The First Image Of Earth Is Served Up By MSG-4’s SEVIRI
On August 10, the Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI) instrument on MSG-4 captured its first image of Earth.

This demonstrates that Europe’s latest geostationary weather satellite, launched on July 15, is performing well and is on its way to becoming fully operational when needed after six months of commissioning. The European Space Agency (ESA) was responsible for the initial operations after launch (the so-called launch and early orbit phase) of MSG-4 and handed over the satellite to EUMETSAT on July 26.
The first image is a joint achievement by ESA, EUMETSAT, and the European space industry. For its mandatory programs, EUMETSAT relies on ESA for the development of new satellites and procuring the recurrent satellites like MSG-4.
The MSG satellite’s main payload is the optical imaging radiometer, the so-called Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI). With its 12 spectral channels, SEVIRI will provide 20 times more information than the current Meteosat satellites, offering new and, in some cases, unique capabilities for cloud imaging and tracking, fog detection, measurement of the Earth-surface and cloud-top temperatures, tracking of ozone patterns, as well as many other improved measurements. The SEVIRI instrument has been manufactured by European industry under the leadership of Astrium SAS in Toulouse, France.
SEVIRI is a 50 cm-diameter aperture, line-by-line scanning radiometer, which provides image data in four Visible and Near-InfraRed (VNIR) channels and eight InfraRed (IR) channels. A key feature of this imaging instrument is its continuous imaging of the Earth in 12 spectral channels with a baseline repeat cycle of 15 min. The imaging sampling distance is 3 km at the sub-satellite point for standard channels, and down to 1 km for the High Resolution Visible (HRV) channel.
The SEVIRI instrument is composed of a Telescope and Scan Assembly (TSA), a Focal Plane and Cooler Assembly (FPCA), and an Electronic Unit Assembly (EUA). The EUA consists of three electronics boxes located on the satellite main platform, namely the FCU, the DE, consisting of the MDU and the Preamplifier.
Solar Array Design, Test + Production Capability Expands At Sierra Nevada Corporation
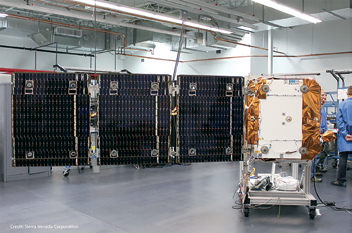
The SNC OG2 satellite with deployed solar array. Photo courtesy of SNC.
Sierra Nevada Corporation’s (SNC) Space Systems continues to expand its Space Technologies product line, by growing its capability in solar array design, production and verification, which includes a broad portfolio of flight-proven mechanisms, components and complex subsystems.
As announced in late 2014, SNC was awarded a contract to develop and build a next-generation science and technology demonstration satellite known as STPSat-5 for the Department of Defense’s (DOD) Space Test Program.
In addition to being the prime contractor for the satellite, SNC is also designing, manufacturing and testing the solar arrays and positioning mechanisms that will provide power to the satellite upon orbit insertion.
SNC will provide a complete turnkey system to be integrated into the STPSat-5 satellite that will include the solar array wings, hinges, hold-down mechanisms, solar array drive and integrated slip ring, allowing for 360 degrees of continuous rotation, maximizing available power to
the spacecraft.
This turnkey power system builds on SNC’s successful heritage and years of experience in manufacturing individual components that includes over 45,000 hours of combined on-orbit performance of six 600-Watt solar arrays as a part of the ORBCOMM Generation 2 (OG2) constellation.

Artistic rendition of STPSat-5. Image courtesy of SNC.
SNC’s Space Systems, based in Louisville, Colorado, houses state-of-the-art test facilities, including the recently commissioned Large Area Pulsed Solar Simulator (LAPSS) used to verify solar array performance. This large-scale testing zone simulates the sun to obtain accurate electrical performance measurements of solar panels up to 3.5 m2.
“With the addition of this instrument, SNC can provide fully-optimized turnkey solutions for solar arrays,” said John Roth, vice president of business development for SNC’s Space Systems.
“We improve efficiency and reduce risk by designing a system that integrates with the satellite from the start, and then we validate that with system level performance verification, rather than individual component testing. These efficiencies provide overall cost savings which we pass on directly to the customer.”
The Louisville facility also houses thermal vacuum chambers, a radio frequency anechoic chamber, vibration table, shock table and dimensional inspection lab, among other satellite test and production equipment. In SNC’s Space Systems 25-plus-year history, it has provided thousands of components on hundreds of missions.
www.sncorp.com/
Indigenous Peruvian Tribes In The Andes Gain Connectivity

Improving quality of life for people living in remote regions around the world is a key mandate for NewCom International.
The company has been able to provide Internet access and global connectivity to the indigenous Q’eros Nation tribe living high up in the Andes of Peru.

Working in partnership with Kidnected World, an NGO that provides online creative tools to connect young people globally as a catalyst for greater humanity, NewCom donated a year’s worth of satellite-based Internet access to a school serving the village of Qocha Moqo, which involved trekking a satellite dish up steep mountain trails to an elevation of more than 16,000 feet.
Now, after living completely cut off from the rest of the world, students and their families have a way to connect and engage with people across the globe.
They also have the ability to learn about other cultures and world events, share their cultural traditions and access the endless educational materials the Internet provides.
“Our students and their parents are very happy to be connected to the world in this digital age,” said Hannah Rae Porst, director for Willka Yachay, a Peru-based NGO that built and oversees the school for the village. “There were many happy dances and lots of hugging when the satellite dish was installed.”

Porst, whose organization is dedicated to helping indigenous communities thrive in the modern world, says the Internet connectivity—powered by solar energy—has been life changing for everyone involved.
Thanks to the Internet and creative tools provided, she says students have been able to connect with other students and indigenous tribes around the world and share their cultural knowledge and way of life. After school, says Porst, the computer and Internet are open to anyone who wishes to use it—benefiting all forty families in the village.
She adds that the Internet connectivity has also made a huge difference in the lives of the teachers—not just in terms of the educational content they can share with students, but in terms of their own quality of life.
“We have incredibly dedicated teachers in Q’eros,” added Porst. “They come from as far away as 22 hours of travel and live and teach in the remote villages for three weeks straight and then have one week off. There is no telephone signal in Q’eros. However, now, for the first time ever, our teachers can communicate with their families while here.”
www.newcominternational.com/
www.willkayachay.org/
www.thewonderment.com/
HISPASAT Getting Good With Goonhilly
HISPASAT has reached an agreement with British teleport owners Goonhilly Earth Station (GES) Ltd. to provide television distribution services throughout Europe.

A transponder from the Hispasat 1E satellite will provide the capacity contracted over the next three years, which will be transmitted by means of one of the teleport antennas. The entire process chain of transmission has been set up and will be provided by GES. Through this agreement, both companies are introducing an attractive commercial offer to the market, which is aimed at achieving maximum flexibility so that the television channels can avoid the traditional barriers they come across, both in terms of cost and time scale, when they want to distribute their channels.
The addition of services from Goonhilly adds to the teleports that already offer a shared solution on HISPASAT 30° West digital platforms. With these solutions, HISPASAT offers great flexibility to audiovisual content producers seeking to transmit their signals, either directly to the user (DTH) or indirectly by transporting TV channels to cable head-ends. In addition, this enables transmissions in both DVB-S format and DVB-S2 –ensuring not only optimized power transmission, but also bandwidth consumption.
Goonhilly was commissioned in 1962 and received the first transatlantic images broadcast over Telstar. It also broadcast numerous historic events to Europe including the first lunar landings. Currently, Goonhilly is open to commercial services and is fully operational as teleport for satellite communications.
Steve Jones, Commercial Director at GES, said, “As part of our ongoing investment in our site’s capabilities we are delighted to offer the broadcast uplink market an alternative, attractive route to market. Working alongside HISPASAT, with our collective experience and knowledge, we aim to make it easier for channels to get their content to their customers.”
HISPASAT Chief Commercial Officer Ignacio Sanchis also voiced his approval for this agreement and said, “which enables us to widen our offer in Europe and provide television operators with adaptable and scalable solutions for every situation.”
Image above: HISPASAT 1E during build. Photo courtesy of SSL.
RSC Energia + RSCC Sign Advanced Comms + Satellite Broadcasting Agreement
Vladimir Solntsev, Energia President, and Yuri Prokhorov, RSCC Director-General, have signed an agreement to cooperate in the field of developing advanced communications and broadcasting satellite systems.

Working together, the two companies intend to use more efficiently the resources they have in order to design such systems.
The plan is (i) to develop jointly the technical requirements regarding prospective systems of satellite-supported communications and broadcasting, including those for RSCC, (ii) to assess feasibility of applying new requirements to future communications and broadcasting satellites using the R&D and production potential of Russian space industry, and also (iii) draft proposals regarding the use of prospective domestic satellite launch systems.
Among those contributing to the development of new spacecraft will be Energia specialists who have attended training programs at Airbus D&S under the Express-series project.
“I am convinced that our joint efforts will make it possible to expedite implementation of state-of-the-art processes and standards to ensure appropriate quality and reliability of satellite-supported communications services.
“Our cooperation will serve the objective of further development of Russia’s infrastructure of satellite communications and broadcasting”, said Energia President, Vladimir Solntsev, following the signing ceremony.
For his part, Yuri Prokhorov, RSCC Director-General, said, “The agreement we have signed is called upon to spur implementation of the 2016-1025 program to develop the domestic orbital constellation of civilian communications and broadcasting satellites involving Russia’s leading space industry enterprises that have the requisite knowhow and unique competencies in the area of space hardware.”
www.rscc.ru/
SAIT Communications Is Being Acquired By SpeedCast International
SpeedCast International Limited (SpeedCast—www.speedcast.com/) has signed a definitive agreement to acquire SAIT Communications, a fast-growing maritime communications service provider in southern Europe.
SAIT Communications is one of the leading suppliers of L-band satellite services in the southern European maritime market, in particular Greece, which is one of the largest maritime markets in Europe, as well as Cyprus. The acquisition will bolster SpeedCast’s strength in the global maritime market, enhance its services portfolio with additional offerings, and significantly expand SpeedCast’s exposure to the important shipping sector.
SAIT Communications has been active in the maritime communications business for close to 10 years. The company’s customer list includes most of the top Greek shipping companies and services about 2,500 ships and has rolled out Inmarsat Fleet Broadband to nearly 1,500 vessels over the past few years and has more recently started providing VSAT broadband services. The Company is based in Cyprus with employees in Cyprus and Greece.
SAIT Communications uniquely complements and extends SpeedCast’s maritime business thanks to its long term customer relationships with large Greek shipping companies, a strong L-band expertise, an innovative portfolio of value-added services, and a very experienced management team that will drive the growth of SpeedCast’s business globally.
With this transaction, SpeedCast acquires a strong foothold in Southern Europe, a region with continued L-band growth and ripe for accelerated VSAT services growth, in particular in Greece and Cyprus, countries that host many large ship owners and fleet managers. The combined entity will be one of the largest service providers to the maritime sector in the market today, servicing over 5000 vessels with a wide portfolio of communications and IT services, and an impressive global support network. Joining SpeedCast, SAIT Communications will now be able to offer its maritime customers a wider portfolio of products and services, including the widest range of VSAT services in the market, and to better support its customers globally leveraging SpeedCast’s network of field engineers in key ports around the world.
SAIT Communications will further expand SpeedCast’s global maritime network in the strategic Greek market. The transaction is expected to close on 31 July 2015. SAIT Communications’ management team will remain with the SpeedCast group.
Arianespace Chalks Up Successful Mission Number 81—EUTELSAT 8 West B + Intelsat 34 Lift Off
Arianespace successfully launched their fourth Ariane 5 flight in 2015 and seventh launch overall this year—performing a heavy-lift mission today for Eutelsat and Intelsat, two key customers for the past 30 years.

Lifting off from the Spaceport in French Guiana, Arianespace’s workhorse vehicle deployed EUTELSAT 8 West B and Intelsat 34 into geostationary transfer orbit, delivering a total payload performance estimated at 9,922 kg., which included the two satellites and Ariane 5’s dual-payload deployment system.
Arianespace Chairman and CEO Stéphane Israël recognized all of the key players in this latest operational success, including the French CNES space agency, the European Space Agency and the on-site teams at the Spaceport; along with Ariane 5 prime contractor Airbus Safran Launchers and Arianespace’s own teams. He said Arianespace remains on target to best its own record of calendar-year launches, with 12 total flights on tap for 2015.
“My thanks to European industry, which—under the leadership of Airbus Safran Launchers [ASL]—produces such a reliable launcher,” Israël stated. “Today with Ariane 5, and tomorrow with Ariane 6…Arianespace will work hand-in-hand with its number one shareholder, ASL.”
The numbers associated with today’s flight, designated VA225 in Arianespace’s mission numbering system, further underscored the company’s role as the launch services industry leader. It marked the 67th consecutive success for Ariane 5 and the launcher’s 81st mission overall; while the EUTELSAT 8 West B and Intelsat 34 satellites were the 513th and 514th payloads lofted to date by Arianespace. Flight VA225 was the 67th consecutive success for Ariane 5 and the launcher’s 81st mission overall.
Arianespace’s heavy-lift Ariane 5 is shown at the Spaceport’s ELA-3 launch site, ready for liftoff with its dual payload of the EUTELSAT 8 West B and Intelsat 34 satellites.
EUTELSAT 8 West B was riding in the upper payload position on Ariane 5, deployed at 28 minutes into the flight. Once in service for Eutelsat, it will bring powerful new satellite broadcasting resources to the Middle East and North Africa—primarily serving direct-to-home markets from an 8 degrees West orbital slot. The 5,800-kg.-class relay spacecraft, built by Thales Alenia Space using the Spacebus platform, also is to introduce a C-band mission to this geostationary orbit position, covering the African continent and reaching to South America.
“Eutelsat 8 West B is the 30th satellite launched by Arianespace for Eutelsat in a cooperation that spans more than 30 years with our two companies,” Israël explained. “We’ve been friends and partners with Eutelsat for 30 years, and we intend to continue! We have three satellites to launch for Eutelsat during the next two years—including the first all-electric satellite ever to be launched by Ariane 5.”
Israël also noted that EUTELSAT 8 West B was the 47th Spacebus-series platform carried by Arianespace from the 143 total Thales Alenia Space-built spacecraft entrusted to missions performed by the launch services company.
During today’s mission, the 3,300-kg. Intelsat 34 payload was deployed from the lower passenger position on Ariane 5, and will be utilized by Intelsat for the media distribution requirements of leading programmers for Latin America, operating from an orbital slot of 304.5 degrees East.
Produced by Space Systems Loral (SSL) using its SSL 1300 platform, Intelsat 34 also is to support advanced broadband coverage for maritime and aeronautical providers serving the North Atlantic.
Emmanuel Macron, France’s Minister of Economy, Industry and Digital Affairs, visited the Ariane 5 control center as part of his presence at the Spaceport for today’s Flight VA225 mission.
“Intelsat 34 is the 55th satellite launched by Arianespace for Intelsat: our cooperation also started more than 30 years ago…with the launch of Intelsat 5 F7 in October 1983 on Ariane, and will continue at the same pace with four more satellites already in our order book,” Arianespace’s Israël said. “Arianespace is especially proud to start deploying your next-generation EpicNG satellites next year.”
Intelsat 34 was the 51st Space Systems Loral-built (SSL) satellite launched by Arianespace, and the 45th based on the manufacturer’s 1300 bus —with 10 more in Arianespace’s backlog, Israël added.
Following today’s mission, Arianespace is maintaining its sustained launch pace, with preparations and launch vehicle components at the Spaceport for multiple upcoming missions across its family of heavy-lift Ariane 5, medium-weight Soyuz and light-lift Vega vehicles.
The company’s upcoming launch is set for September 10 with Soyuz on Flight VS12, which is to orbit Europe’s latest two Galileo navigation satellites. Also scheduled in September is an Ariane 5 launch with two commercial telecommunications satellites: NBN Co 1A for Australia’s National Broadband Network, and ARSAT-2 for Argentinean satellite operator ARSAT.
The company’s next Vega mission is planned for November with Europe’s LISA Pathfinder scientific space probe, which will observe the Universe in a completely new way.
www.arianespace.com/