current fleet of approximately 200 satellites on-orbit, working to provide a continuous, and complete view of the world from above every day.
Each Planet SuperDove is equipped with eight spectral-bands and improved on-orbit capacity that helps to quickly deliver sharp, analysis-ready data to Planet’s customers.
The data collected by Planet’s SuperDoves allows organizations in agriculture, government — both intelligence and civilian agencies — forestry, sustainability, and other industries to make informed, timely decisions.
Further, a select number of these Planet SuperDoves will be adorned with artwork and quotes that celebrate the legacy of Star Trek creator, Gene Roddenberry, as a part of Planet’s collaboration with The Roddenberry Foundation’s Boldly Go Campaign.

The Roddenberry Foundation launched this campaign in 2021 to celebrate Gene’s hopeful vision of humanity’s future — one of inclusion, scientific progress, and cooperation.
Five of the Planet SuperDoves on this mission will have artwork laser-etched onto their side panels that is inspired by the more than 1,500 submissions to the Boldly Go campaign, which asked the world to share what gives them hope for humanity’s future.
This will be Planet’s eighth overall launch with SpaceX. Since its founding, Planet has launched over 500 imaging satellites, more than any commercial company in history.
www.planet.com
Ovzon receives SAS orders worth millions of Swedish Krona
Ovzon has received from partners Swedish Space Corporation (SSC) and Nigma Conseil first orders for the company’s SATCOM- as-a-Service (SAS)

Ovzon’s SAS combines the firm’s ultra-small, mobile satellite terminals, highly resilient and high-performance satellite networks with services and support from Ovzon’s Network Operations Center (NOC).
With this contract, Ovzon deepens their collaboration with SSC, which acts both as the main party in dialogue with customers, mainly within the Swedish government, and as a partner in the delivery of the service. Both are important parts of the end-to-end solution that has now been created to meet the specific and critical needs of these end customers.
Nigma Conseil provides world-class communications solutions, security, business intelligence, and digital security consulting for clients across the globe. Ovzon’s fully managed (24/7) SAS delivers reliable solutions to customers with the highest demands for secure, no-fail, easy-to-use SATCOM.
“We are very happy and proud to receive this first order in collaboration with SSC as well as the opportunity to work with our new French partner, Nigma. We provide the customer with a world-leading and highly efficient satellite communication service based on Swedish technology and innovation. The service enables a new level of capability needed in a world of heightened geopolitical unrest. Of course, we also hope for continued cooperation around our satellite Ovzon 3 and its unique features with increased mobility, performance, and resiliency. Ovzon 3 will further strengthen the ability of customers who must be able to conduct vital societal functions and protect critical infrastructure during operations in complex and vulnerable situations. We look forward to working with both SSC and Nigma to meet the growing demand for superior performance, mobility, and resiliency in their markets,” said Per Norén, CEO.
Flann Microwave assists with NASA’s SWOT satellite development
In 2015, Flann Microwave was selected by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) to provide critical hardware for the high-resolution radar components on a new multinational satellite, that being the SWOT satellite.
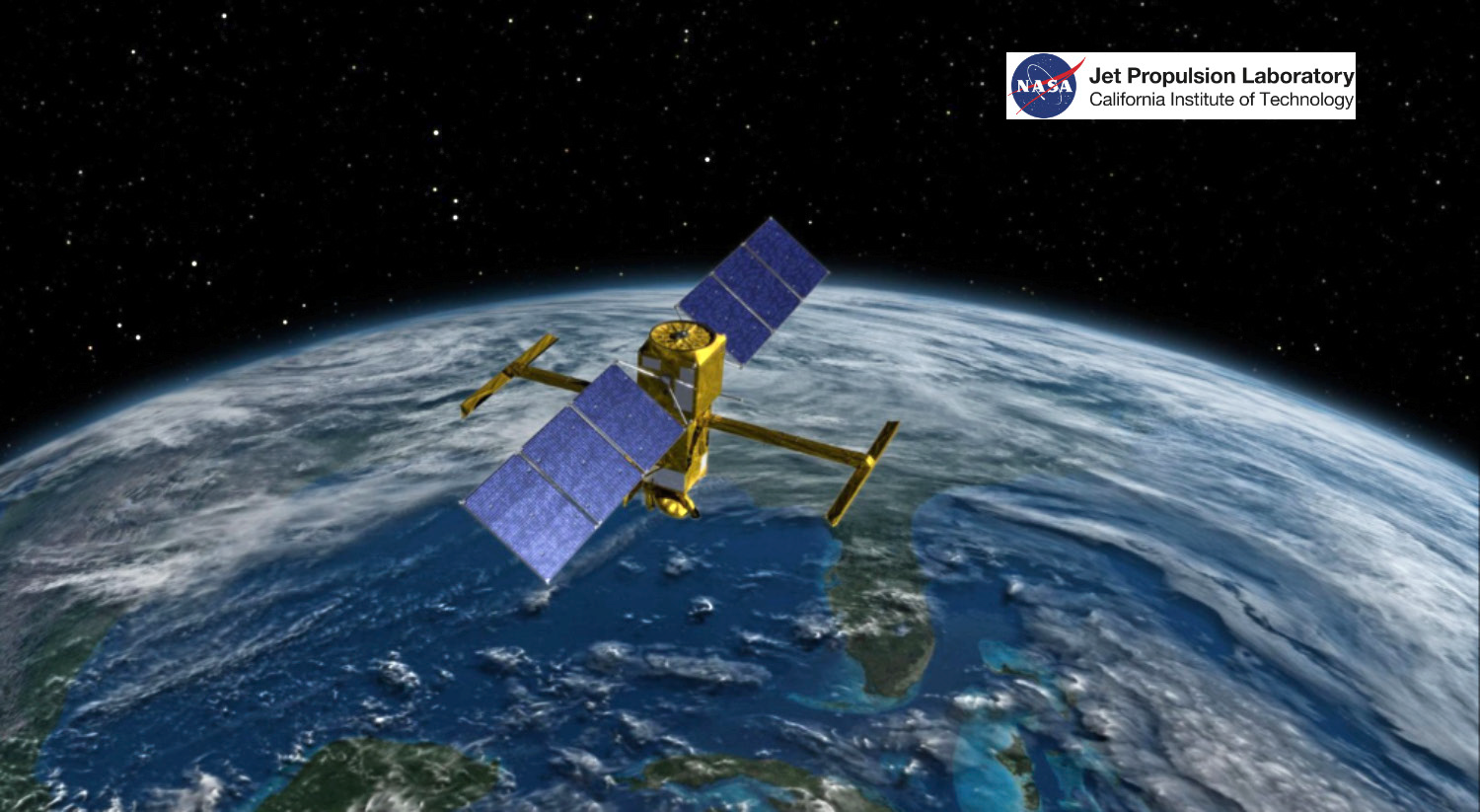

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite is the first-of-its-kind to survey the surface water on Earth, observe ocean surface topography and measure the changes in these bodies of water over time.
The NASA/JPL illustration above depicts the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite, a mission led by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES). The scientific heart of the SWOT satellite is the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument, which will measure the height of water in Earth’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and ocean. To do that, KaRIn will transmit radar pulses to Earth’s surface and use two antennas – seen to the left and right of the spacecraft bus – to triangulate the return signals that bounce back. Mounted at the ends of a boom 33 feet (10 meters) long, the antennas will collect data over two swaths of Earth’s surface at a time, each of them 30 miles (50 kilometers) wide and located on either side of the satellite.
Launched on December 16, 2022, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, the SWOT satellite was jointly developed and managed by NASA, the French Space Agency, the Canadian Space Agency, and the UK Space Agency.
Following JPL’s previous adoption of Flann Microwave’s high- precision test and measurement product range, the SWOT is the first collaborative spaceflight project between Flann and NASA. Due to the critical performance requirements of the project, Flann worked in close collaboration with the engineers at JPL to develop custom-made waveguide equipment for spaceflight operations.
Flann’s innovative waveguide equipment was designed to withstand the rigors of spaceflight and help provide higher accuracy and precision measurements of Earth’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs and oceans, as well as mapping ocean surface height, in greater detail than previous measurement systems.
Flann’s uniquely-designed microwave components were installed on the satellite and linked to NASA’s high-resolution, state-of-the-art, radar interferometry systems to help accurately measure Earth’s surface water, weather and climate predictions as well as assist in freshwater management.
Tamlin Pavelsky, the SWOT Science Team Lead (2022-2024), said, “SWOT will usher in a new golden age for the science of rivers and lakes. Right now, we can measure how the amount of water in lakes and reserviors changes for a few thousand lakes worldwide. With SWOT, we’ll be able to observe millions, […] help[ing] us to understand changing risks from flooding, opportunities for sustainable water use, and the fundamental natures of these important natural systems.”
Launched: SpaceX’s 2Gen Starlinks + ImageSat International’s EROS-C3
On Wednesday, December 28th at 4:34 a.m., ET, SpaceX launched 54 Starlink satellites to LEO from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC- 40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
This was the 11th launch and landing for this Falcon 9 first stage booster, which previously launched GPS III Space Vehicle 04, GPS III Space Vehicle 05, Inspiration4, Ax-1, Nilesat 301, and now six Starlink missions.

This launch marked the first of Starlink’s upgraded network. Under the company’s new license, SpaceX is now able to deploy satellites to new orbits that will add even more capacity to the network.

Photo of the SpaceX launch of the ISI EROS-C3 satellite
from Vandenberg SFB.
Ultimately, this enables SpaceX to add more customers and provide faster service — particularly in areas that are currently over-subscribed. According to the company, Starlink now has more than 1,000,000 active subscribers across the globe.
Then, on Thursday, December 29th at 11:38 p.m. PT, a Falcon 9 launched the ImageSat International (ISI) EROS C-3 (Earth Resources Observation Systems C) mission to a LEO from Space Launch Complex 4E (SLC-4E) at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.

Artistic rendition of ImageSat International’s
EROS-C satellite.
This was the 11th launch of this booster, which previously supported the launch of Crew-1, Crew-2, SXM-8, CRS-23, IXPE, Transporter-4, Transporter-5, Globalstar FM15, and two Starlink missions.
According to the company, Starlink now has more than 1,000,000 active subscribers across the globe.




