SED Systems
Over the past year, the theme for Calian’s SED Systems division (CGY:TSX), continues to be growth and innovation. SED Systems is a global supplier of sophisticated satellite communication systems, solutions and products, and we’ve been serving our customers for more than 50 years.

Communications Ground Systems
and Services.
The company’s systems engineering services line includes communication ground systems and services, communication gateways and planning systems, and a line of SED communication products tailored to support customers in the satellite industry. SED offers a tightly integrated approach with our engineering design services and manufacturing capacity co-located in a single purpose-built facility. We have the expertise, capacity and resources required to design, build and fully test each component of the deliverable ensuring performance in the harshest of conditions.
Satellite advancements in capacity, functionality, speed and complexity are bringing significant opportunities, as well as, industry challenges including requirements for increased performance and flexibility of the ground system hardware and software. SED, along with our partners, has been developing innovative new technologies to ensure these challenges are overcome. Recent contract wins are evidence of our leading position in the delivery of complex satellite Earth station projects and programs.
Communication Ground Systems and Services
At SED, the communication ground systems and services business unit provides RF ground systems for satellite tracking, communications and control. After a busy year of deploying a number of fixed and transportable RF ground systems, SED announced its largest satellite ground systems contract, including numerous RF gateways incorporating advanced technologies.
The President of SED, Patrick Thera, said, “We have been investing in new technologies to support future satellite ground systems requirements in anticipation of opportunities in need of these technologies. We are very pleased to see that we are now in a position to capitalize on these investments. Commercial advanced technologies are just starting to emerge in the industry, which enable satellite operators to add increased bandwidth and throughput to their network offerings. This new work helps to establish us as a front-runner in ground system offerings.”
Communication Gateways and
Planning System.
With its focus on customer satisfaction and management of requirements, the ground communication systems group, provides solid turnkey RF gateway solutions for L-, S-, X-, C-, and Ku-band frequencies as well as higher frequency bands with challenging requirements such as Ka-, Q- and V-bands. During the year, SED also supported a number of programs for Earth Observation (EO) and deep space exploration.
Communication Gateways and Planning Systems
The firm’s communication gateways and planning systems business unit provides software solutions for satellite communications, capacity management and performance monitoring. Over the past year, a variety of satellite capacity and real-time management solutions have been deployed around the world.
Large LEO constellations and high throughput satellites with complex payloads have been driving demand for intelligent planning and capacity management tools to support services on these networks. SED has been addressing demand for intelligent planning and capacity management with innovative real-time satellite resource management and capacity planning software solutions.

The company’s innovative software solutions provide operators of complex networks with the tools they need to efficiently direct satellite capacity to meet geographical demands.
SED has invested in a large engineering staff with experience in systems engineering, software development, hardware development and embedded logic design. With the growth of our engineering pool over the past year our team has the agility and experience required to support the most complex needs of our customers and the satellite industry in general.
Communication Products
SED’s line of satellite communication products continues to provide customers with innovative and high performance units that they use in their networks or integrate into their service offerings. They also serve as the building blocks for the systems we deliver enabling us to offer a more compelling value proposition based on innovative technology, reduced risk and time to market, and lower costs.
While the firm’s existing modulator product line supports standard DVB-S/S2/S2X applications, SED specializes in developing innovative products based on newer technology and architectural concepts. Our multichannel modulator and intelligent switching technologies offer an attractive and reliable way to reduce capital and operating expenses. In addition, our SDTS modulator saw a significantly increased presence in the satellite precise positioning market. We have development underway in several new and exciting areas with product announcements forthcoming in 2019.
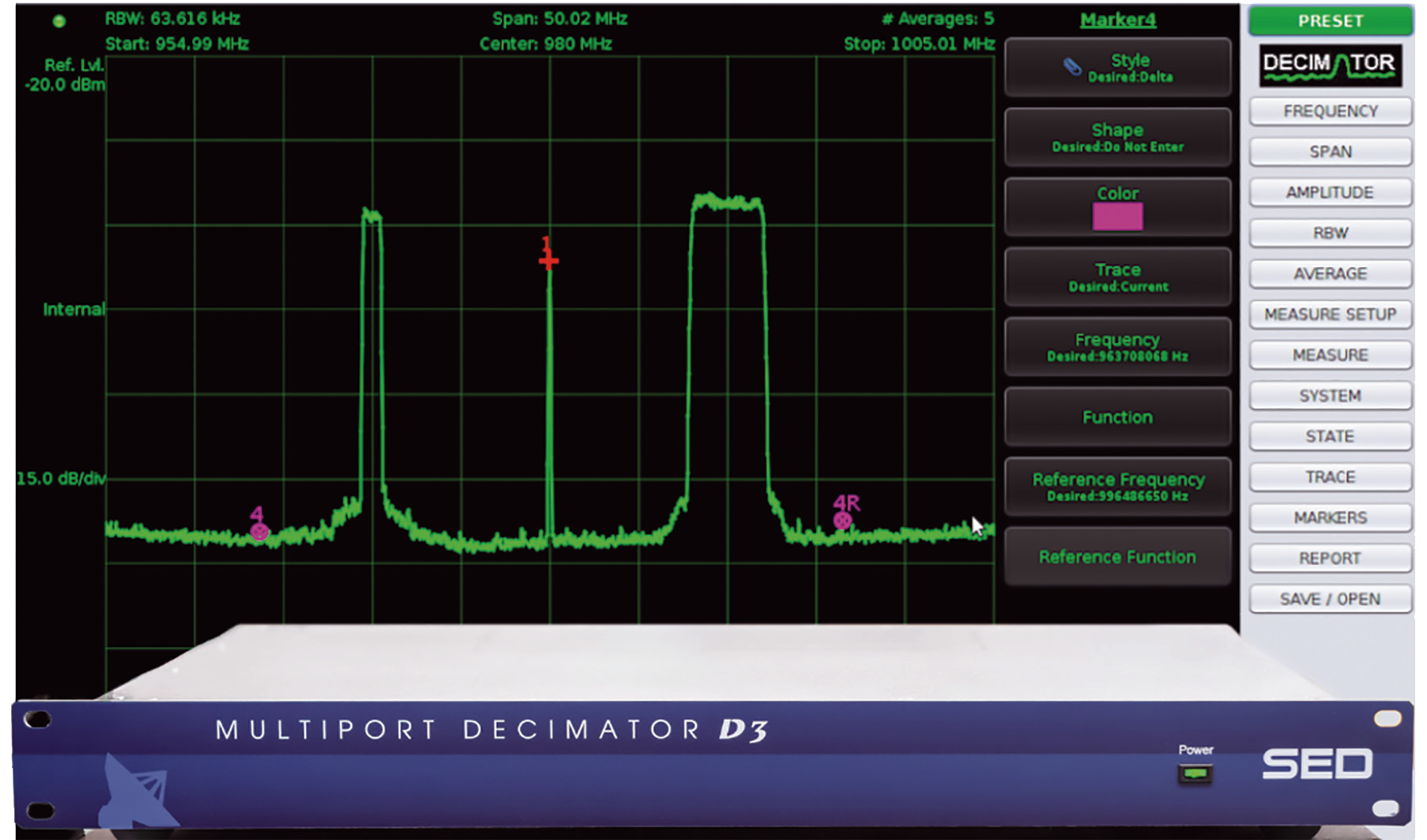
SED’s Decimator Spectrum Analyzer product had its best year ever in 2018. Decimator is extremely popular for standalone operations in teleports and gateways, as well as inclusion in satellite carrier monitoring systems from SED and other vendors.
Over the past year, the company has continued to evolve the capabilities within Decimator and provided new features within the unit firmware. The recently introduced CarrierWatch software which cost effectively enhances the Decimator’s built-in carrier monitoring and reporting functionality was very popular with satellite gateway and teleport operators. Stay tuned during 2019 for more Decimator evolution as the product’s capabilities are enhanced even further.
2018 has been an exciting year for SED Systems. Together with our partners, we’re looking forward to continued growth, challenges and opportunities in 2019.
www.sedsystems.ca
Sky and Space Global
By Meir Moalem, Co-Founder and Chief Executive Officer

The 2018 end-of-year represents the beginning of a new chapter for Sky and Space Global Ltd. (SAS), bringing the company even closer to reaching its goal of connecting the underserviced globally with full 24/7 cellular coverage by 2020. With over three billion people across the equatorial belt alone that have no access to reliable and affordable communications, SAS is poised to transform people’s lives over next 24 months.
In October 2018, SAS began construction on the world’s first commercial constellation of nanosatellites, the “Pearls,” on track to launch this coming year, ultimately launching 200 smallsats but with service immediately available upon the launch of the first batch of 15-30 satellites. The Pearls will make SAS the first telecommunication and New Space company to use smallsats to provide cost-effective narrowband communication connecting people, businesses and machines in remote geographies and rural areas across the globe. After the launch and deployment of the first batch of Pearls, SAS will be able to provide Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity. Once the constellation is launched, SAS will offer instant voice and instant message services via local service providers to anyone in the equatorial belt, anywhere, anytime.
2018 was filled with challenges and successes’ that have shepherded both product development and preparing for 2019 with a focus on realizing the company’s vision. Since June 2017, SAS has launched and maintained a first of its kind communication network of three nanosatellites, called the “3 Diamonds,” that have served as the company’s proof-of-concept. This is the foundation by which we have successfully proven our technology. 2018 saw many partnerships and Memorandum’s of Understand (MoU) established and signed upon the Pearls’ launch.
2018 — The Year
2018 began with the company’s announcement of its first field trial for Point-of-Sale (POS) device connectivity with Paratus Group, a Pan-African telecommunications company. This agreement has and will continue to create a path for SAS to deliver connectivity to thousands of POS devices across Africa by 2019. POS is a multi-billion dollar global market growing at a fast rate, and SAS will service it through its Pearls at a fraction of current costs.
Additionally, in February 2018, SAS commenced with M2M and IoT tests in partnership with Globalsat Group, the first Pan-American Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) consortium. Upon completion of the testing program, the companies entered negotiations for a binding commercial agreement to offer SAS’s services to the customer base in May 2018. The relationship between the two companies will enable Globalsat and SAS to offer services in South and Central America. Our disruptive approach to satellite connectivity will translate to zero-forklift deployment or ground infrastructure buildout while radically reducing Capex investment and OpEx costs for service provider partners in these regions.

The Sky and Space Constellation (by SCISYS).
Later in March 2018, two major milestones were reached. First, SAS raised $15 million in a Heavily Oversubscribed Placement. Then, SAS created a PSTN gateway via its Chatellite app, enabling calls and texts from any Public Switched Telephone Network (PTSN) number. Lastly, the company announced its first revenues generated through its “3 Diamonds” nanosatellite network, and as expected, shared $1million in annualized revenue from current contracted customers. This month represented a key turning point for the company in overcoming typical new market and startup challenges to legitimize its core services.
Furthermore, two key company milestones related to the design of the product occurred in June 2018. One was the completion of its first Spectrum Monitoring via the “3 Diamonds” nanosatellite network. The other was the successful completion of a Critical Design Review (CDR) with D-Orbit, a satellite system company focused on convenient orbital management. By successfully proving their products ability to perform spectrum monitoring and the confirmation that their nano-satellite network surpassed industry standards, SAS increased their communication solutions’ credibility to build passed the proof-of-concept project.
Later in October 2018, the company completed another CDR of the Pearls by GomSpace, a leading global aerospace construction partner. This was a major milestone that resulted in SAS immediately beginning the production phase of the “Pearls” hardware.
SAS also signed contracts with a series of service providers including in many regions around the world including Ghana, China, the Caribbean and Brazil. Later in 2018, SAS also signed MoU agreements with Briskcom, SkyX, Penteon, Surge Telecom, Unizen Technologies, and Applied Satellite Technology. These agreements highlight SAS’s dedication to providing connectivity to the unconnected worldwide by 2020, not just in some regions.
From pioneering the deployment of communication nano-satellites to enabling financial transactions and ensuring cyber-security integrations, SAS is on track for its commercial product launch in 2019. Due to their efforts, the company received the 2018 Global Company of the Year Award from Frost & Sullivan for its demonstrated accomplishments and superior performance in leadership, technological innovation, customer service and strategic product development.
Key Industry Predictions for 2019
As the world’s population continues to grow, and businesses require more and more interconnected operations, terrestrial communication networks will not be able to meet the huge demand required as a result of infrastructure limitations, specifically in rural regions. Smallsat communication networks are the only existing solution that will solve this issue and SAS will be the first to provide it.
The company also predicts that the New Space industry, specifically for smallsats, will become more prominent and capabilities will be more clearly defined in 2019. The industry is starting to formalize with clear winners and losers. New Space companies’ innovative solutions will meet expectations or fall flat, and those that are first-to-market will have the upper hand.
www.skyandspace.global
Mr. Meir Moalem is a Co-founder and CEO of Sky and Space Global Ltd. and has been its Managing Director and CEO since its establishment in 2015. Mr. Moalem is a jet fighter pilot, Lt. Col (Res.) of the Israeli Air Force. He has more than 20 years of experience in management, R&D and operation of state-of-the-art projects in Space Systems and Unmanned Aerial Systems, among those acting as a deputy squadron commander and leading the MEIDEX experiment on Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-107) as the project manager for Israel’s first astronaut flight, Managing Israel’s satellite projects (such as Ofeq, Tecsar) and more.
ThinKom Solutions, Inc.
By Bill Milroy, Chairman and Chief Technology Officer

As 2018 comes to a close, ThinKom Solutions, Inc. continues a path of rapid growth in the company’s core business of airborne satellite antenna technology and is well positioned to take advantage of the opportunities opening as new LEO and MEO constellations come into play over the next few years.
First, here’s a quick overview of our company and technology. ThinKom was founded in 2000 and received its first major U.S. government contract for K/Q-band airborne antennas in 2003. In 2011, we developed the first low-profile antenna proven for high-speed Ka-band and EHF communications on a U.S. military wide-body aircraft.
We achieved a major milestone when Gogo selected our antenna for inflight connectivity in 2013 and the following year Gogo launched its 2Ku IFC powered by ThinKom’s ThinAir® Ku3030 antenna. The Ku3030 received blanket worldwide FCC regulatory approval in 2015 and the next year Delta Airlines began a major program to fit 2Ku on more than 600 aircraft. Since then, the list of 2Ku airline partners has grown to more than 20, including American Airlines, Alaska Airlines, Air Canada, GOL, Cathay Pacific, British Airways, KLM, Air France, and Japan Airlines — to name a few.
Steep Growth Curve
Today,there are nearly 1,000 aircraft flying with ThinKom’s Ku3030 terminals, averaging about 3,700 flights per day, with a total of four million hours of inflight service at above 98 percent availability.
To support this steep growth curve, we are investing in expanding and upgrading our facilities and infrastructure. We’ve added 4000 sq. ft. of office space, continued to expand and optimize the firm’s production flow, added new temperature test chambers, new test positioners and a spherical nearfield chamber. The ThinKom facility has an approved FAA Part 145 Repair Station and we also recently updated our company certification to AS9100D.

The growth in our Ku-band airborne satellite antenna business is primarily driven by two factors. The first is the insatiable appetite among today’s passengers for uninterrupted, reliable, high-quality, high-bandwidth connectivity in the air. The second is the unique value proposition of our patented VICTS phased-array antenna technology, which combines the technical benefits of gimbaled mechanically steered and electronically scanned arrays to deliver consistent high performance in the harshest environments. The result is gap-free, pole-to-pole coverage, high beam agility for network flexibility, a low-profile antenna radome producing near-zero drag in flight, low prime power consumption and installation flexibility, along with the IFC Industry’s highest spectral (OPEX) efficiency.
At the same time, we have made substantial progress with a new family of Ka-band airborne antennas. The ThinAir® Ka2517, introduced to the market in 2016, completed DO-160 certification in 2017 and we expect to receive STC on Airbus 320 airframes by mid-2019. Ka2517 terminals were installed earlier this year and are currently in service on a fleet of U.S. command-and-control aircraft under a modernization program to replace aging Ku-band phased-array systems.
Land-Based SATCOMs
While our airborne antenna business is booming, we are also continuing to build the terrestrial SATCOM antenna business. ThinKom works with major third-party integrators and prime contractors to supply Ku-, Ka- and X-band systems for mobile, man-portable and fixed antenna solutions to a wide range of corporate and government customers. They are used in broadcast/media applications, military, homeland security, disaster recovery, and emergency management missions.
In April, the company partnered with COMSAT, Inc., to complete a coast-to-coast expedition to test and validate a seamless continuous high-speed satellite communication solution in a moving vehicle under a wide range of conditions. The demo SUV was fitted with our roof-mounted low-profile ThinSat® 300 phased-array antenna with a package of modems, routers, switches, power inverter and operator interface inside the vehicle. The ThinSat unit supported broadcast-quality links at highway speeds and in off-road terrain and delivered an average of 1 bit/Hz spectral efficiency (without the need for “spreading”).
Multi-Constellation Interoperability
The pages of SatMagazine and other industry media are filled with stories on the proliferation of proposed low-cost smallsats in constellations of hundreds or even thousands of satellites in Low Earth Orbits (LEO). Even if only a small percentage of these systems are actually deployed, they will have the potential to disrupt the market with inexpensive bandwidth, promising unique benefits in terms of latency, coverage, throughput and redundancy. At the same time, the major operators of GEO satellites are upgrading their fleets with HTS, dramatically increasing the available bandwidth.

At ThinKom, we are watching these developments carefully. Lower-orbit satellites offer an attractive value proposition. On the other hand, GEOs are ubiquitous and redundant and thoroughly proven. ThinKom’s position is that users and sellers of satellite connectivity should not have to make an either-or choice. Why not have the best of both worlds? To that end, the firm has designed our antenna systems with the versatility to support an integrated, multi-constellation solution that offers gap-free, pole-to-pole coverage, with automatic beam switching, rapid outage recovery and network optimization for different geographical regions.
In recent months we have achieved several milestones toward that goal.
In September, ThinKom and Telesat signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for joint development of a Ka-band enterprise user terminal (EUT) for Telesat’s planned LEO constellation. As a first step, ThinKom’s Ka2517 phased array antenna system, which is currently in production for commercial and government in-flight connectivity, will be used for over-the-air testing on Telesat’s Phase 1 LEO satellite in the coming months.
In August, ThInKom completed the first successful ground tests of the Ka2517 antenna with the SES O3b MEO satellite network. For the test, a vehicle-mounted Ka2517 aeronautical antenna acquired successive O3b satellites at 13 degree elevation and successfully tracked them for 30 minute periods while the satellites traversed across the sky from west to east. These ground tests will be followed in the next few months by in-flight tests over the O3b network. This will be the first in-flight demonstration of a ThinKom antenna communicating through a Non-Geostationary (NGSO) constellation and will demonstrate the ability of the VICTS phased-array to auto-track and perform seamless beam switching through the full range of aircraft roll, pitch and yaw motions.
These and other agility tests reveal that ThinKom’s antennas consistently achieve beam switching speeds of less than one second, which is fast enough to ensure continuous connectivity while moving seamlessly from beam to beam and constellation to constellation. In short, our phased array VICTS technology provides all the benefits of electronically steered arrays with none of their limitations in terms of instantaneous bandwidth, limited low-angle performance, high power consumption and low aperture efficiency.
To summarize, ThinKom had a great year in 2018 and stands poised to play an important role as the industry leader in phased-array antenna technology as the next generation of satellite services takes shape.
www.thinkom.com
Tyvak
By Taylor Cantwell, Marketing Communications Specialist
Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems, Inc., a Terran Orbital Corporation, has grown exponentially over the past year.
Tyvak quickly outgrew their first U.S. headquarters in Irvine, California, at the end of 2017. Having doubled in size, Tyvak is now celebrating the first year spent in the new 40,000-square-foot facility this November. More than half of the building is dedicated lab space, which houses state-of-the-art equipment to support the development of new space systems.

Tyvak’s Cicero smallsat deployer. Photo is courtesy of NASA.
With this growth came the need for an organizational restructure at Tyvak in order for the firm to freshly address the increasing demands of their customers. Tyvak recently welcomed David Caponio as their new Vice President of Commercial Space and Launch, and Todd Mosher as Vice President of Civil Space and Domain Awareness. Joining Karen Anderson, Vice President of Defense Space and Intelligence, Caponio and Mosher round out Tyvak’s three business units.
These additions will lead ongoing satellite programs, while developing new applications in their market segments.
Tyvak International’s European headquarters also has a new, 10,000 square foot home in Torino, Italy. The Italian are actively acquiring new contracts and have ten smallsats in development for a diverse set of customers.
In addition to their employees, mission success has always served as a main priority for Tyvak. Despite experiencing a few launch delays, the milestones achieved over the past 12 months outshine the challenges.
Tyvak and NASA JPL successfully developed RainCube, the first radar instrument on a 6U smallsat, sponsored by NASA’s Earth Science Technology Office (ESTO) through the InVEST-15 program. Tyvak is responsible for the spacecraft and integration of the JPL-built payload. Tyvak also spearheaded the vehicle’s launch integration and managed on orbit operations from their Mission Operations Center in Irvine, California. This mission will enable future precipitation profiling Earth science missions on a timely and economical platform.

Tyvak’s smallsat deployer. Photo is courtesy of the Rocket Lab.
Most recently, Tyvak’s CICERO 6U nanosatellite for GeoOptics successfully deployed from Rocket Lab’s Electron, “It’s Business Time.” The GPS radio occultation satellite, used to enhance weather monitoring, launched from Auckland, New Zealand.
CICERO uses Tyvak’s Endeavor platform that has been further developed to increase its responsiveness and autonomous operations. As part of this demonstration, CICERO automatically reached a fully controlled state in less than 20 minutes and obtained nominal payload data just 12 hours after launch. The data was then automatically downloaded by Tyvak, verified and processed by GeoOptics, and immediately made available to users.
However, this is not the first time that Tyvak has accomplished this goal. Tyvak’s GEOStare, a 3U smallsat mission, launched earlier this year, was fully functional during its first pass and successfully completed an enhanced situational awareness (SSA) demonstration shortly thereafter.
Anticipating further growth, Tyvak has ambitious plans moving into 2019. LunIR, formerly known as SkyFire, a 6U smallsat developed by Tyvak for Lockheed Martin, will test game-changing instrumentation in a lunar fly-by mission to characterize the surface of the moon and inspect landing sites. Once deployed into lunar trajectory, LunIR will also collect spectroscopic and thermographic data from the moon’s surface.
Tyvak’s CubeSat Proximity Operations Demonstration (CPOD) is also expected to launch in 2019. The pair of 3U smallsats will complete additional demonstrations of rendezvous, proximity operations and docking to continue validating and identifying new miniature, low-power proximity operations technology.
During the new year, Tyvak will remain mission centric with an Agile Space perspective and an unwavering focus on their customers. The company plans to unveil several iterations of their next-generation smallsat platform and conducting in-flight testing of their avionics system.
Furthermore, the company is also preparing for a record-breaking number of missions that are currently in development. These missions include the deployment of sub-meter imaging satellites and demonstrating unprecedented synthetic aperture radar (SAR) capabilities, resulting in high-resolution data.
Platform development for Tyvak’s mini-geosynchronous telecommunications satellite will also be finalized next year.
Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems, Inc. continues to understand the unique challenges and unlimited opportunities of satellite miniaturization while remaining the default choice for customers with advanced operational needs.
www.tyvak.com

