SSL, a Maxar Technologies company, designs and builds advanced spacecraft systems that enable the firm’s customers to connect, inform and protect people around the globe.
The company is focused on next-generation small satellites (smallsats) for Earth Observation (EO) and communications, and has a growing business with the U.S. government. The company also brings innovation and technical advances to the world’s highest performance geostationary satellites.
Satellites that can help farmers better manage their crops, or help identify remote populations for vaccine programs, all help to make the world a better place. The satellites built at SSL incorporate advanced technologies that bring internet connectivity to remote locations where building out terrestrial infrastructure simply is not practical. The satellites assist in delivering better healthcare and education to these populations and enable economic development that improves lives.

Photo of the Telstar 19 VANTAGE satellite, courtesy of SSL. 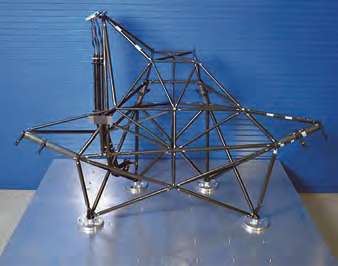
SSL’s first antenna strut tower design.
Image is courtesy of SSL.
SSL is a leader in commercial geostationary satellites with 90 commercial GEOs on orbit today, more than any other satellite manufacturer. SSL delivered four advanced communications satellites to the launch base in just several of the summer months of 2018. Each spacecraft will be used to connect people and transform lives around the world. SSL has a long history of iterative satellite design and gradually incorporates advances into every spacecraft system. These advances range from solar electric propulsion and more efficient antenna designs, to advanced payload architectures and new spectrum utilization. By building on its heritage, the company provides very innovative systems that also ensure the reliability that comes from a 60 year history of success.
Today’s smaller satellite platforms require a leap in design and technology advances. SSL is based in Silicon Valley in California and is influenced by the latest digital technologies, disruptive next-generation manufacturing, and creative, out-of-the-box thinking about what satellites and spacecraft can and should do. SSL builds spacecraft constellations for EO; robotics systems for building and fixing spacecraft on orbit; and is collaborating with NASA to provide a spacecraft that will travel to the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter that will enable scientists to study a mysterious, all metal asteroid.
Technology Advances
The company is focused on advances that provide higher value, greater flexibility and shorter schedules for their customers’ most critical missions. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a great example of a technology that is now regularly incorporated into all SSL spacecraft. In 2016, SSL launched their first antenna, a strut tower design (see the photo to the left) that was enabled by additive manufacturing. The company was one of the first satellite manufacturers to actually fly 3D printed components when JCSAT 14, built for Japanese satellite operator Sky Perfect JSAT, was launched. More recently, the company announced that 3D printing and other advanced technologies were used on a satellite for Spanish operator Hispasat.
The strut-truss design methodology used on the satellite, which brings a range of communications services to Europe, the Americas, and North Africa, contains more than 200 carbon fiber composite struts, making the antenna three times the size of the tower flown on JCSAT-14. In addition to the 3D printed nodes that enabled the antenna tower, more than 200 additively manufactured metal and polymer components were incorporated throughout Hispasat 30W-6. The use of this technology improved the overall assembly schedule, performance, and operational lifetime for the spacecraft.
Four Satellites This Summer
The high performance of the SSL satellites launched during the summer of 2018 is enabled by additive manufacturing, as well as many other advances. These satellites include improved power systems, more automation and some have very high throughput spotbeam architectures to meet the growing demand for massive amounts of data sent over the internet. A strong team effort was required to launch four commercial GEOs between mid-July and early September; thankfully, SSL’s passionate workforce always demonstrates that they are up to the task.
Telstar 19 VANTAGE, launched in mid-July, is one of a new generation of Telesat spacecraft designed to serve today’s bandwidth intensive applications. The satellite supports a range of services, including advanced broadband connectivity for consumer, enterprise and mobility users across the Americas and Atlantic from a prime orbital location of 63 degrees West, the same location used today by Telesat’s Telstar 14R.
In early August, the SSL built satellite for Telkom called Merah Putih, launched from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Merah Putih is named for the red and white colors of the Indonesian flag and was designed as part of the critical telecommunications backbone connecting thousands of islands in Indonesia, other parts of Southeast Asia, and to expand service to South Asia.

Photo of the Telstar 18 VANTAGE satellite.
Image is courtesy of SSL. 
Photo of the Merah Putih satellite.
Image is courtesy of SSL.
Merah Putih’s all C-band payload enhances both internet and telephone service for populations in remote regions and offloads backhaul for cellular service. With a launch mass of roughly 5,800 kg, the satellite incorporates many technology advances, including an antenna strut tower that was built using 3D printed parts. Merah Putih has 24 C-band transponders and 12 transponders for Extended C-band covering South East Asia and 24 C-band transponders covering South Asia.
Telkom decided upon a C-band payload for to ensure high reliability in regions that are characterized by heavy rainfall. Telstar 18 VANTAGE is the third in Telesat’s VANTAGE series of satellites. These are designed to maximize throughput and spectral efficiency while optimizing network performance by combining broad regional beams with powerful HTS spot beams for Telesat’s customers in enterprise, mobility and government markets.
Telstar 18 VANTAGE packs exceptional performance onto a single spacecraft with multiple payloads for high-speed internet service. The satellite provides extensive C-band coverage of Asia and possesses Ku-band high throughput spot beams over Indonesia and Malaysia. In addition, the satellite has five additional Ku-band regional beams. These high performance beams will enable Telstar 18 VANTAGE to meet growing demand for mobility, enterprise networks and telecom services across the Asia region.
In early August SSL, also shipped the multi-mission Azerspace-2/Intelsat 38 communications satellite to the European Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana, for launch in early September. This is one more SSL-built satellite that integrates state-of-the-art technologies and design to bring information, connectivity and entertainment on the ground.
Azerspace-2 will assist the Azerbaijani company, Azercosmos, meet the growing demand for Direct-to-Home (DTH) television, government, and network services in Europe, Central and South Asia, the Middle East and Sub-Saharan Africa and is Azercosmos’ second telecommunications satellite and will expand on the service currently available from Azerspace-1.
For Intelsat, the satellite has a payload that will provide continuity of service for the Intelsat 12 satellite, which was also built by SSL and was launched in 2000. At 45 degrees East, the satellite enables Intelsat’s media customers to deliver enhanced service offerings across Central and Eastern Europe and Asia Pacific and also provides the broadband connectivity needed to support the services rendered by Intelsat’s corporate network and government customers operating in Africa.
Next Generation Satellite Systems
In addition to all of SSL’s advances to provide the highest performance and capacity to the firm’s geostationary customers, the company focuses on next-generation LEO-based infrastructure solutions and EO satellites. SSL has built, or is building, more than 90 smallsats — since 2016, the company has delivered 11 satellites for Planet, with two more planned for launch later this year.
The company takes an agile, “new space” approach to building smallsat constellations, an approach that is supported by a long heritage of expertise. SSL’s cost-efficient solutions for emerging applications include the use of Commercial-Off-The-Shelf (COTS) hardware that is screened to meet appropriate radiation levels, together with flight-proven high reliability hardware and software.
A state-of-the-art “factory of the future” will speed production for standard platforms, such as the SSL 100 and SSL 500. However, SSL’s experience with industry leading processes is what ensures the correct balance of high reliability, speed to market and value. The company is simplifying space for start-ups and can deliver the correct resources to help customers from mission concept to on orbit operation.
The linchpin in this next-generation capability is the highly advanced satellite constellation that SSL is currently building for DigitalGlobe, the global leader in Earth imagery and information about the changing planet. Called WorldView Legion, the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites will more than double DigitalGlobe’s high-resolution capacity in important regions.
DigitalGlobe and SSL are both Maxar Technologies companies and this program demonstrates SSL’s emerging leadership in EO satellites as well as Maxar’s broadening corporate capability to provide end-to-end solutions from the space to the ground segment to the delivery of decision-driving analytics. The WorldView Legion constellation is a cost-effective solution to deliver high-resolution, sub-meter accuracy, and fast revisit rates and SSL will leverage this design for U.S. government and allied government space infrastructure needs.
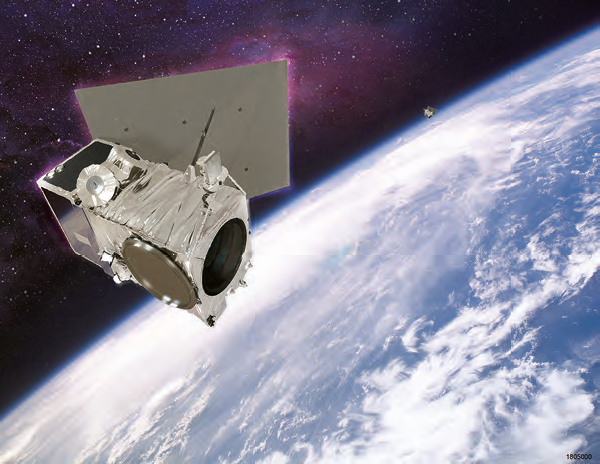

Artistic rendition of the finalized, SSL-built WorldView
Legion for DigitalGlobe. Image is courtesy of SSL.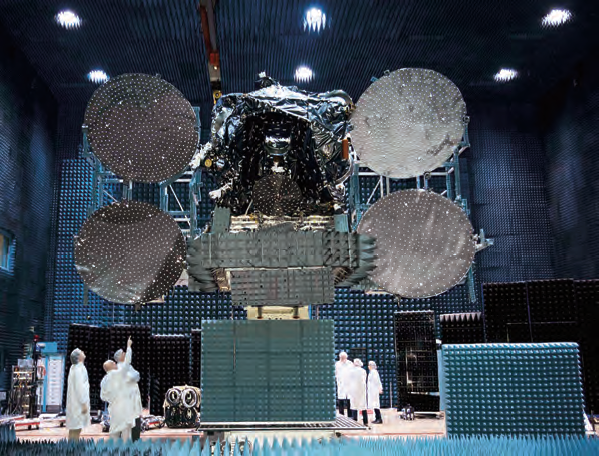 
Photo of the Azerspace-2 / Intelsat-38 satellite.
Image is courtesy of SSL.
Communications Satellite Constellations
However, innovation in LEO doesn’t end with EO. SSL is also developing technologies for innovative communications satellites that benefit from the low latency orbit that can serve Internet of Things (IoT) applications. The company formed a consortium with Thales Alenia Space to pursue the development and manufacture of Telesat’s highly advanced global LEO satellite constellation and end-to-end system.
Telesat’s LEO constellation is expected to provide global availability and to become a core component in satisfying many of the world’s most challenging communications requirements, such as accelerating 5G expansion, ending the digital divide and establishing new levels of performance for commercial and government broadband on land, sea and in the air.
Thales Alenia Space and SSL were selected by Telesat to complete a preliminary design as well as to perform a series of technical reviews leading to a firm proposal for manufacture and launch of the LEO satellites and deployment of the ground system infrastructure. Telesat anticipates deciding by mid-2019 on a prime contractor for the program, with the Thales and SSL consortium one of two competitors.
Innovation for a Better World
As a Maxar Technologies company, SSL is committed to developing new technologies and tools with a commercial mindset that benefits not only customers but human kind.

SSL and the additional Maxar Technologies companies are accelerating innovation for the new space economy. Accelerating innovation means bringing technologies and capabilities together at a much faster pace, driving solutions that improve performance, removing complexities, and realizing economic benefits. With an eye to the future, the SSL team continues to innovate to meet the many challenges on Earth that can only be solved from space.
www.sslmda.com
Rob Schwarz is the Chief Technology Officer at SSL. He has more than 20 years’ experience in the space industry working in space systems engineering and product development. He is passionate about uncovering challenges and working with talented teams to find creative and innovative solutions that improve performance and reduce time to market. Rob holds degrees in Mechanical Engineering and Aeronautics/Astronautics from Rutgers University and MIT.
Innovation is Crucial
Mr. Robert Zitz, the Chief Strategy Officer for SSL, offered his thoughts regarding Innovation, an element that is so critically important to SSL as well as for any company in this industry.
“As in any business endeavor, innovation is the key to continued growth. Customers and consumers’ needs are evolving and the space industry is evolving to meet those needs. Participants in the space industry are fortunate because we can help make life better on Earth with innovations in environmental science, sustainable energy, medicine, and connecting more people to the world economy. In addition, space innovation in the areas of earth observation, communications and positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) improves our national security. SSL is proud to be a leader in many of the enabling technologies.”
When asked what innovative missions or projects does SSL have underway he noted, “SSL is an industry leader in high throughput, focused beam communications satellites in geostationary orbit and expect to be a driving force in low earth orbit communications satellites. We build high resolution Earth observation satellites that are delivering critical information to our commercial and government customers. SSL is playing a leading role in solar electric propulsion, space robotics and we have key projects underway developing on orbit servicing and on orbit assembly capabilities.
When discussing the innovative technologies he believes will drive the space and satellite industry over the next year or so, Mr. Zitz said, “I believe we will see much more 3D printing to enable geometries and large structures that were not possible before. Miniaturization of electronics and more efficient antenna designs and power systems will contribute to increasingly capable spacecraft in smaller form factors. Robotics will flourish and revolutionize space by permitting on orbit manufacturing, assembly and servicing.“

He added, “I envision large constellations of smaller satellites using advanced onboard processing performing missions autonomously.
Not all space technologies are in orbit, much of the future depends upon ground system technologies. We are working closely with our Maxar sister company Radiant Solutions, which does advanced mission management
and big data processing. We recognize machine learning, artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies will be crucial to success in future space-based capabilities.



