Rocket Lab launches first of two NASA climate change satellites
“Today we successfully launched the first of two back-to-back launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) climate change-focused mission.” — Peter Beck, Rocket Lab’s Founder and CEO.

Rocket Lab’s statement...
After a slight delay at T-12 minutes due to ‘ground winds’, Rocket Lab USA, Inc. (Nasdaq: RKLB), a provider in launch services and space systems, today launched the first of two back-to-back launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) climate change-focused mission.
‘Ready, Aim, PREFIRE’ lifted-off from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand at 7:41 pm NZST on May 25th, 2024. The launch deployed the first of two satellites for the PREFIRE mission to a 525km circular Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
Now that the first satellite has been successfully deployed, the second will follow on another dedicated Electron launch in just a few days. The launch date for the next mission, ‘PREFIRE and Ice’ will be confirmed early next week.
Rocket Lab’s ability to launch dedicated missions to precise orbits on demand is critical to the success of PREFIRE. The mission requires two separate satellites to follow similar trajectories but along different paths to overlap with each other every few hours near the Arctic and Antarctica and capture accurate heat loss measurements.
Both PREFIRE satellites are equipped with a device called a thermopile, similar to sensors found in household thermostats, to measure heat loss at far-infrared wavelengths which have never been systematically measured before. This data collected by the PREFIRE mission will help to improve climate and ice models and provide better predictions of how the planet’s sea level and weather are likely to change in the future.
Rocket Lab founder and CEO, Peter Beck added, “Missions like PREFIRE demonstrate the unique benefit of Electron – dedicated launch for small satellites to precise orbits on precise schedules. We’ve demonstrated this back-to-back launch capability for NASA once before with the TROPICS mission and we’re excited to deliver it once again
for PREFIRE. Climate change-focused missions like this are essential to understanding and safeguarding the future of our planet. It’s a privilege to support them on Electron.”
Additional information: rb.gy/jalmuv
IQ spacecom + RBC Signals collaborate on Go.BIC
IQ spacecom and RBC Signals have joined forces to deliver Go.BIC, the first, dynamic, Global On-Demand, Bi-directional Intersatellite Connection Service, aimed at supporting inter-satellite connections for LEO operators — connectivity for the service will be powered by Viasat’s global, L-band satellite network.
RBC Signals, a pioneering provider of satellite data communication solutions with a vast ground station network, is partnering with IQ spacecom, a product branch of the German IQ Technologies for Earth and Space GmbH, known for its more than 15 years of experience in broadband data communication for small satellites.

Together, the companies have launched Go.BIC, a highly flexible service set to support inter-satellite connections for LEO satellites. Go.BIC will use dynamic, on-demand capacity from Viasat’s global L-band network of GEO satellites.

This first of a kind service ensures real-time allocation of L-band capacity on a global scale, specifically tailored to meet the needs of LEO operators.
The service complements existing ground station networks to extend coverage to previously unconnected regions like remote oceans, bridging communication gaps for satellite operators worldwide and making their satellites reachable at any point of time. This enhances operational efficiency and offers cost-effective telemetry and telecommand options, empowering LEO satellite operators with improved flexibility and control over their missions.
Additional information: rb.gy/vwbs0w
Rivada Space Networks announces new APAC partners
Rivada Space Networks has announced new partners in the Asia Pacific (APAC) region — the company has now lined up more than $9 billion of business across the globe for the company’s LEO network.

As the first unified global communications network, Rivada’s Outernet is transformative. A global low-latency, point-to-point network of 600 LEO satellites, the constellation combines inter-satellite laser links with advanced onboard processing and routing to create a ubiquitous optical mesh network in space.
This “orbital network,” in which data stays in space from origin to destination, creates an ultra-secure, private satellite network with pole-to-pole coverage, offering end-to-end latencies much lower than terrestrial fiber over long distances. By routing traffic on a physically separated network, it provides a layer of defense for any enterprise or government organization that needs to securely share data across Asia and beyond.
For Enterprise and Government customers, the key attributes of the outernet are ideal for a variety of applications, for example, to give banks and global companies secured networks with distributed offices, provide significantly more bandwidth for oil & gas exploration than is available today, enable seamless connectivity for shipping and fleet management, or provide 5G satellite backhaul connectivity network expansion for cellular operators. Connectivity providers in Asia can offer a competitive advantage by expanding these markets, enabling new opportunities through secure, multi-gigabit bi-directional performance, combined with worldwide reach.
KT SAT – Korea Connecto Network Systems Inc. (CNSI) – Philippines
NiAT – Brunei AT Communications - Japan Teleport Access Services - Taiwan
Declan Ganley, CEO of Rivada Space Networks, said, “We are seeing a huge uptake in our business in Asia, underlining the growing appetite for our unique space-based network. The outernet’s ability to meet the requirements of Asia’s connectivity providers in terms of security, latency, capacity, and coverage is a game-changer for the region. Our completely new type of LEO constellation will provide the whole of Asia with a transformative next-generation infra tructure for secure, resilient communications and network expansion.”
HawkEye 360 expands their state-of-the-art advanced R&D facility
HawkEye 360 Inc. will soon be opening the firm’s new Vibration Testing Facility within the company’s 19,000-square-foot advanced R&D, engineering, and manufacturing facility.

This new capability will be essential for vibration testing of satellite clusters, ensuring they meet the highest durability and performance standards.
The Vibe Facility, equipped with cutting-edge technology, can simulate the intense conditions satellites encounter during launch and space operations. This addition includes an electrodynamic shaker system featuring an H-series shaker with an ST series slip-table and magnesium head expander.
This renovation adds 450 square feet of lab space, which houses the shaker table and our existing large thermal chamber from Thermotron.
This allows us to perform comprehensive environmental testing at unit and spacecraft levels.
The Cluster 11 satellites will be the first to undergo vibration testing in the new Vibe Facility.
This milestone marks a significant step in HawkEye 360’s ongoing efforts to enhance the quality and resilience of our satellite constellations by establishing a turnkey, end-to-end production facility where the company can better control costs, production time, scalability, and quality.
ESA selects Open Cosmos to build an optical constellation for Greece
Open Cosmos has gained a €60 million contract to deploy an Earth Observation (EO) constellation consisting of seven satellites that will supply daily high-resolution and very-high-resolution imagery for Greece.
This flagship project forms part of the Hellenic Government’s procurement of an advanced satellite constellation, demonstrating its commitment to delivering economic and environmental benefits for Greece and European citizens at large.
The data collected from this constellation will be instrumental in improving public services such as the land registry, combating sea pollution, and increasing agricultural efficiency.
The seven satellites in the Greek constellation will gather data from a multi-sensor instrument suite in LEO, including very-high resolution optical multispectral and hyperspectral cameras, Internet-of-Things (IoT) and Automatic Identification System (AIS) receivers, complemented by on-board AI to maximize efficiency. The program will be delivered in partnership with the European Space Agency and complement existing systems such as EU Copernicus, while being fully compatible with the Atlantic constellation.
The satellites will be built and operated by Open Cosmos Aegean, a new manufacturing center that will enhance sovereign capabilities in satellite technologies and attract further investment to the country.
By overseeing regional sales and complementing other European operations, it will play a crucial role in future European and international programs.
Open Cosmos was founded in 2015 with a mission to address global sustainability challenges by making actionable information from space available to everyone.
Part of this vision is the OpenConstellation, a mutualized constellation, set to become the largest shared infrastructure in space. Greece is set to join in this global partnership of nations and companies in the private sector, exchanging valuable data in respect of disaster responses and environmental monitoring.
Additional information: rb.gy/ci5y7m
Firefly Aerospace adds Alpha Launch capability on Wallops Island, Virginia
Firefly Aerospace, Inc., an end-to-end space transportation company, is adding an Alpha launch capability at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) on Wallops Island, Virginia. In support of Firefly’s responsive space missions, Pad-0A will be configured to launch Alpha as early as 2025 in addition to Antares 330 and the Medium Launch Vehicle (MLV) that Firefly is co-developing with Northrop Grumman.
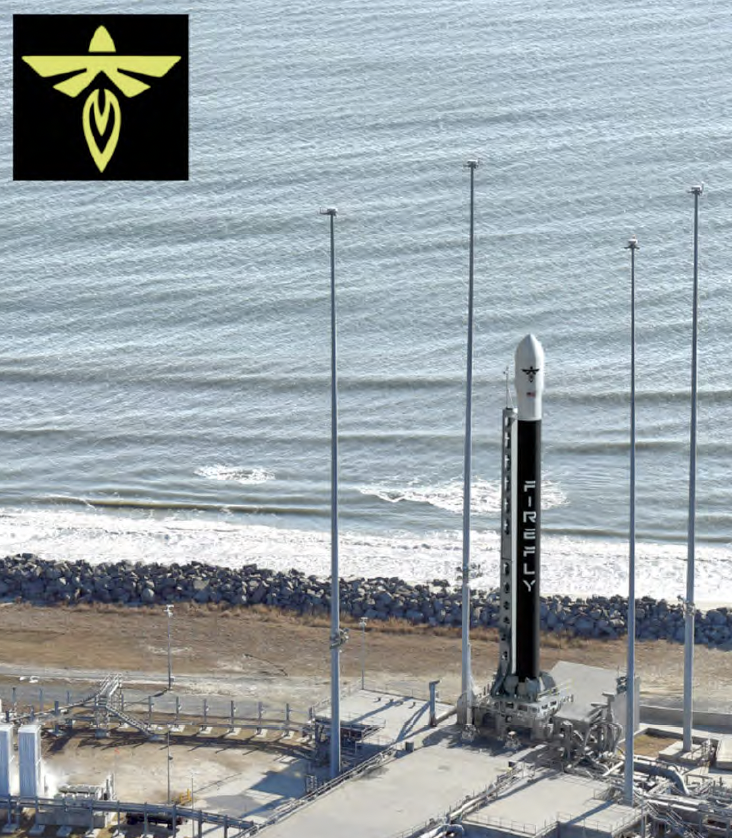

The new launch capability on Wallops Island will supplement Firefly’s existing Alpha launch facilities and further enable Firefly to support rapid, on-demand missions for government and commercial customers.
In addition to the launch pad, Firefly plans to operate a launch control center, horizontal integration facility, and administrative office space on Virginia’s Eastern Shore.
Firefly will also use existing infrastructure in the area, such as vehicle and payload processing facilities, to eliminate bottlenecks and retain Firefly’s rapid launch capabilities, recently demonstrated for the VICTUS NOX mission that was executed with a 24-hour launch notice.
Capable of lifting more than 1,000 kg to LEO, Firefly’s flight-proven Alpha rocket uses patented propulsion technology and carbon composite structures built with automated machinery to provide a reliable, low cost, responsive solution for the domestic and international launch market. With East and West Coast launch capabilities, Firefly will further increase Alpha’s launch cadence to a monthly basis by 2026 after launching up to four times in 2024 and six times in 2025.
Additional information: rb.gy/vu79ca
Rocket Lab’ celebrates 50th Electron launch and successful ‘No Time Toulouse’ mission for Kinéis
Rocket Lab USA, Inc. (Nasdaq: RKLB) a global provider in launch services and space systems, today successfully launched its 50th Electron mission, deploying satellites for French Internet-of-Things (IoT) company Kinéis.

Photo captured by Satnews from Rocket Lab
video stream.
Electron has reached the milestone of 50 launches faster than any commercially developed rocket in history.
The ‘No Time Toulouse’ mission lifted-off from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand at 6:13 am on 21 June NZST (6:13 pm, 20 June UTC),
successfully deploying five satellites to a 635 km circular orbit. The mission was the first of five dedicated Electron launches for Kinéis, a company backed by private and public investors including the French government’s space agency CNES (Centre National d’Études Spatiales) and CLS (Collecte Localisation Satellites), an international space-based solutions provider, to improve global IoT connectivity.
The Kinéis constellation is designed to make it possible to connect and locate any connected object anywhere in the world, enabling data transmission to users in near-real time, at low bit rates and with very low energy consumption. By enabling internet connection to the Earth’s most remote locations, Kinéis constellation can support forest fire detection, water resource management, infrastructure and energy network monitoring, transport and logistics tracking, and much more.
Rocket Lab founder and CEO Peter Beck said, “When Electron lifted off the pad for the first time in 2017, we knew we’d unlocked a new era in spaceflight, one where small satellites got to call the shots for the first time with frequent, tailored and reliable access to orbit. Fifty launches later Electron is the most successful commercial small rocket globally. Making it to fifty launches faster than any commercially developed rocket in history is testament to the incredible team we have behind us. Today’s precise, tailored mission for Kinéis is yet another demonstration of the value Electron continues to provide to the small sat community. Congratulations to our team and thank you to our customers and supporters for helping us continue to break records and set new industry standards.”
Across 50 launches, Rocket Lab has now deployed 190 satellites for a diverse range of customers and missions, including NASA missions to the Moon, the National Reconnaissance Office and Space Force missions supporting national security and defense, scientific research to combat climate change, and commercial constellations providing vital data and services to millions of people on Earth.
Ubotica achieves breakthrough in Live Earth Intelligence with CogniSAT-6
Ubotica has announced a significant milestone in the CogniSAT-6 mission, that being the successful processing and instant AI-powered detection of the first raw image from the newly launched satellite.

Today’s Earth Observation (EO) satellites are fundamentally data collectors; they simply gather data and downlink that information when passing over a ground station. However, what if they could understand what they’re seeing? With Ubotica’s SPACE:AI, they can, as this technology unlocks the full potential of EO satellites by empowering them with real-time vision processing. Ubotica’s flight-proven, end-to-end, AI platform transforms these satellites into intelligent, efficient and always connected observers.
SPACE:AI at Work: Ship Detection at Jeddah Port — Consider the first raw satellite image (lower left) taken by CogniSAT-6 of the port and ocean near Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
The challenge was to quickly identify all ships in the area. For the first time, an EO satellite, powered by SPACE:AI, understands what is being observed.
Within 90 seconds, SPACE:AI detected every vessel within a 20 x 40-kilometer zone. This achievement demonstrates the model’s exceptional accuracy, even without prior training on CogniSAT-6 data.
CogniSAT-6 is designed to share these insights instantly. Through persistent, inter-satellite communication, ship detection data can be relayed to users on Earth in real-time. This enables users to interact directly with the satellite, requesting more information or adjusting its focus.
SPACE:AI’s ship detection capabilities represent a significant advancement in the field. Unlike traditional methods requiring extensive training on thousands of processed images, SPACE:AI can perform real-time, on-board identification of ships from a single, raw, unprocessed image without prior training specific to the imager or sensor.
This breakthrough technology dramatically simplifies and accelerates the process of extracting valuable information from Earth Observation data.
“This successful demonstration proves the advanced capabilities of CogniSAT-6 and our commitment to unlocking the true potential Earth Observation,” said Fintan Buckley, CEO of Ubotica. “Near real-time analysis of satellite data unlocks new possibilities for timely and effective decision-making across numerous sectors.” Sean Mitchell, Chief Commercial Officer at Ubotica, added, “The performance of our ship detection model, combined with our rapid processing pipeline, showcases SPACE:AI’s transformative potential. We’re excited to see this technology in action and anticipate the significant impact CogniSAT-6 will across industries.”



