Euroconsult: A $74 billion untapped opportunity
Connectivity for all is becoming an increasing priority for governments across the world, especially in developing and remote regions where broadband services are being enabled by the lowering costs of emerging satellite constellations. Euroconsult estimates that service revenues within the universal satellite broadband access market will reach $18 billion by 2031 at a CAGR of 15%.

Internet usage has doubled in the past eight years, with an estimated 67% of the world population using broadband services in 2022, according to the world’s leading authority on space and satellite-based applications markets, Euroconsult.
From access to public services such as remote health advice to remote working and learning and the ability to communicate opinions and share information, universal connectivity has become an increasing priority for governments across the globe.
While international organizations are encouraging infrastructure development plans for broadband use and accessibility in unserved areas, some 2.6 billion people remain unconnected.
In its latest report on Universal Broadband Access (UBA), Euroconsult mentions that the least-developed and landlocked developing countries are particularly lagging, with just over one-third of their populations connected to the internet. Asia Pacific and Sub-Saharan Africa alone hold 85% of the world’s unconnected people, with a quarter located in India.
Mobile Internet has been the primary growth driver for network expansion and Internet subscriptions in recent years.
However, despite mobile network availability to over 95% of the world’s population, at least in the form of 3G, service affordability and lack of digital skills are yet to be fully addressed.
This has created an “adoption gap” – people do not use Internet services even when coverage exists where they reside. In 2022, only 100+ countries met international broadband affordability targets.
More notably, however, governments and international organizations are shifting their focus toward ‘meaningful connectivity’ – a combination of sufficient download speeds and data allowances with an adequate device and frequent access to the Internet.
Governments are adopting multiple strategies to expand and secure meaningful connectivity for all, turning to satellite as the more cost-effective option for low-density areas where terrestrial network deployments are not economically feasible.
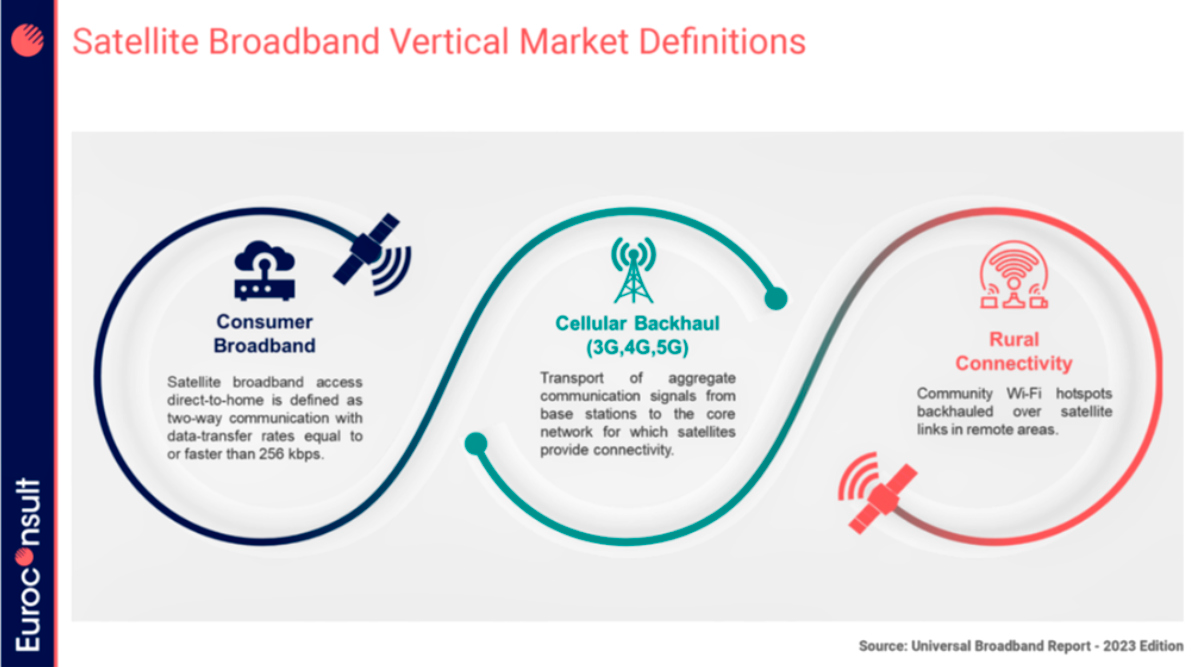
Today, three main satellite solutions are used to address the universal access broadband market: consumer-grade broadband, cellular backhaul and rural connectivity.
According to Euroconsult’s report, the addressable market for satellite solutions reached 591 million people in 2022, with 71 million people connected to satellite broadband services at the end of the year, a number expected to more than double in 2031 to reach over 150 million users.

Consumer broadband is currently the dominant satellite option in advanced economies, while cellular backhaul is the most frequently used option in emerging markets, mainly due to the lower cost of services for end-users.
The rollout of satellite constellations and next-generation, high-throughput satellites (HTS) planned in the coming years will be crucial in helping reduce the digital divide, enabling satellite services to offer increasingly affordable entry-level satellite services.
Upcoming HTS services will also provide ‘better quality’ packages to users through unlimited plans and higher data rates.
Other opportunities exist for satellite services to expand their addressable market in the coming years. These include vehicles in motion like RVs, such as the Starlink Roam ser vice, and the direct-to-device (D2D) market.
The D2D satellite service landscape is particularly gaining momentum, supported by new regulations — such as the FCC rule-making — and new 5G standards (through 3GPP) to integrate satellites into terrestrial networks more seamlessly.
“With access to broadband services increasingly recognized by governments as a driver of economic growth, this represents a significant untapped opportunity for service providers, estimated at $74 billion in 2022. This highlights the need for government and commercial initiatives to refocus efforts to close the digital divide beyond the expansion of coverage. We anticipate that at least one billion people, mainly those living in extreme poverty and uninterested in accessing internet services, will remain off the grid by the early 2030s.” — Dimitri Buchs, Managing Consultant at Euroconsult and the Editor in Chief of their Universal Broadband Access report
Euroconsult ’s latest ‘Universal Broadband Access’ repor t is available now at this dire ct link and provides detailed insights into the three satellite connectivity segments and the ef fects of satellite constellation ser vices on the UBA market.
AWS Ground Station now supports Wideband DigIF
Amazon Web Services has announced the general availability of Wideband Digital Intermediate Frequency (DigIF) for satellite operators using Software Defined Radios (SDRs) with AWS Ground Station.

With Wideband DigIF, satellite operators can use an SDR of their choice to perform demodulation and decoding of data in their Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), resulting in more control and flexibility of downlink data.
Wideband DigIF provides satellite operators the ability to downlink up to five channels, 400 MHz total, per polarity.
This feature delivers Wideband DigIF data across AWS’s low-latency, high bandwidth global network into a satellite operator’s Amazon VPC.

To use Wideband DigIF, satellite operators use Amazon CloudFormation to set up the required resources to deliver data to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) for real-time processing or store data in Amazon Simple Storage Ser vice (Amazon S3) for asynchronous processing.
Wideband DigIF is available in the following locations: North America (Hawaii), Africa (Cape Town), Europe (Ireland, Stockholm), Asia Pacific (Singapore), and the Middle East (Bahrain).
To learn more about AWS Ground Station, access this direct link…
To get started with AWS Ground Station, visit the AWS Management Console at this direct link…
Astræa launches satellite imagery
Astræa has initiated a new ordering service that offers access to advanced satellite imagery sources from providers such as Planet Labs PBC, among others — with the launch of the ordering service, Astræa customers get scalable access to the most advanced commercial satellite imagery on the market.

By providing access to all of the world’s best imagery providers within a single solution and a flexible, pay-per-use pricing model, Astræa is making imagery-derived insights more accessible and an enterprise-grade space strategy more obtainable. The unique pairing of Astræa’s platform with the new ordering service helps position Astræa as an industry leader in strategic imagery collection and spatiotemporal analysis.
Enterprises can now maximize the value of Earth Observation (EO) by leveraging scientific imagery for broad analysis and zeroing in on risk and opportunity indicators with commercial imagery. Flexible delivery operations support integration into existing business systems and platforms.
Astræa is continually adding new data partners, including non-EO datasets, which provide customers with unique, low-latency data sources on market-leading commercial terms. Customers will no longer need to concern themselves with managing multiple data contracts, APIs or data formats as Astræa has the explicit mission to deliver data in a consistent and standardized format across different imagery providers, like with their partner Planet, all on one platform.
After ordering imagery through Astræa, enterprises can gain geospatial insights faster. This is enabled by creating custom analytics to derive the right answers, optimized dashboards that are tailored to glean insights at scale and over time, and seamless integrations.
To leverage the full extent of the utility of the new satellite tasking capabilities on the Astræa platform, first customers can import all existing site information that is in any standard geospatial format and both query and report on all sites with a single API for both publicly available imagery sources like that of Sentinel 2 and near-daily satellite imagery from Planet. Then, teams can share a common view of projects and associated imagery by leveraging in- app mapping tools and sharing notes and comments over space and time.
Next, users can derive aggregated and site-specific insights over time and uncover trends in human-readable and customizable dashboards. Tabular data can be exported directly for further analysis within an enterprise database. Finally, tailored analytics allow customers to leverage the expertise of Astræa’s team of data scientists to detect changes, assess risk, monitor competition, and build robust solutions to the world’s greatest challenges on top of the most advanced imagery on the market.
www.astraea.earth
L3Harris engaged by the JMA to build weather satellite sensors
L3Harris Technologies (NYSE: LHX ) has received a contract to provide next- generation geostationar y imaging and sounding instruments for the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) that will monitor and predict severe weather events more accurately — the award continues L3Harris’ legacy of producing critical space - based weather instruments for Japan.
Under the terms of the contract with the Mitsubishi Electric Group, L3Harris will build and deliver an advanced imager and sounder for JMA’s Himawari-10 satellite.
The imager will use a similar technical platform as L3Harris’ Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) on NOAA’s Geostationary
Operational Environmental Satellite-R (GOES-R). The imager will also carry enhancements beyond its predecessor, Himawari-8/-9, including tailored Japanese spectral bands to supply the most advanced geostationary weather information for the international community.
 Artistic rendition of the Himawaril-10 satellite on-orbit, courtesy of Mitsubishi Electric
Artistic rendition of the Himawaril-10 satellite on-orbit, courtesy of Mitsubishi Electric
The addition of a next-generation, hyperspectral, infrared sounder on the Himawari-10 mission will provide improved weather prediction accuracy and enhanced environmental monitoring for extreme weather events impacting Japan. This includes enabling precise measurements, such as temperature, moisture and pressure, throughout the atmosphere.
The Himawari-10 imager and sounder will be developed and built at L3Harris’ Fort Wayne, Indiana facilities.
“L3Harris’ expertise in delivering the most advanced weather instruments in the world continues to be validated through international collaborations like this one with the Mitsubishi Electric Group for Japan’s critical weather needs. Our next-generation capabilities will enable forecasters to make better real-time decisions to counteract the threat of severe weather and disaster events in Japan and throughout much of Asia-Pacific.”
— Ed Zoiss, President, Space and Airborne Systems, L3Harris
“This award continues L3Harris’ role of being a trusted, multi-generational partner of advanced weather satellite technology for civil, commercial and international markets and demonstrates our commitment to advance and improve our customers’ capabilities for the future. For more than 60 years, we have proudly developed critical technology for customers like the Mitsubishi Electric Group and JMA — advancing climate science, increasing severe weather warning time and ultimately saving lives.”
— Rob Mitrevski, Vice President and General Manager, Spectral Solutions, L3Harris
Ruggedized lenses for space projects
Resolve Optics is a leading designer and international supplier of ruggedized lenses and optical systems for spaceborne applications.

The cost of launching payloads into space is considerable, incorporating only ‘space ready’ ruggedized lenses or optical systems into satellite or space observation system is, therefore, critical for achieving longer term, high- performance operation.
During launch into space, lenses in high precision instruments and cameras are subject to vibration and shock. While slight vibration might cause malfunction in lenses, severe vibration can result in damage that is beyond repair. Additionally, shock waves are highly detrimental to the performance and operation of high precision optical devices.
To minimize the effects of vibration and shock, it is advisable to keep your optical components small and light. The less mass you have the less effect vibration and shock will have on optical components.
To stop components in your optical system from moving requires that all parts are retained as tightly as possible and that retaining rings cannot work loose.
This can be done by staking the retaining rings so that they cannot come loose. However, if your required optical components are heavier then it may be preferential to bond all the elements in position. Consequently, the mechanical design of space ready optics must consider the mass of the elements and determine what method of retaining is required.
Also, importantly, the effects of vibration and shock must be considered across the operating temperature range of space launch to ensure optical components cannot become loose due to temperature cycling.
Over the last 20 years, Resolve Optics has developed the expertise to design ruggedized lenses and optical systems proven to withstand the vibration effects and shocks encountered during launch.
To ensure all ruggedized lenses and optical systems produced can withstand the launch vibration and shock profile provided by the customer, Resolve Optics has invested in in-house testing equipment.
To learn more about ruggedized lenses for space projects watch the informative video at this direct link...
Ursa Major to provide upper stage rocket engines for Astra’s Rocket 4
Ursa Major has an agreement with Astra that will support nexgen comms, national security and defense, as well as Earth Observation (EO).

Under the agreement, Ursa Major will provide “Hadley ” engines for the upper stage of Astra’s Launch System 2 on that firm’s newly architected, higher-capacity, Rocket 4 launch vehicle.
Launch System 2 is designed for customers that need affordable, frequent, and reliable orbital launch, deploying spacecraft directly into operational orbits.
Launch System 2’s upper stage will use the vacuum variant of Hadley, an oxygen-rich staged combustion (ORSC) engine fueled by liquid kerosene.
The vacuum variant of Hadley provides 6,500 pounds of thrust, compared to Hadley’s sea-level configuration, which provides 5,000 pounds of thrust.
To enable longer missions, Hadley features an ignition system capable of multiple restarts.
Reliable rocket propulsion is critical to maintaining the space supply chain and growing the space industry.
Ursa Major focuses solely on propulsion to lower the cost and risks of the most expensive, time-consuming, and risky aspect of space launch.
Ursa Major’s f lexible rocket engines can be used for various missions, from air launch to hypersonic f light and on - orbit missions.
“The Ursa Major- Astra par tnership marks an impor tant industr y milestone in outsourcing propulsion to unlock grow th and innovation for launch providers and their customers. We’re excited to be a par t of Astra’s Launch System 2 and the company’s next chapter of success.” — Joe Laurienti, founder and CEO of Ursa Major
Startups selected for the AWS 2023 Space Accelerator

AWS has selected 14 startups from across the globe for the 2023 Space Accelerator. This year’s Space Accelerator Program focuses on startups that are innovating sustainable space technology as well as startups that aim to positively impact life on Earth.
The selected startups will receive valuable business development resources, such as expert mentorship and networking opportunities with startups in the cohort, AWS customers, and members of the AWS Partner Network (APN). The selected startups will also receive $100K in AWS promotional credits to help accelerate their missions in the cloud.
Meet the 2023 Cohort
Delta-V Analytics Inc.
Delta-V Analytics provides a cloud-based platform that automates satellite constellation operations using digital twin technology.
GATE Space
GATE Space enables the next generation of
in-space mobility by providing scalable and cost- efficient plug-and-play mobility to satellites and orbital transfer vehicles.
GRASP
GRASP’s mission is to develop satellite instruments and products that provide a complete picture of the Earth’s atmosphere and surface. These will be designed specifically to help decision-makers select paths that minimize climate change and improve air quality and human health.
In Orbit Aerospace
In Orbit is building infrastructure to support mass manufacturing in space. This startup operates uncrewed orbital platforms and re-entry vehicles, with the goal of providing more accessible and cost-effective service to and from space.
Integrate
Integrate is building a program logistics platform for complex hardware development and deployment scenarios for the space industry. The company’s collaboration-first approach allows program managers to organically pull together hardware specifications, high level requirements, and schedules into a single collaborative software platform for faster execution.
Kawa Space
Kawa provides space-powered signals intelligence (SIGINT), electronic intelligence (ELINT), and maritime domain awareness (MDA) as a service.

Little Place Labs
Little Place Labs specializes in providing near- real-time space analytics for both ground and space-based applications, using advanced machine learning algorithms deployed directly on satellites and other space infrastructures. This enables rapid, precise, and cost-effective delivery of critical insights across commercial and national security sectors, with the ultimate purpose of making the world a better place.

The AWS Space Accelerator 2023 cohort members and the AWS Venture
Capital (VC) and Startups teams met to launch this year’s program.
Photo is courtesy of AWS.
Lunasonde
Lunasonde is making the underground world visible, transforming humanity’s approach to subsurface exploration and resource extraction. Using low-frequency radar, Lunasonde can identify objects and materials hundreds of meters underground, resulting in the first three-dimensional map below the surface of the Earth, and eventually the Moon, Mars, asteroids, and beyond.
Nominal
Nominal builds continuous validation software for hardware organizations testing and deploying high-stakes, complex systems. The Nominal platform equips engineering teams to explore, monitor, and enrich mission-critical test data — all in one place.
Raven Space Systems, Inc
Raven Space Systems is building entirely 3D printed reentry capsules for on-demand cargo return from space. The company’s automated factory will enable cheaper and faster capsule production with adaptability for any mission.
Rogue Space Systems
Rogue Space Systems provides in-space services through autonomous robotic systems, and aims to support a future vision of growth and expansion in space, including the tools and resources humanity will need to flourish.
Space Kinetic
Space Kinetic is turning solar power into low-cost, in-space mobility with a novel electromechanical propulsion system. With several diverse applications across the space domain, the company’s long-term goal is to build a cislunar logistics network for sustainable space operations.
Violet Labs
Violet Labs is building cloud-based software integration for complex hardware engineering. The Violet platform aggregates data from software tools used across the hardware development lifecycle into a powerful single source of truth.
Xona Space Systems Inc.
Xona Space Systems enables modern technologies to operate safely in any environment, anywhere on Earth. Using the efficiency of smallsats, Xona’s PULSAR service is a commercial “Super-GPS” designed to provide unprecedented precision, protection, and availability.
aws.amazon.com
The AWS Space Accelerator 2023 cohort members and the AWS Venture Capital (VC) and Startups teams met to launch this year’s program.
Photo is courtesy of AWS.

