Strategic relationship initiated between BridgeSat and Es’hailSat
Es’hailSat Qatar Satellite Company and BridgeSat have joined together with a strategic relationship that will provide businesses and governments across the Middle East with affordable access to laser-based satellite broadband services.
This is the latest milestone toward BridgeSat’s goal of providing organizations worldwide with a faster, less expensive and most secure alternative to traditional radio frequency (RF) solutions for LEO and GEO applications.
BridgeSat owns and operates a growing global network of optical ground stations (OGS) and complimentary satellite terminals that provide high-bandwidth, high-security solutions for unique applications while complementing RF in hybrid networks.
Es’hailSat owns and operates a growing number of Ka- and Ku-band satellites that serve broadcasters, businesses and governments in the MENA region and beyond.
Under this strategic relationship, BridgeSat will build their first OGS for the Middle East, which will be co-located at Es’hailSat’s new satellite operations center in Doha, Qatar.
The new OGS will support LEO and other satellite systems owned by Es’hailSat and other companies that are equipped with BridgeSat and other compatible space terminals.
Barry Matsumori, BridgeSat CEO, said this new relationship with Es’hailSat gives the company a critical gateway to the MENA region and is a major milestone toward the firm’s goal of providing organizations worldwide with fast, secure, enterprise-grade broadband services.
Ali Al Kuwari, President and CEO of Es’hailSat, noted that the Es’hail-1 and Es’hail-2 satellites are fully operational and the company recently commenced satellite control and other satellite services from the firm’s state-of-the art teleport in Doha.
He added that collaboration with BridgeSat is step forward for the company in expanding the type of services provided to customers in the region, beyond the traditional satellite services.
www.bridgesatinc.com
www.eshailsat.qa
Newtec collaborating with Wind River for development of 5G solutions
Newtec is collaborating with Wind River to use the Wind River Titanium Cloud virtualization platform to develop a Newtec 5G solution based on the Newtec Dialog® multi-service platform.

3GPP has defined a service-based architecture where flexibility and dynamic adjustments are the key drivers to meet performance and cost requirements. This architecture defines network functions which can be triggered by other services, leveraging virtualization and network slicing.
Wind River’s complete Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) software platform infrastructure will help Newtec Dialog leapfrog these 5G requirements. The Titanium Cloud platform delivers the features needed to successfully build and deploy a virtualized network running multiple Virtual Machines.
Newtec has signed a joint statement with the European Space Agency (ESA) and a number of industrial companies to carry out trials to demonstrate the use of satellite communications capabilities integrated and interoperable in the 5G environment, achieve interoperability of networks and demonstrate the functionality, performance and benefits brought by the use of satellite.
A first phase is leveraging existing space and ground segment assets and trialling the latest developments, including with newer LEO and MEO constellations.
Bart Van Poucke, VP Product Management at Newtec, said NFV promises lower-cost, highly flexible and scalable infrastructure, as well as providing customers with the ability to get better service access anywhere in the world. The combination of Newtec Dialog with Wind River’s Titanium Cloud platform will enable the firm’s customers and service providers to scale services up or down quickly to address changing needs. It also simplifies the architecture and enhances scalability, which is paramount for 5G.
Paul Senyshyn, VP of Telecommunications at Wind River, added the company is delighted that Newtec has selected the Wind River Titanium Cloud platform for use in their new, 5G satellite infrastructure solution. Titanium Cloud delivers the high service reliability, ultra-low latency and low-cost deployments that are critical for scalable satellite communications infrastructure.

Semir Hassanaly, Market Director Mobile Backhaul at Newtec, noted that a number of use-cases for 5G over satellite require close interworking with terrestrial mobile networks where NFV/SDN technologies are becoming key and satellite architecture must leverage network orchestration, virtualization and slicing functions to offer a truly seamless connectivity service. The integration of Wind River’s Titanium Cloud platform is an additional step Newtec is making toward 5G. The same architecture principles will be also leveraged in Newtec’s terminals in the near future, paving the way for a 5G solution addressing Mobile Backhaul, OTT Broadcast, Broadband and Mobility markets.
www.newtec.eu
www.windriver.com
Virgin Galactic’s SpaceShipTwo Accesses Space
Virgin Galactic conducted their fifth powered test flight and second space flight of its commercial SpaceShipTwo, VSS Unity.

In this powered test flight, Virgin Galactic reached space for the second time in the skies above Mojave, California. Spaceship VSS Unity reached its highest speed and altitude to date and, for the first time, carried a third crew member on board along with research payloads from the NASA Flight Opportunities program.
This space flight means Chief Pilot Dave Mackay and co-pilot Michael “Sooch” Masucci become commercial astronauts and the 569th and 570th humans in space. Beth Moses, Virgin Galactic’s Chief Astronaut Instructor, flew as the third crew member in a first, live evaluation of cabin dynamics. She is the 571st person to fly to space and the first woman to fly on board a commercial spaceship.
VSS Unity flew higher and faster than ever before, as its world record-holding hybrid rocket motor propelled the spaceship at Mach 3.04 to an apogee of 295,007ft. The glide back home was followed by a smooth runway landing.
This flight notched several additional firsts for the industry: The flight was the first time that a non-pilot flew on board a commercial spaceship to space, and it was the first time that a crew member floated freely without restraints in weightlessness in space onboard a commercial spaceship; it was the first time that three people flew to space on a commercial spaceship, and Dave Mackay became the first Scottish-born astronaut (Brian Binnie, who was raised in Scotland, flew to space in 2004).
Dave said, “Beth, Sooch and I just enjoyed a pretty amazing flight which was beyond anything any of us has ever experienced. It was thrilling yet smooth and nicely controlled throughout with a view at the top, of the Earth from space, which exceeded all our expectations. I am incredibly proud of my crew and of the amazing teams at Virgin Galactic and The Spaceship Company for providing a vehicle and an operation which means we can fly confidently and safely.”
Sir Richard Branson added, “Flying the same vehicle safely to space and back twice in a little over two months, while at the same time expanding the flight envelope, is testament to the unique capability we have built up within the Virgin Galactic and The Spaceship Company organizations. I am immensely proud of everyone involved.“
www.virgingalactic.com
Senior leaders from SpaceX and Virgin Orbit join the Relativity Space executive team
Relativity has appointed three aerospace veterans to the company’s executive team and has received an industry-leading, new, patent grant for their autonomous 3D printing technology.
The company has now hired 12 former senior leaders from SpaceX, Blue Origin, Virgin Orbit, Aerojet Rocketdyne, Waymo, Zoox, and Tesla, and has also secured a key patent for 3D printing metal using machine learning.

Tim Buzza, recognized as one of the world’s foremost experts in rocket development, as well as among the first leaders and a 12 year at SpaceX, as well as the former Co-President and Vice President of Launch at Virgin Orbit, officially joins Relativity as Distinguished Engineer after serving as an Advisor to the company.

Josh Brost, a nine year veteran at SpaceX responsible for securing $3 billion in contracts with the U.S. Government and commercial entities, joins as VP, Government Business Development.

David Giger, a 13 year SpaceX veteran who directed engineering, program, and leadership responsibilities for more than 200 engineers in the design, testing and build of the multi-billion dollar Cargo Dragon and Crew Dragon spacecraft programs, joins as VP, Launch Vehicle Development for Relativity’s Terran 1 rocket.
Relativity was recently granted US Patent Number US20180341248A1, Real-time adaptive control of additive manufacturing processes using machine learning, for the company’s groundbreaking 3D metal printing technology using advanced sensors and control software.
Disrupting 50 years of aerospace technology, Relativity is the first and only aerospace factory to use a proprietary and patented autonomous 3D printing technology, machine learning and software to optimize every aspect of the rocket manufacturing process.
Relativity’s Stargate, the largest metal 3D printer in the world — Built for rockets. Photo is courtesy of the company.
Relativity can print their next-generation Terran 1 rocket in less than 60 days, while traditional rockets require 18 months or more to complete.

Relativity’s Stargate, the largest metal 3D printer in the world — Built
for rockets. Photo is courtesy of the company.
Terran 1 is the world’s first completely 3D printed rocket, with 100x fewer parts than traditional rockets, vastly better manufacturing reliability, rapid build time, and faster time to launch.
Relativity is on track to conduct their first full orbital launch by the end of 2020 and continues to grow a global customer manifest of commercial and government payloads.
The company recently became the first venture-backed company to secure a launch site Right of Entry at Cape Canaveral from the U.S. Air Force, adding to the firm’s portfolio of major government partnerships, including a 20 year, exclusive-use, CSLA agreement at the NASA Stennis Space Center E4 test complex as well as a NASA ACO test award.
The company is expanding its infrastructure this year with a fourfold expansion to more than 240,000 square feet of operations, production, testing, and launch facilities.
Relativity’s team has grown almost 5x since March, from 14 to 64 full time employees in under a year.
Tim Ellis, the CEO of Relativity, said the company’s progress toward launching the first 3D printed rocket is fueled by a deeply experienced team that has built and scaled other space companies — Tim, Josh, and David are renowned leaders in their fields. These executive appointments, combined with the company’s recent patent grant, are great indicators of Relativity’s market momentum.
Jordan Noone, the CTO of Relativity, added that the grant of this patent is a recognition of how the company’s autonomous 3D metal printing technology can quickly and iteratively optimize rocket production on Earth and other planets and is a pivotal step toward our technology differentiation and leadership in the market.
www.relativityspace.com
SSTL’s RemoveDEBRIS satellite capture mission is a success
A successful capture was completed by the SSTL-developed RemoveDEBRIS satellite.
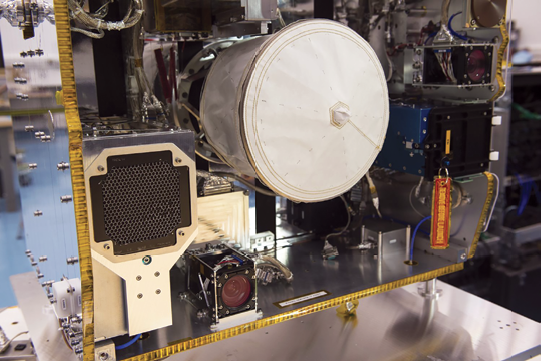
The harpoon was fired at a speed of 20 meters per second and penetrated a target made of satellite panel material.
The harpoon and 1.5 meter target boom were designed by a team at Airbus in Stevenage, UK.
The photo shows the harpoon target bottom left, with the onboard camera to the right. The spherical structure in the center with the white cover is the net housing.
The success of the harpoon firing marks the third successful experiment for the RemoveDEBRIS project which has already demonstrated a net capture experiment and trialed its state-of-the-art LiDAR based vision navigation system to identify a target cubesat.

The RemoveDEBRIS satellite platform was designed and manufactured by SSTL to house two target cubesats and four debris removal technologies — a net, a harpoon, vision based navigation using cameras and LiDaR, and a de-orbit dragsail. The spacecraft is operated in orbit by SSTL’s engineers from the company’s Spacecraft Operations Centre in Guildford, UK.
The RemoveDEBRIS team is now preparing for the final experiment, which is scheduled to take place in March and will witness the RemoveDEBRIS spacecraft inflate a sail that will drag the satellite into Earth’s atmosphere for destruction.
A video produced by SSL is available for viewing at https://youtu.be/_uPw9KP4Ii0?t=7
The U.S. Space Surveillance Network tracks 40,000 objects and the estimate is that there are more than 7,600 tons of ‘space junk’ in and around Earth’s orbit — with some moving faster than a speeding bullet, approaching speeds of 30,000 miles per hour. The RemoveDEBRIS consortium is:
• Mission and consortium coordination – Surrey Space Centre (UK)
• Satellite system engineering – ArianeGroup (France)
• Platform, avionics and spacecraft operations – SSTL (UK)
• Harpoon – Airbus (UK)
• Net – Airbus (Germany)
• Vision based navigation – CSEM (Switzerland)/ INRIA/ Airbus (France)
• CubeSat dispensers – Innovative Solutions in Space (Netherlands)
• Target CubeSats – Surrey Space Centre (UK)/ Stellenbosch University (South Africa)
• Dragsail – Surrey Space Centre (UK)
The RemoveDEBRIS project is co-funded by the European Commission and the research leading to the results has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Program (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement n°607099.
www.sstl.co.uk




