The New Space and Non-geostationary (NGSO) Constellations are the fastest alternative to the traditional heavy satellites for building reliable networks that enable high-performance connectivity and ubiquitous coverage with no limits for connected devices, bandwidth-intensive applications, greater quantities of data, and time sensitive applications. NSR reports that NGSO’s are on track to secure more than $68 billion in revenue by 2029, and that represents massive growth.
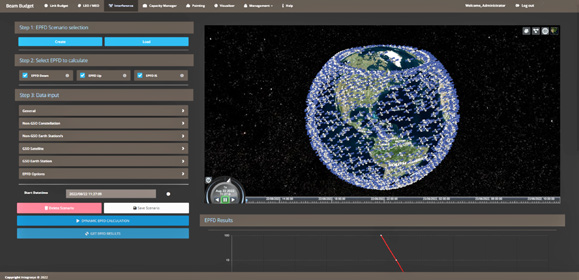
INTEGRASYS Beam Budget tool screenshot, courtesy of the company.
The efforts on bridging the digital divide (3.1 billion people around the world remain ‘unconnected’) brings Consumer Broadband into the spotlight, as this market segment will be the direct beneficiary of this technology — the challenge will be to reach remote areas at lower CAPEX and OPEX than fiber for improving connectivity. The market will experience unprecedented growth and will also change the comms structure that we know and use today. Nowadays, launching communication satellites (COMSATS) is becoming a commodity and is now less expensive, quicker, and easier to acquire, and that equates to space becoming the wild west — for our own business health, we must better regulate this growth.
Smallsats the key enabler to unlock the NGSO’s potential
LEO constellations require a vast and distributed infrastructure that enables the network to cover a selected area of the world and to comply with service requirements. At this point, smallsats enter the room. These compact satellites are characterized by lower cost, smaller size and lighter weight and are proliferating across multiple market segments.
Smallsats are easy to launch and manufacture and present a lower risk in the event of in space disasters. The defense and government markets, which were quite accommodating with GEO satellites (especially due to the ongoing war in Ukraine), have also shown the utility of smallsat apps by allowing commercial operators to promote their capabilities and constellations for govsatcom use. In order to promote the sector’s expansion, an increasing number of government organizations are considering purchasing their own smallsat systems or allocating funds for the acquisition of third-party, commercial, smallsat-based services. Example include Maxar for Earth Observation (EO) and IRIS2 in Europe for govsatcom. The greatest advantage of the smallsats is their significant latency reduction, and thanks to that, they are able to offer clients high speed, radio frequency (RF) data for quick detection and surveillance of activities on Earth.
LEO smallsats are using Ku- and V-band. These frequencies lead to narrower beams, compact antennas as well as faster data speeds, an extra security layer but high rain fade, and the attenuation of a RF signals by atmospheric conditions. Fortunately, there are ways to mitigate such vulnerabilities, including better ground-station architecture, adaptive coding and signal modulation. The amount of data a system sends can also be increased by improved spectral efficiency and spectrum-reuse rates. This all boils down to the constellation design process.
Nexgen ground
Access to a competitive and extensive ground station network will continue to set satellite- based services apart, particularly those provided by New Space participants. These companies are developing new services to support their commercial business models, moving from the time when they were fighting for a position in the space industry to business reliability. They have started the expansion phase of brand-new, more accessible, cost- effective, and aggressive space industry segments which has led to the rise of the ground segment as a service.
The virtualization of the ground segment enables scale, increased reliability, better distribution, and data storage, as well the negation of expensive hardware, refresh cycles. Moreover, with Cloud availability, only an API call is needed, or a few mouse clicks, to deploy virtual servers that are totally customizable. Additionally, being able to manage all the available virtual server resources expands a businesses capacity to automate the implementation and configuration processes, and that lowers the amount of human involvement formerly required to maintain hundreds or even thousands of satellite links. Smallsats require ground systems that are able to innovate as quickly and as cost effectively as possible. This necessity is made possible through the use of COTS products and the appropriate technology. A virtual ground system environment is the ideal answer for small satellite users as conventional architectures cannot quickly adapt to the constantly changing needs of smallsats.
Some constellations are becoming oversubscribed due to their successes and bring traffic, and price increases, to their customers, especially in those regions where demand is greater than the available resources. Therefore, design and management tools could be significantly helpful in such cases. Ground network service providers can swiftly and affordably enroll customers using virtual environments. End users can send network service provider system configuration files for professional examination. Virtual solutions are unaffected by problems that beset physical solutions, such as different hardware configurations and incompatible pin outs on serial lines. Furthermore, different ground networks or network providers may all use the same configuration or even the same instance of the solution (contained in either a virtual machine or container).
End-to-end network automation aligned with New Space
These days, it is mandatory to develop APIs that could be completely integrated with these new, satellite-based networks that populate a worldwide, cloud-scale, network ecosystem. An open, automated operating environment that enables the new ground and space actors to conveniently design and deploy new, innovative services faster and for any location is essential to accomplish the objectives for the smallsat success.
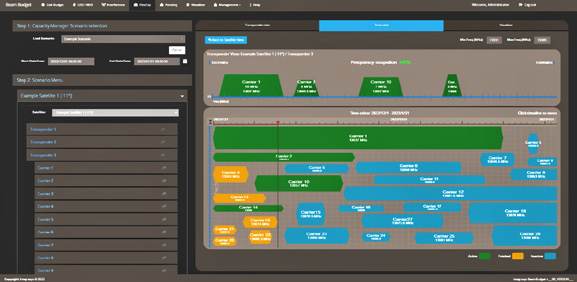
INTEGRASYS FlexCap. Image is courtesy of the company.
The addressed technologies enable the reduction of operator issues and ensure that the deployment of the satellite network is secure and the services optimized. The inclusion of cloud-based systems brings easy access for technical teams who are seeking a reliable ecosystem to obtain the needed measures for the establishment of the network.
Another point to consider when deciding to implement specific, network design technologies is the management of the capacity that shows gains and losses on any given satellite link. These tasks that cover network design smart solution or a link budget calculation tool can be arduous processes that require a great deal of time and, as they are manual in implementation, they are not accurate. Incorrect calculations and computations result in an unsuitable satellite selection and that leads INTEGRASYS BeamBudget tool on a tablet.
INTEGRASYS BeamBudget tool on a tablet.
to signal degradation. Correct calculations, on the other hand, and completing link budgets quickly and effectively, means a satellite operator can maximize revenue and provide the correct capacity to the customer every time, with a positive customer experience. Network design tools, ranging from long Excel sheets to complex software apps, are not customizable and are complex to use. The new space era demands less effort when using technology, as the main aim is to simplify technical tasks without extra effort. From the technical side, an engineering team needs to make link budget calculations and satellite footprints accurately to acquire the necessary inputs in seconds.
One of the mandatory keys to thrive in New Space is to obtain the necessary licenses from government organizations such as ITV, FCC, and so on. With virtualized tools, it is now possible to make certain regulatory rule compliance is achieved within seconds, as well as to optimize these constellations, painlessly, prior to their launch. One example is Beam Budget by INTEGRASYS. This is an innovative, link budget tool, that is available in the market. The new release of this technology also has a cloud option available through AWS and Microsoft Azure. The user can get obtain Beam Budget instantly, without the need of logistics or customs work, directly when they need it. This technology is a highly accurate simulation tool, able to model constellations, spacecraft transponders, beams, and footprints as well as ground equipment to assess the global performance of wide-area satellite networks in multiple time scales. The EPFD (Equivalent Power Flux Density) module also allows users to report the ITU filing and improve network designs. Beam Budget is the ideal link budget calculation tool for Satellite Operators, Service Providers or End-users.
Capacity management which, due to the number of satellites that comprise these new constellations, needs to be perfectly planned to make appropriate use of available capacity. FlexCap from INTEGRASYS is a capacity management tool that allows for the visual and autonomous organization of the capacity pool. The tool organizes and plans capacity dynamically by allocating different kinds of users and agreements. Moreover, this system optimizes the Mbits/s in capacity leases as well as the spectrum within the available frequencies. FlexCap is integrated with Link Budget, Network Sizing and Spectrum Monitoring via API.
Due to the growth of smallsat market and NGOs, cloud-based systems — especially for the ground segment — are mandatory for satellite network design in this New Space era. Network design technologies must be flexible, scalable... and intuitive.
www.integrasys-space.com


