Airbus Completes 2nd Ocean Satellite Sentinel-6B
Airbus has completed Sentinel-6B, the second ocean monitoring satellite of the European Copernicus program and is now testing it extensively over the next six months in preparation for its use in space.

Sentinel-6B loaded in a container for shipment.
Image is courtesy of Airbus / T. Locher.
The Copernicus Sentinel-6 mission is already delivering high-precision measurement of the topography of ocean surfaces through the first of two satellites, Sentinel-6A, launched in November of 2020. The mission’s two satellites are built to measure the distance to the sea surface to an accuracy of a few centimeters and map it in a 10-day rhythm over a mission duration of up to seven years. Their purpose is to record changes in the height of the sea surfaces, variations in sea levels and analyze and observe ocean currents. Accurate observation of sea surface height changes provides information about global sea levels, the speed and direction of ocean currents and the heat stored in the oceans. The measurements — obtained from 1,336 km. above the Earth — are crucial for ocean mod-elling and predicting sea level rise.

Artistic rendition of Sentinel-6B on-orbit.
Image is courtesy of ESA.
This information helps governments and institutions to establish effective protection for coastal regions. The data is also valuable for disaster management organisations, and for authorities carrying out urban planning, flood protection schemes, or dyke construction.
Global sea levels are currently rising by an average of 3.3 millimeters per year, with potentially dramatic consequences for countries with densely populated coasts.
Part of Europe’s Copernicus, Sentinel-6 is also an international collaboration between ESA, NASA, NOAA and Eumetsat.
Satixfy’s Baseband Modem

To Integrate With Telesat’s Lightspeed Earth Stations Across The Globe Telesat (NASDAQ and TSX: TSAT) and SatixFy have agreed to deploy the latter’s baseband modem equipment for Telesat Lightspeed gateway Earth stations throughout the world.
The SatixFy advanced Sx3099 landing station modems will be capable of processing up to 1.6 GHz of bandwidth in each direction, supporting 10 wideband carriers, uplink power control (UPC) and adaptive coding and modulation (ACM), and network data processing.

Each landing station antenna will be capable of transmitting approximately 12 Gbps on the forward link and receiving approximately 6 Gbps on the return link.

SatixFy’s Baseband Modem for Landing Stations
This manufacturing agreement follows a previously announced early access program to validate and qualify the Sx3099 modem ASIC for use in the Telesat Lightspeed ground infrastructure.
Capabilities validated during the early access program include simultaneous high throughput transmit and receive performance, and passing end-to-end traffic between the Sx3099 Ethernet ports and the RF interface using multicarrier operations over the DVB-S2X air interface.

“Packaged in a small, lightweight outdoor enclosure, SatixFy’s innovative technology and equipment delivers a powerful value proposition for our gateway earth station network,” said Aneesh Dalvi, Telesat’s Director of LEO Landing Stations and User Terminals. “With SatixFy’s solution, we have further optimized our landing station size and capacity while reducing deployment and operating costs.”
“We are honored to be awarded the first significant terrestrial equipment program for the Telesat Lightspeed LEO network,” said Yoel Gat, SatixFy’s CEO. “We are confident that the high performance of the Sx3099 modem will serve as a solid basis for the advanced global Telesat Lightspeed network.”
Astranis + Andesat and Sign Two-Satellite Agreement To Expand Broadband Access In Peru
Astranis has signed an agreement to provide broadband capacity with Astranis MicroGEO communications satellites to Grupo Andesat (Andesat), a cellular services backhaul provider that connects cell towers in Peru to the internet backbone, in a new partnership that will bring broadband internet access to thousands of rural communities across Peru for the first time.

In a deal worth more than $90 million, an initial Astranis satellite will launch into service in 2023 to become the first satellite in history dedicated solely to serving the people of Peru.
The contract also features an option for a second satellite to create additional capacity in the future. These advanced MicroGEO satellites are 1/20 the size of traditional legacy satellites, and roughly 1/10 the cost, which will allow Andesat to upgrade cellular services from 2G to 4G, expand broadband internet access in remote areas of Peru, and increase its coverage footprint while dramatically lowering operator costs per cell site.

Andesat has broad reach across Latin America (LATAM) with teleports in multiple countries (Argentina, Chile, Ecuador and Peru) and prospective global capabilities. Andesat offers end-to-end services like cellular networks in rural areas, cellular backhaul, IoT solutions design and more.
The company estimates that this partnership will allow more than three million Peruvians, many in rural and otherwise remote areas, to access affordable 4G service on their mobile devices for the first time.

Astranis satellites provide service in smaller geographies or medium size countries, delivering dedicated satellite bandwidth to boost broadband internet capacity.
The capital-efficient design of an Astranis MicroGEO satellite requires only a modest investment by cell backhaul providers, which translates into dramatically lower costs for middle-mile bandwidth and faster network speeds for end users at an affordable price point.

Astranis’ first commercial communications satellite, set to
provide service for Alaska from geostationary orbit, will launch
as a secondary payload on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on
a direct-inject mission set for the Spring of 2022.
In addition to building, launching, and operating the satellite, Astranis will be constructing its first-ever ground teleport in Peru and operating as a full- stack managed service provider for all spaceflight operations, with Andesat owning ground operations.
“This is a landmark deal not only for Andesat, and not only for Peru, but for all of Latin America,” said Pablo Rasore, CEO of Andesat. “One Astranis satellite is a great first step, and will extend affordable 4G service from the jungle to the mountains and up to the seas in Peru. But Andesat has larger plans as we see demand for additional Astranis satellites in the near future, and have secured an option for a second satellite to promote the expansion of our business in Peru and bring the benefits of connectivity far and wide.”
“This deal with Andesat is closely aligned with our mission of connecting the unconnected by making broadband internet access available to everyone, even in the most remote locations on Earth,” said John Gedmark, CEO and co-founder, Astranis. “Through this new partnership, Astranis has the opportunity to help make a dramatic improvement in the lives of millions of people. I’m proud to be working alongside Pablo and the team at Andesat to make the vision of a connected Peru a reality.”
Northrop Grumman Gleans Space Launch System (SLS) Rocket Booster Production Contract From NASA
NASA has awarded Northrop Grumman Corporation (NYSE: NOC) a booster production and operations contract valued up to $3.19 billion to support the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket through 2031. The award includes follow-on production and flight sets for Artemis IV through Artemis VIII, as well as production of the Booster Obsolescence and Life Extension (BOLE) boosters for Artemis IX.

The award supports the design, development and testing of the next generation five-segment solid rocket boosters to supplement and replace the eight remaining reusable Space Shuttle Program-era assets.

The new BOLE boosters will replace the steel cases used for the shuttle with a weight-saving composite case and upgraded structures, electronic thrust vector control systems and propellant materials to address obsolescence.
This improved design additionally provides process simplification, improved interface, and streamlined ground processing at Kennedy Space Center, leading to greater productivity and efficiency.

NASA completed stacking Oct. 21, 2021,
of the agency’s Space Launch System
rocket and Orion spacecraft for the Artemis
I uncrewed mission around the Moon.
The stacking operations were conducted
inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at
NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Photo is courtesy of NASA. 
NASA’s Space Launch System will be the most
powerful rocket we’ve ever built. When completed,
SLS will enable astronauts to begin their journey
to explore destinations far into the solar system.
Artemis II booster production is complete and segments await transportation to Kennedy Space Center upon NASA’s request. All ten segments for Artemis III have been cast with propellant, and Artemis IV segments began casting in November.
The first composite BOLE booster segment case to be used for development testing completed winding in October.
Northrop Grumman has been awarded multiple contracts to support NASA’s Artemis program including the abort motor and attitude control motor for the Orion spacecraft’s launch abort system, designed to ensure astronaut safety during launch and ascent, atop the SLS rocket.
The company is also providing the Habitation and Logistics Outpost module for NASA’s Lunar Gateway and was recently awarded a contract to develop Lunar lander concepts under NASA’s NEXTStep-2 Appendix N contract.
“BOLE leverages our previous investments and existing infrastructures in SLS and supports long-term sustainability of NASA’s exploration programs,” said Wendy Williams, vice president, propulsion systems, Northrop Grumman. “This new booster design will provide additional heavy lift performance and support greater payload volume A for deep space human and science missions.”
EUMETSAT Council’s ‘Green Light’ For Weather + Climate Data Improvement
The European meteorological satellite agency, EUMETSAT, has consolidated their position as a leading provider of weather, climate and Earth system data and has announced a series of new agreements, contracts and data exchange arrangements today.

Many of the new arrangements, approved by EUMETSAT’s governing council this week, flow from the organization’s recent signing of the Copernicus 2.0 agreement with the European Union.
The EUMETSAT Council approved a four-party arrangement between EUMETSAT, the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), Mercator Ocean International and the European Environment Agency to continue to cooperate on the Copernicus data and information access service platform, WEkEO, from 2022 to 2028.

WEkEO is the EU Copernicus DIAS reference service for environmental data, virtual processing environments and skilled user support. A platform for all audiences.
“The WEkEO platform makes Copernicus data easily available to a growing number of Earth observation data users through a federated, cloud-based platform that brings each of the organization’s particular strengths into play,” EUMETSAT Director-General Phil Evans said. “As an operational agency, one of EUMETSAT’s strengths is its end-to-end responsibility for satellite systems. The council today approved the implementation arrangement for cooperation between EUMETSAT and the European Space Agency (ESA) on the Copernicus anthropogenic carbon emissions monitoring mission, CO2M. EUMETSAT will operate the CO2M satellites and receive, process and disseminate their data, which will be crucial for monitoring carbon emission reduction efforts globally, in line with the Paris Agreement.”
The council also approved a multi-annual agreement for EUMETSAT to provide satellite data records to the ECMWF for the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S), which it hosts.
“EUMETSAT has a unique capability to generate these records in a traceable way that is unprecedented in Europe and has already proven invaluable to the C3S,” Evans said. “The agreement approved today extends that cooperation between EUMETSAT and the ECMWF at a time when precise and verifiable data about the Earth’s climate has never been more important.”
The council has also agreed that the European Weather Cloud platform, a joint EUMETSAT and ECMWF initiative, should transition from a pilot project to fully operational status in 2022.
“The European Weather Cloud is a critical development for meteorological services throughout Europe,” Evans said. “It provides access to data from EUMETSAT, the ECMWF and national meteorological services on one cloud-based platform and allows meteorological services and other users to process the data on the platform. The aim of the initiative is to bring tangible improvements to weather forecasting accuracy through access to data and ease of use.”
Meanwhile, EUMETSAT will sign a 9.5 million euros contract with CloudFerro to procure cloud services for its own data access platforms and the European Weather Cloud.
Additionally, the EUMETSAT Council approved arrangements with two of the organization’s key international partners, Russia and Canada. EUMETSAT will enter into an arrangement to receive data from Roshydromet’s Arctica-M N1 mission, if consent can be received to redistribute the data without restriction. The Arctica satellites will fly on a highly elliptical orbit, which provides data about arctic weather, ice cover and climate, and also information for aviation meteorology and disaster monitoring, that is not obtainable from other orbits.
And EUMETSAT will also renew its memorandum of understanding with Canada’s Department of Environment for long-term cooperation relating to meteorological satellites, climate monitoring from space and space weather.
AXESS’ Satellite Growth In Latin America Serves To Advance The Growth Of MNOs
AXESS has a global infrastructure, recognized by the WTA (World Teleport Association), and operates three main teleports located in Germany, Mexico and Colombia and two alternatives in UAE and Peru. In the last two years AXESS Networks has positioned satellite technology in Latin America as the most suitable means for the growth of the main MNOs (Mobile Network Operators) and Wholesale Mobile Operators.

The satellite cellular backhaul solutions designed and implemented by AXESS Networks have become an alternative for the expansion of mobile operators, providing them with advantages such as a fast deployment response, performance with low latencies, high speeds and a convenient cost structure tailored to their business.
AXESS optimized satellite solutions operators from different countries in the region have been able to quickly advance to close the digital gap in remote populations with difficult access.
In addition, these solutions are also enabling the growth of Wholesale Operators and providing the creation of new MVNOs and MVNEs (Mobile Virtual Network Enablers), that expands the industry’s value.
Some of the most important projects that have had a great social impact with the growth and coverage of the operator´s networks are:
Mexico: AXESS has enabled the rapid and efficient expansion of one of the main Cellular Operators’ network, and has also deployed most of the backhaul links for the main wholesale operator in its progress towards the goal of connecting 92 percent of the Mexican population.

In these two large implementations, AXESS has provided comprehensive solutions, supplying the satellite infrastructure, installing and putting into operation the sites, managing the network, optimizing the use of capacity and providing all the necessary support to meet the parameters of the operators and the regulatory requirements.
Colombia: The support of AXESS allowed a leading cellular operator to expand its commercial offer in unattended areas, growing its market share, with 30 Mbps channels and latencies of 650 ms for highly available LTE (Long Term Evolution) voice and data services. With this operator, an AXESS client for many years, other projects have begun work, such as enabling of connectivity in the island of San Andrés, which was badly affected after Hurricane Iota, and the implementation of the 700 MHz band with 150 regulatory points in 23 regions of the country.
The AXESS cellular backhaul solution was key to the market entry of a new operator, which, as a result of the efficient deployment of satellite cellular coverage, was able to quickly reach its initial goal of having one million users. With this same company, AXESS achieved a milestone for the satellite industry, by its backhaul satellite solution being selected, competing directly with a fiber optics alternative. The reasons mentioned by the client were the very fast implementation, standardization of the solution, optimized costs, and support and service capacity.
Peru: AXESS has been in operation for several years, a sophisticated redundant solution to provide a 1GB backhaul channel in the isolated and very rainy area of Iquitos. And recently, coverage expansion projects have been deployed for two other major operators, reaching populations difficult to access for terrestrial technologies with cellular coverage in areas such as the Amazon and Yauyos.
Additionally AXESS’s satellite cellular backhaul solutions was awarded a large cellular backhaul channel for the city of Leticia in Colombia, which has recently been put into operation.
In order to become the satellite technological ally of the main cellular operators in the region, AXESS made significant investments in infrastructure, incorporating 2 state-of-the-art satellite hubs, expanding its teleport in Colombia and implementing a second Tier3 teleport in Mexico.
The Arianespace VS26 Mission Launches Successfully Via A Soyuz Rocket
Arianespace’s 13th launch of 2021 via the 8th Soyuz mission of the year successfully launched the Galileo FOC 23-24 satellite passengers for the European Space Agency (ESA) into Medium Earth Orbit (MEO). The launcher lifted a total payload of approximately 1,645 kg. The launch was performed from Kourou, in French Guyana, at 21:19 Kourou time, (December 5, 00:19 UTC; December 4, 7:19 p.m., EST).

Operational since 2016, Galileo is the global navigation satellite system that is fully financed and owned by the European Union. Under civilian control, it offers high-precision positioning, navigation and timing services to more than 2,3 billion users worldwide, offers dual frequencies as standard and is designed to deliver real-time positioning accuracy down to the meter range.
The Galileo satellites are built by prime contractor OHB System, with the payloads supplied by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd. (SSTL), an Airbus Defence and Space subsidiary.

Undertaken by a European partnership, the European Commission manages Galileo, with European Space Agency (ESA) as the design authority overseeing its development, procuring satellites and the ground segment, and the European Union Agency for the Space Program (EUSPA) overseeing Galileo operations and service provision.

The medium-lift Soyuz (produced by Progress Space Rocket Center, part of the Russian space agency Roscosmos) entered service from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana in October of 2011, bringing the industry’s longest-operating launcher to the world’s most modern launch base.
Soyuz is a four-stage launcher, designed with extremely high reliability requirements for its use in manned missions.
This flight also marks 10 years of Soyuz operations in French Guiana and its 26th mission for the European Spaceport.

A Galileo FOC payload laid out in the SSTL
cleanroom for final tests. The rubidium atomic clocks
and hydrogen maser units are center right and left.
Photo is courtesy of SSTL
“Congratulations Europe! With this 11th launch for Galileo, the constellation is now counting 28 satellites in orbit. Arianespace is proud to guarantee a secure and autonomous access to space with the deployment of Galileo, marking another step towards European independence in satellite navigation,” said Stéphane Israël, CEO of Arianespace. “I would like to thank the European Union, especially the European Commission, as well as the European Space Agency, our direct customer for this launch, for continuing to trust us with their satellites.”
VS26 ise the 150th mission launched by Arianespace for European institutions, the 46th mission of Soyuz at the service of institutional needs. This flight will also mark 10 years of Soyuz operations in French Guiana.
Out of 26 Galileo satellites already in orbit, 14 have been launched by Soyuz between 2011 and 2016; and 12 by Ariane 5 between 2016 and 2018. VS26 will raise Galileo’s total fleet to 28 satellites, before Soyuz and Ariane 6 orbit six additional Galileo FOC satellites. The target for a full deployment of Galileo’s first generation is approximately 2025.
AsiaSat + Turbidite Secure Partnership For Satellite + Ground-based Connectivity
Turbidite Limited (“Turbidite”) and Asia Satellite Telecommunications Company Limited (“AsiaSat”) have cemented a partnership into place that will leverage AsiaSat’s existing satellite and ground infrastructure with Turbidite’s dynamic, edge data center platform to support the accelerated demand for digital services. The partnership will bring together the expertise and skills of the two companies to provide hosting services alongside satellite and ground- based connectivity from AsiaSat’s Tai Po Earth Station.

AsiaSat has been awarded ISO/IEC 27001: 2013 Information Security Management System Certification for its hosting services provided from Tai Po Earth Station in Hong Kong.
“We are delighted to enter into this partnership with AsiaSat as we broaden our edge data center solutions to support new mandates by the growing number of OTTs and media companies as they continue to drive up digital traffic,” said Bill Barney, Co-Founder & Chief Executive Officer, Turbidite. “Together with AsiaSat, we are able to further empower these customers to transform into digital ready organizations with secure access, flexible transport/bandwidth options and real time deployment.”

“We see this partnership as one of our strategic moves to support customers with a breadth of new services to cope with the rapid pace of digital transformation,” said Roger Tong, Chief Executive Officer, AsiaSat. “Turbidite’s extensive expertise in the data center and network infrastructure deployment and management will truly complement our current satellite and ground-based solution portfolios. We look forward to working with Turbidite to further develop and enhance our infrastructure to meet the flexibility and diversity required by our customers.”
Turbidite’s Edge Data Center Platform was launched in March 2021 to support Asia Pacific’s growing tech infrastructure demands.
Based in Hong Kong, Turbidite is acquiring and developing a series of carrier neutral edge data centers, with comprehensive value-added services to support multinational corporations, large Internet companies and other hyperscalers expanding across the region.
Anuvu Constellation Receives Growth Capital Commitment
Anuvu has secured a commitment for a total of $50 million of growth capital to support the expansion of the Anuvu Constellation and other growth initiatives.
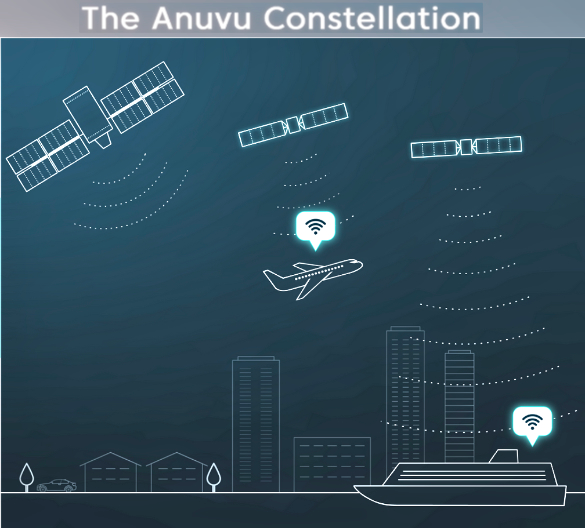
In addition, Anuvu secured board authorization for new equity as required to support additional expansion of the Constellation. This capital initiative accelerates Anuvu’s growth strategy and received the full support of the company’s investors including the following companies or their managed investment funds: Apollo Capital Management, L.P., Sound Point Capital, and Arbour Lane Capital Management, LP, among others.
The capital is anticipated to support the expansion of the Anuvu Constellation ground and space networks, including its network management and data platforms and advanced mobility-focused antennas. With two digital payload satellites expected in service in early 2023 and an advanced ground network already ready for service, Anuvu is redefining geosynchronous orbit (GEO) mobility connectivity and paving the way for hybrid GEO and Low Earth Orbit (LEO) network operations.
“Since announcing the Anuvu Constellation, the demand from our global mobility customers has been extraordinary. More than ever, our clients are looking to Anuvu to provide flexible satellite capacity built for mobility, without the inherent compromises of traditional geostationary designs. Today’s announcement is a testament to the success of the Anuvu Constellation and our strategy for hybrid networks,” said Josh Marks, CEO of Anuvu.
Sean Bratches, chairman of Anuvu’s Board of Directors, said, “Anuvu is at the forefront of advanced connectivity. Today’s announcement is an affirmation of Anuvu’s technology leadership and demonstrates the strong confidence and commitment of Anuvu’s investor base.”
Anuvu’s team manages connectivity and content requirements for demanding mobility markets that include airlines, cruise lines, and mission-critical maritime, energy and government applications. Through long-standing customer relationships, the company has a proven track record for meeting customers’ needs, even as the world changes. Anuvu’s flexible and agile approach enables the firm to adopt the newest technology to optimize clients’ experience and the company maximizes the performance of today while optimizing for tomorrow. Anuvu’s goal is to provide clients with reliable, scalable, and affordable solutions.

