GOES-R’s Grand Ascension
On schedule, a United Launch Alliance’s Atlas V embraced GOES-R and lifted the satellite high, along with the spirits of those who anticipate that the much improved and highly heralded technology will vastly improve weather
data services.
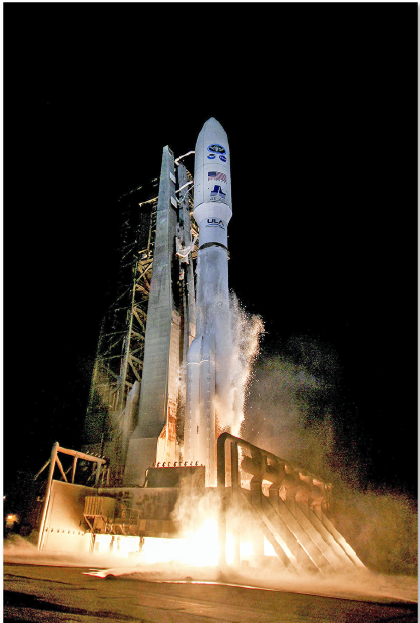

The launch of the GOES-R aboard an Atlas V launch vehicle. Photo is courtesy of United Launch Alliance.
GOES-R is NOAA’s most advanced geostationary weather satellite to-date. But how different can this satellite truly be?
Imagine going from a black and white TV to HD overnight. GOES-R is faster and clearer than current GOES satellites and will provide forecasters with more detail and information than previously obtainable.
Using a powerful new instrument called the Advanced Baseline Imager, or ABI, GOES-R will provide data and imagery about weather over the entire Western Hemisphere in real-time—the satellite can even accomplish this work as frequently as every 30 seconds! This enables NOAA to gather data using three times more channels, four times the resolution,
at five times faster than before.
This faster, more accurate data means better observations of developing storms. The ABI will be used for a wide range of applications related to weather, oceans, land, climate and hazards.
The GOES-R Series includes four satellites and is the nexgen of GOES satellites that will provide continuous imagery and atmospheric measurements of the Earth’s Western Hemisphere.
GOES-R will produce images of weather patterns and severe storms as frequently as every 30 seconds, which will contribute to more accurate and reliable weather forecasts and severe weather outlooks, including thunderstorm, hurricane and tornado tracking and intensity forecasting.
GOES-R will also provide improved detection and observations of meteorological phenomena that directly impact public safety, protection of property and economic health and development.
Designed and built by Lockheed Martin, the GOES-R satellite includes six instruments that fit into three classifications: Earth-pointing, solar-pointing and in-situ (near environment). Lockheed Martin is providing three instruments:
• The Solar Ultraviolet Imager (SUVI)
• The Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM)
• The magnetometer
Three additional instruments include:
• The Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) developed by the Harris Corporation
• The Extreme Ultraviolet X-Ray Irradiance Sensors (EXIS) from the University of Colorado’s Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics
• The Space Environmental In-Situ Suite (SEISS) from the Assurance Technology Corporation
The GOES-R Series is a collaborative effort between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) to develop, launch and operate the satellites.
GOES satellites have played a vital role in weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research since the first GOES was launched on a Delta rocket in 1975. ULA’s Atlas and Delta rockets have launched every satellite in the GOES series.
ATLAS V 541
One of the most powerful rockets in the Atlas V fleet, the 541 configuration, with four solid rocket boosters, provides the optimum performance to precisely deliver a range of mission types.
In addition to completing two national security missions, an Atlas V 541 configuration rocket launched NASA’s Curiosity rover on its 10 month, 354 million mile journey to the surface of Mars.
• First Launch: November 26, 2011 Launches to date: 3
• Performance to GTO: 8,290 kg (18,270 lb)
• Performance to LEO-Reference: 17,410 kg (38,400 lb)
Aerojet Rocketdyne, a subsidiary of Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings, Inc., successfully supported the launch of this GOES-R satellite for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA.
Aerojet Rocketdyne propulsion systems on the Atlas V included the RL10C-1 upper-stage engine, four Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs), six helium pressurization tanks and a dozen Centaur upper-stage Reaction Control System thrusters (RCS).
On the GOES-R satellite, Aerojet Rocketdyne provided all of the monopropellant hydrazine rocket engines as well as the electric propulsion subsystem.
“Weather is constantly changing, and the faster scientists can predict those changes, the better communities can prepare for severe conditions and phenomena, such as forest fires and volcanic ash. Aerojet Rocketdyne is honored to help launch this critical satellite that will help keep people and their neighborhoods safe,” said Aerojet Rocketdyne CEO and President, Eileen Drake.
Aerojet Rocketdyne’s role in the launch began during liftoff when four SRBs ignited to provide 1.5 million pounds of total increased thrust to launch the Atlas V rocket. (Each 67-foot-long, 5-foot-wide composite motor case contains more than 90,000 pounds of propellant, providing more than 375,000 pounds of liftoff thrust.) All Atlas V launches requiring extra boost have flown Aerojet Rocketdyne SRBs.
After separation of the first stage, a single RL10C-1 upper-stage engine ignited to place the payload into orbit, with the RCS thrusters maintaining vehicle orientation and the pressurization tanks maintaining pressure levels in the liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen tanks.
The RL10C-1 delivers 22,890 pounds of thrust to power the Atlas V upper stage, using cryogenic liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen propellants during its operation.
The RL10C-1 was developed from the RL10 family of upper-stage engines, which have accumulated one of the most impressive track records of accomplishments in the history of space propulsion.
More than 470 RL10 engines have supported launches over the last 50 years, helping to place military, government and commercial satellites into orbit, and powering scientific space-probe missions on every planetary mission in our solar system.
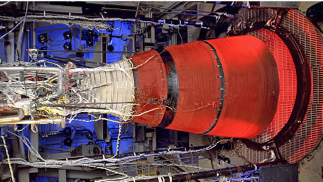
An RL10 upper stage engine. Photo is courtesy of Aerojet Rocketdyne.
Aerojet Rocketdyne developed a new MR-401 Low Thrust Rocket (LTR) for the GOES-R program that enables compliance with the unique GOES-R mission requirements.
The GOES-R satellite has 16 of these MR-401 rockets onboard providing vehicle attitude control, momentum wheel desaturation and east/west stationkeeping.
In addition to the 16 LTRs, Aerojet Rocketdyne also provided the 4.4kW MR-510 electric propulsion subsystem which provides all north/south stationkeeping for the GOES-R mission, as well as end of life decommissioning.
The MR-510 Electric Propulsion (EP) subsystem consists of four MR-510 Arcjet thrusters, one 4.4kW Power Conditioning Unit (PCU), and the electrical harnessing to connect the PCU to the thrusters.
The MR-510 EP system enables increased payload capability for the GOES-R mission due to the significant savings in propellant mass provided by the 3x improvement in fuel efficiency.
ARDÉ, a subsidiary of Aerojet Rocketdyne based in New Jersey, provided the pressure vessels on the first and second stages of the launch vehicle.
Providing critical hardware for the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V vehicle and NASA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-R Series (GOES-R) NASA weather satellite that was launched on Saturday, November 19th, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, was Orbital ATK.
Using advanced fiber placement manufacturing and automated inspection techniques, Orbital ATK produced three components for the ULA Atlas V vehicle, including the 10-foot diameter composite heat shield that provides essential protection to the first stage engine, the Centaur Interstage Adapter that houses the second stage engine, and the boattail that adapts from the core vehicle to the five-meter diameter fairing.
Orbital ATK fabricated these structures at its Iuka, Mississippi, facility. This is the 66th Atlas V launch using Orbital ATK-built composite structures.
This flight also marked the 32nd successful flight of the Orbital ATK retrorocket motors. Eight of these solid motors supported separation of the spent first stage.

GOES-R launch, photo courtesy of United Launch Alliance.
The Atlas V retrorocket is built by Orbital ATK’s Defense Systems Group at its facility in Elkton, Maryland.
In addition, Orbital ATK manufactured the Reaction Control System propellant tank for the ULA Atlas V at their Commerce, California, facility.
The GOES-R series satellites will contribute to more accurate and reliable weather forecasts and severe weather outlooks via continuous visual and infrared imagery and atmospheric measurements of Earth’s Western Hemisphere, total lightning data, solar imaging and space weather monitoring.

NOAA manages the GOES-R program with an integrated NOAA-NASA program office organization co-located at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
The company’s Space Components Division facilities in Maryland, California and Utah provided numerous subsystems for the GOES-R satellite, including loop heat pipes for thermal control of the Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) and Global Lightning Mapper (GLM) instruments, fuel, oxidizer, and pressurant tanks, the primary bus structure, also containing thermal control elements, and three optical bench stable structures supporting the ABI and Solar Pointing Platform (SPP).
Orbital ATK also provided a coilable lattice boom for the GOES-R Magnetometer, continuing the success of company-built booms on previously launched GOES-N, -O and -P satellites.
orbitalatk.com
Galileo x4 Seize The Day—Constellation Completed
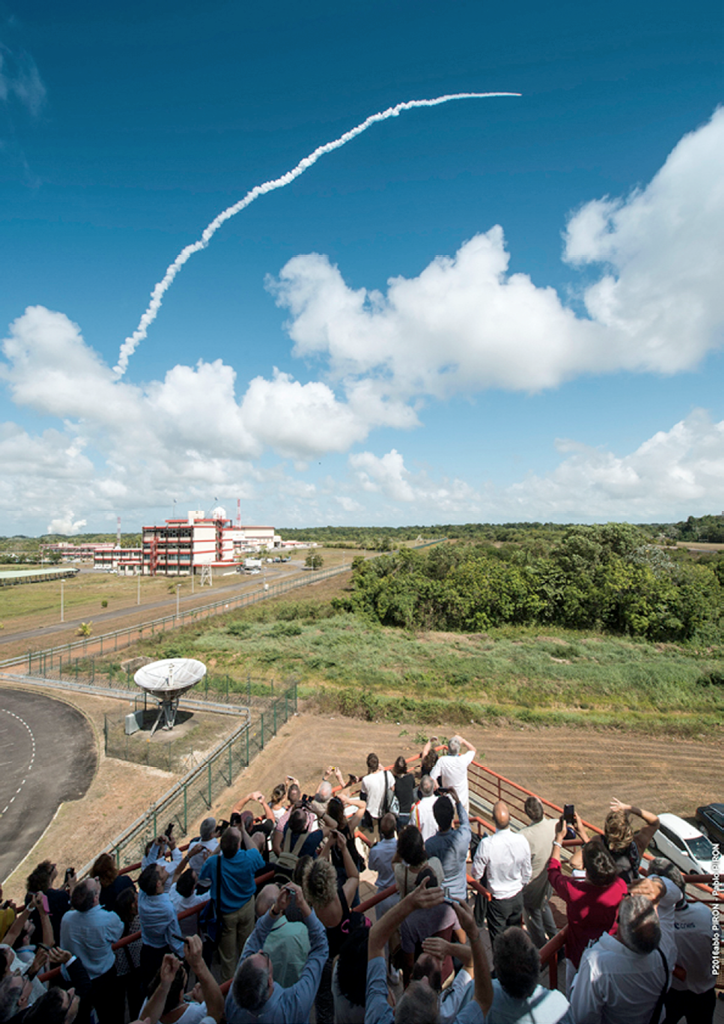
An Arianespace Ariane 5 launch vehicle has successfully placed four satellites into orbit, thereby completing the European Galileo satellite navigation constellation.

The Ariane 5 launch of flight VA233 with a payload of four
Galileo satellites. Photo is courtesy of Arianespace.
This was the 75th time an Ariane 5 has completed a mission from the European space port in Kourou, French Guiana.
This 233rd launch noted that the upper stage for this Ariane 5 mission was powered by the re-ignitable Aestus engine, which has already been used successfully for launches of the European ATV space vehicle.
The launch performance of this Ariane 5 ES is 3276 kg to a circular orbit at an altitude of 22,922 km (of which 2,858 kg were accounted for by the four satellites at 714 or 715 kg each). They were injected into orbit by a 418 kg dispenser that was specifically developed and built by Airbus Safran Launchers for these Galileo launches.
This launch was also the first opportunity to fly a Vulcain engine part produced by additive layer manufacturing (ALM) using direct metal laser sintering, which significantly shortened the production cycle and reduced the quantity of material lost through machining.
The Ariane 5 launcher once again demonstrated full flexibility, which enabled the rocket to carry heavy payloads into LEO, two satellites into geostationary transfer orbit, a single satellite with an optimized service lifetime, or several satellites to MEO, as was the case today.

Artistic rendition of Galileo satellites.
Airbus Safran Launchers is lead contractor for the Ariane 5 launchers. The company coordinates an industrial network of more than 550 companies in 12 European countries (including more than 100 small and mid-sized Enterprises - SMEs).
Airbus Safran Launchers oversees the entire industrial chain, from management of launcher performance upgrades, to production management, to final adjustment and supply of the mission flight software.

The Galileo satellite build. Photo is courtesy of OHB.
This chain includes equipment and structures, engines manufacturing, integration of the various stages and finally launcher integration in French Guiana.
Airbus Safran Launchers is also industrial lead contractor for Europe’s future Ariane 6 launcher, which is scheduled for a first flight in 2020 and which will replace Ariane 5 in about 2023.
The Ariane 233 flight in figures:
• 8th launch of an Ariane 5
• 6th Ariane 5 ES launcher equipped with its reignitable Aestus engine
• 12th Ariane 5 launch with Airbus Safran Launchers as lead contractor
• 63rd consecutive success by a launcher fitted with a Vulcain® 2 engine
• 21st consecutive success by a launcher fitted with the Aestus engine

Alain Charmeau, the CEO of Airbus Safran Launchers, said, “This 6th launch of 2016 combines a new record with innovation. Not only has Ariane 5 broken the consecutive successful launch record of its predecessor Ariane 4, but it has once again demonstrated its flexibility by placing four satellites in a circular orbit simultaneously and at an altitude of 22,922 km.
“I wish to congratulate the industrial teams who once again demonstrated the extraordinary flexibility of Ariane 5. This year, in addition to the usual dual launches, the launcher has shown itself capable on two occasions of placing a single satellite in orbit for commercial customers, and now it has successfully carried out this quadruple launch for a European institutional customer. I wish to thank ESA, the European Commission, Arianespace and CNES for their confidence and for their constant support.”
Arianespace infosite: arianespace.com
Airbus Safran infosite: airbusafran-launchers.com
The European Commission infosite: ec.europa.eu/growth/sectors/space/galileo
The ESA infosite: esa.int/Our_Activities/Navigation/Galileo/What_is_Galileo
OHB System infosite: ohb-system.de
SSTL infosite: sstl.co.uk
Newtec Addresses The “Underserved”
Indonesian SATCOM service provider Pasifik Satelit Nusantara (PSN) has selected Newtec to connect the nation’s underserved rural areas with broadband access.

Using the Newtec Dialog platform, PSN has been supplied with a 4IF Hub module and hundreds of MDM3100 Satellite Modems that feature Mx-DMA® technology to provide services using C-band transponders.
The multi-service platform will be used by PSN to deliver satellite Internet access to schools, government offices and Puskesmas (community health clinics) as part of the universal service obligation for MCIT—Indonesia’s Ministry of Communication and Information Technology.
PSN evaluated various options based on SCPC and MF-TDMA technologies and concluded that the Newtec Dialog platform provides the best fit and total cost of ownership, based on the high throughput VSAT capabilities and Newtec’s award-winning return link technology Mx-DMA, which delivers the efficiency of SCPC with the dynamic bandwidth allocation capability of MF-TDMA.
As a multiservice platform, Newtec Dialog enables tailored services and guarantees optimal modulation, bandwidth allocation, service availability, reliable automation of link setups and flexible workflow support, whether being used to provide broadcast, consumer broadband, cellular backhaul or mobility services.
Adi Rahman Adiwoso, the CEO at PSN, stated that this access will make a huge difference to the lives of those in the rural areas of Indonesia, where more traditional means of connectivity are unreliable or non-existent.
newtec.eu
psn.co.id/
A Rebirth For UK Satellite Broadcasting Group
The Broadcasting & Satellite Network (BSNUK), a UK-based satellite and broadcasting professionals networking group, is entering a second decade of existence—to mark this landmark, the group is relaunching with a new logo, website and identity.

As part of its re-birth, Martin Coleman, Executive Director of the Satellite Interference Reduction Group (IRG), has been appointed to BSNUK’s Board to aid in invigorating the goal of providing a platform for UK industry professionals to share knowledge, experience, and encourage new young talent into the industry.
Martin has worked in the broadcast and satellite industries for more than 40 years and has been instrumental in improving process control for a variety of broadcasters and satellite operators through his own company, Colem. He was also a key figure in establishing the ground rules for adding Carrier ID to digital video carriers, prior to taking the position of Executive Director of IRG in 2011.
bsnuk.org/
A New VANTAGE For Telesat
A new satellite that will possess two high throughput payloads—one Ku and the second Ka-band—is going to be procured by Telesat

Artistic rendition of the Telstar 19 VANTAGE satellite.
To be named Telstar 19 VANTAGE, this satellite will co-locate with Telesat’s Telstar 14R at 63 degrees West, a prime orbital slot for coverage of the Americas.
Telesat expects to enter into a construction agreement for Telstar 19 VANTAGE in the coming weeks.
Telstar 19 VANTAGE will be the second of a newgen of Telesat satellites that have been optimized to serve the types of bandwidth intensive applications that are increasingly being used across the satellite industry.
Hughes Network Systems LLC (Hughes) has made a significant commitment to use the satellite’s high throughput Ka-band capacity in South America to expand their broadband satellite services.
The satellite has additional high throughput Ka-band capacity over northern Canada, the Caribbean and the North Atlantic Ocean and will also provide high throughput and conventional Ku-band capacity over Brazil, the Andean region and the North Atlantic Ocean.
According to Dan Goldberg, Telesat’s President and CEO, Telstar 19 VANTAGE will be a versatile, state-of-the-art satellite optimized to serve growing markets in the Americas from Telesat’s prime 63 degrees West location. The company is pleased to have Hughes as an anchor tenant on this spacecraft and will be delivering new, high throughput capacity to serve Latin America, northern Canada and mobile broadband requirements in the Caribbean and North Atlantic.
telesat.com/
Noordwijk Witnesses Successful Testing Of Sentinel-2B
The test program for Europe’s next Copernicus satellite, the Sentinel-2B, has been successfully finished at ESA’s technology Center ESTEC in Noordwijk, The Netherlands.
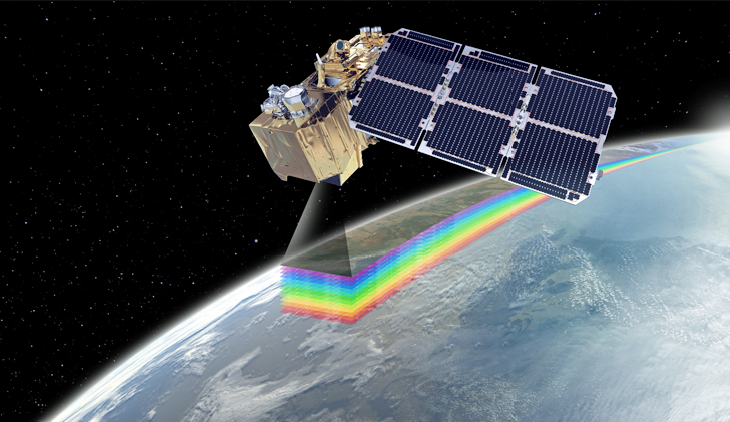
Artistic rendition of the Sentinel-2B satellite. Image is courtesy of Airbus Defence and Space.
The second Sentinel-2 Airbus built satellite will now be readied for shipment to the Kourou spaceport in French Guiana in January of 2017.
The satellite is scheduled for an early March 2017 lift-off via Vega. Copernicus, Europe’s environmental monitoring program, is led by the European Commission (EC) in partnership with the European Space Agency (ESA).
The Copernicus Sentinels supply remote sensing data of the Earth, delivering key operational services related to environment and security.
Offering “color vision” for the Copernicus program, Sentinel-2B, like its twin satellite Sentinel-2A, will deliver optical images from the visible to short-wave infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
From an altitude of 786 kilometers, the 1.1 ton satellite will deliver images in 13 spectral bands with a resolution of 10, 20 or 60 meters and a uniquely large swath width of 290 km.
The optical design of the Multi Spectral Instrument (MSI) has been optimized to achieve state-of-the-art imaging quality across its very wide field of view.
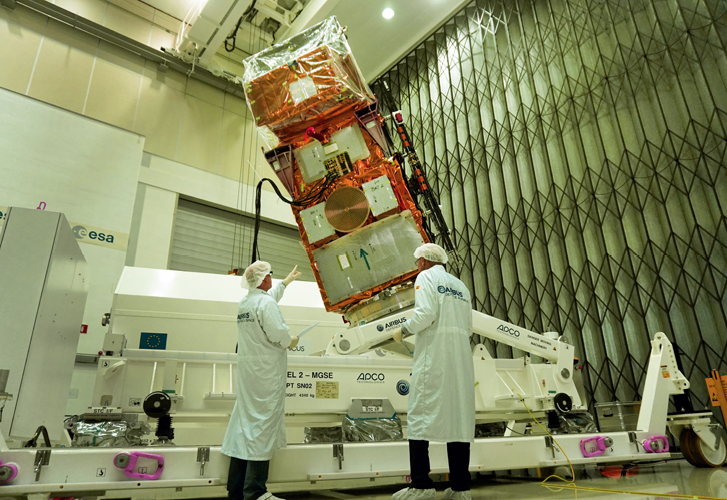

Sentinel-2B during the build process. Photo is courtesy of Airbus Defence and Space.
With its multispectral imager and wide swath coverage, the Sentinel-2 mission not only offers continuity, but with its more than 100 km increase in swath width, also expands on previous missions.
The telescope structure and the mirrors are made of silicon carbide, which provides very high optical stability and minimizes thermo-elastic deformation, resulting in an excellent geometric image quality. This is unprecedented in this category of optical imagers.
The data gathered are used for monitoring land use and changes, soil sealing, land management, agriculture, forestry, natural disasters (floods, forest fires, landslides, erosion) and to assist humanitarian aid missions. Environmental observation in coastal areas likewise forms part of these activities, as does glacier, ice and snow monitoring.
The Sentinel-2-mission is based on a constellation of two identical satellites, Sentinel-2A and Sentinel-2B, in the same orbit, 180 degrees apart for optimal coverage and data delivery.
The satellites are orbiting the Earth every 100 minutes covering all Earth’s land surfaces, large islands, inland and coastal waters every five days. Sentinel-2A, which is identical in design, was launched on June 23, 2015. Since then, the satellite has been performing as expected.
A total of 51,762 users have self-registered on the Sentinels Scientific Data Hub. About 168,000 products are available for download for a total volume of 433 TB. Overall, a total volume of 1.9 Petabytes has been downloaded by user communities.
The Sentinel-2 mission has been made possible thanks to the close collaboration between ESA, the European Commission, industry, service providers and data users.
The mission’s development has involved around 60 companies, led by Airbus Defence and Space in Germany for the satellites and Airbus Defence and Space in France for the multispectral instruments, while Airbus Defence and Space in Spain is responsible for the mechanical satellite structure.
airbusdefenceandspace.com
Better Satellite World Award Honorees Brought To Light By SSPI
Founded in 1983, the Society of Satellite Professionals International is on a mission to make the satellite industry one of the world’s best at attracting and engaging the talent that powers innovation—with more than 4,000 members in +40 nations, this is the largest satellite industry association in the world.

The Society of Satellite Professionals International (SSPI) has now revealed the four recipients of their second annual Better Satellite World Awards, which honor established companies and disruptive innovators for making our world a more prosperous, healthier, better-educated, more sustainable and inclusive home for all humankind.
Selected by an international jury for their achievements were: DigitalGlobe, Disaster Tech Lab supported by Globalstar, Global VSAT Forum and Outernet.
The recipients were honored at the second Better Satellite World Awards Dinner on December 5th at London’s prestigious One Whitehall Place.
“Satellite is the world’s invisible but indispensable technology,” said executive director Robert Bell, “and our awards honor both for-profit companies and nonprofit organizations for using satellite in ways that make our world a better place. Our awards dinner in London gives us the chance to salute organizations that are quietly having a global impact.”

According to SSPI, recipients for the Better Satellite World Awards were evaluated in four categories. These were global or regional impact; distribution of knowledge for the improvement of living standards; governance and commerce; and communication and humanity.
The selection of the recipients for the Better Satellite World Awards was made by an international jury consisting of members of the SSPI Satellite Hall of Fame and distinguished industry professionals.
The Better Satellite World Awards Dinner in London was produced by SSPI and the organization’s UK and Isle of Man Chapters, with the support of international law firm Milbank as well as Globecomm, Arianespace, ManSat and Newtec.
The Better Satellite World Award Recipients
DigitalGlobe
DigitalGlobe is the world’s leading provider of high-resolution Earth imagery, data, and analysis.

The company is a trusted partner of dozens of industries and communities worldwide – from environmental monitoring and mapmaking, to defense and intelligence, to urban planning and public safety.
DigitalGlobe has also become a leader in providing humanitarian aid by supplying local, national, and international authorities and media with imagery and information products that support response and recovery activities in the aftermath of earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and other natural disasters.
In a recent humanitarian victory, DigitalGlobe enabled the Associated Press to expose a slave fishing operation in Papua New Guinea. The company supplied the AP with high-accuracy, high-resolution imagery that only DigitalGlobe satellites can collect, which showed the slave fishing operation in the act and spurred a myriad of positive outcomes. The Seafood from Slaves investigation led to a series of arrests, the dismantling of a slaving operation, the freeing of more than 2,000 slaves, and a change to US law that had previously allowed slave-produced goods to be sold in the United States. For its reporting on the issue, the AP won the 2016 Pulitzer Prize for Public Service. digitalglobe.com
Disaster Tech Lab supported by Globalstar
Disaster Tech Lab (DTL) is a volunteer-based organization that provides Internet access to reconnect disconnected communities in disaster zones across the globe.

Established in 2010 after the devastating earthquake in Haiti, the organization has grown to over 200 volunteers in eleven countries. Since its founding, DTL has deployed teams to almost every major disaster area across the globe.
Disaster Tech Lab makes emergency communications possible in areas where critical infrastructure has been lost, providing reliable satellite technology to NGOs aiding people in crisis. Globalstar provides DTL teams around the world with satellite phones, satellite hotspots, and satellite-enabled tracking and safety devices to enable them to deliver this vital support.
Over the last two years, Disaster Tech Lab has provided aid to Europe in organizing and dealing with the migrant and refugee crisis. DTL provided satellite communications to allow coordination and management of resources within the refugee camps in Greece and also gave migrants the ability to contact their families back home via Globalstar satellite phones.
Disaster Tech Lab also provided emergency communications during the earthquake in Italy in August 2016, equipping the Italian Red Cross with satellite communications tools. DTL assisted NGOs and local authorities during another earthquake in 2016, this one along the eastern coast of Ecuador.
During the devastating floods in Louisiana, DTL helped install communications networks to support individuals, communities, and NGOs throughout the state.
Lastly the organization used Globalstar hardware & services to provide communication services to medical teams deployed in Haiti following Hurricane Matthew. disastertechlab.org/
Global VSAT Forum
Since 1998, the Global VSAT Forum has provided a platform for satellite regulatory issues and professional training in VSAT technologies for organizations around the world.
 In addition to promoting market liberalization, licensing reform and spectrum access, GVF has established an online training and certification program for VSAT terminal installers and operators, which has enrolled more than 13,000 professionals.
In addition to promoting market liberalization, licensing reform and spectrum access, GVF has established an online training and certification program for VSAT terminal installers and operators, which has enrolled more than 13,000 professionals.
GVF training—developed by the association’s partner SatProf and adopted by the world’s leading satellite communications service providers—equips installers and operators with skills they would not otherwise have and, through their strengthened qualifications, improves the quality of VSAT operations, which promotes continued growth in VSAT applications around the world.
GVF has also worked for nearly 20 years to establish a more effective and sustainable paradigm for global disaster preparedness. In coordination with its partners throughout the disaster-response community—including the United Nations Agencies, humanitarian organizations, militaries, national administrations, inter-governmental groups, and others—GVF has facilitated their disaster preparedness and response efforts by training and certifying first responders, identifying qualified local technicians, coordinating satellite industry support, and educating governments on regulatory approaches that enable the use of ICT systems to save lives. gvf.org
Outernet
Syed Karim, the founder of Outernet, describes it as “a universal information service available to all of humanity.”

Founded in 2014 as a private company headquartered in Chicago, Outernet now provides a global data delivery service over three Inmarsat I4 global beams.
The company provides a content delivery service which focuses on making the most useful knowledge from the Internet available to those in areas with no connectivity. Syed Karim conveyed this vision to the world as a speaker at the TedGlobal 2014 event.
In many places around the globe, Internet connectivity is prohibitively expensive, sometimes costing as much as ten times the average monthly income. Outernet creates offline versions of knowledge found on the web and broadcasts that information to people who have no access to the Internet.
The company currently operates a low bitrate global broadcast, which will expand over time to include the delivery of digital curricula and educational videos. outernet.is/
Working with partner associations and dozens of supporting companies around the world, SSPI is changing the global conversation about satellites and their influence on the economy, business and societies everywhere with the Better Satellite World campaign.
More information on the campaign is available at bettersatelliteworld.com.
sspi.org




