Celebrating Seven Years Of Disaster Monitoring
UK-DMC 2 is one of two enhanced DMC (Disaster Monitoring Constellation) Earth observation satellites, UK DMC-2 and Deimos 1.

Artistic rendition: UK DMC-2 satellite.
These satellites are capable of imaging several thousand km along the target track and delivering double the data density of the first generation DMC satellites, increasing the ground sample distance from 32 meters to 22 meters, while maintaining the very wide swath of 660 km.
Seven years ago, another satellite was launched and added to the Disaster Monitoring Constellation (DMC) otherwise called the Earth observation satellite, UK-DMC2.
The DMC delivers valuable geospatial information for agriculture, forestry, land cover mapping, disaster monitoring and environmental sciences, coordinated and specialized in rapidly programmed campaigns.
The ground sample distance was increased from 32 meters to a 22 meter resolution multispectral satellite imagery, and the option for very wide area monitoring, adjustable up to 620km swath.
In addition, because of the daily revisit capacity coupled with rapid data delivery, the DMC is able to deliver up-to-date imagery and rapid whole country coverage. This is a helpful tool for all applications requiring timely image collection.
As an example, in North Africa, prone to yearly plagues of locust, UK-DMC2 data is used by the Algerian Space Agency to assess vegetation conditions. When combined with weather data, locust forecasts can be created and used to focus the application of pesticides, which in turn can help prevent the spread of locust swarms.
Land cover mapping also takes benefit from DMC imagery. Because of their rapid revisit and wide swath imaging capabilities, annual and seasonal maps are easily available, providing a dataset for change detection analysis. Such land cover evolution maps are critical for applications including climate change, ecology and conservation, urban and landscape planning, along with health and hazard assessments.
airbusdefenceandspace.com
MicroWave Imager Comes Complete With Super Powers
CGS SpA Compagnia Generale per lo Spazio, a subsidiary of OHB SE, and Airbus Defence and Space GmbH, are planning on delivering better weather forecasts as they have just contracted for new equipment.
The contract includes the MicroWave Imager preliminary design activity, the selection of all subcontractors necessary to install the device on MetOp Second Generation (SG) weather satellites and the price conversion to firm fixed for the realization phase—the value of the contract is 166 million euros.
The MicroWave Imager is a sophisticated instrument that will be installed on board the Satellite B series.
The instrument will provide Europe’s National Meteorological Services and by extension, the international users and Science Community, with improved and invaluable data for meteorological and climate monitoring.
CGS is responsible for the design and the development of the MWI instrument, from Phase B2 to the final in-orbit verification of three flight models, to be supplied to Airbus DS GmbH, the prime contractor of the MetOp-SG Satellite B.
Roberto Aceti, Managing Director of CGS said, “With the responsibility for this important instrument of these satellites, CGS confirms its role as expert for sophisticated space-systems, we are delighted to contribute to the success of the MetOp-Second Generation project.
“The scientific information that will be provided by the MicroWave Imager with extremely high radiometric accuracy will lead to an outstanding improvement of weather forecasts and a better understanding of climate changes.”
The MetOp-SG satellites will constitute the space segment of the EUMETSAT Polar System Second Generation (EPS-SG) program that consists of two series of satellites, “Satellite A” and “Satellite B” fleet, with a nominal baseline of three units each.
MetOp-SG satellites are developed as a cooperative undertaking between the European Space Agency (ESA) and the European Organization for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT).
www.cgspace.it
www.airbusdefenceandspace.com
Kudos To Kubos & Innovative Solutions In Space
ISIS—Innovative Solutions In Space B.V.— is located in Delft, The Netherlands, and Kubos Corporation, located in Denton, Texas, are joining forces to provide Linux to satellite developers.

These companies have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) related to the port of KubOS Linux to the iOBC, ISIS’ on-board computer.
ISIS has helped democratize space over the firm’s ten years of existence with both their launch services and their CubeSat Shop.
ISIS is now taking their approach to the next level by supporting the development of open source software on their platform.
To assist users in using KubOS Linux for their mission, Kubos has built an open source community, called OpenKosmos.org, where users will find source code, documentation, and a public Slack channel to communicate with other developers.
Kubos also provides a downloadable SDK and a suite of tools. Kubos offers Service Level Agreements to provide support and solutions for missions running KubOS RT and KubOS Linux.
The iOBC with the newly developed operating system will be available by the end of the year from both companies’ websites as well as on CubeSatShop.com.
Jeroen Rotteveel, the CEO of ISIS, believes that Kubos will enable new creative projects from people within the open source community but who have a limited experience of space systems—this move will help to lower the barrier to entry to the smallsat market even further.
www.kubos.co
www.isispace.nl
KOMPSAT-6 To Enjoy An Angara Flight
Now confirmed by the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI) is that the launch of the KOMPSAT-6 (AKA: Arirang 6) satellite will be handled by a Russian Angara 1.2 carrier rocket sometime in 2020.

Artistic rendition of KARI’s KOMPSAT-6 satellite.
The launch will be conducted from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome that’s located in northwestern Russia.

Russia’s Angara launch vehicle. Photo is courtesy of Roscosmos.
The main focus of the satellite’s mission will be disaster detection, although the satellite is also defined as a multipurpose spacecraft, this according to a report from Korea’s Yonhap news agency.
Seoul’s aerospace research institute confirmed that the Russian Angara-1.2 carrier rocket will put the South Korean KOMPSAT-6 satellite, also known as the Arirang 6, into orbit in 2020.
The Angara family of space-launch vehicles is designed to provide lifting capabilities of between two and 40.5 metric tons into LEO and has been in development since 1995.
Angara was the first orbit-capable rocket developed by Russia to replace the older Proton-M rockets.
www.kari.re.kr/
New Contract Finds SST-US Engaged In NanoRacks’ing
Seeking to expand the satellite launching capabilities of the International Space Station, Colorado-based Surrey Satellite Technology US LLC (SST-US) has signed a contract with NanoRacks LLC for future flights of a 100-kilogram-class satellite platform specifically developed by SST-US for deployment from the International Space Station (ISS) using the NanoRacks Kaber deployment system.
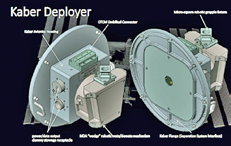
The satellite platform can weigh as much as 100 kilograms, accommodating payloads of up to 45 kilograms in mass in multiple configurations. Each spacecraft will be able to provide an average power of 50 watts and can also be upgraded for missions with higher mission requirements.
The ISS- optimized spacecraft will be shipped to the ISS inside a cargo resupply vessel and deployed from the station using a system called the “Kaber” that was developed by NanoRacks.
The Kaber deployer is on orbit and currently being prepped for operations on the ISS in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). The satellite platform is designed to go from contract signing to launch readiness in just 12 months, with manufacturing, integration, and testing performed at the SST-US facilities in Englewood, Colorado.
NanoRacks is able to provide this space station opportunity via its Space Act Agreement with NASA’s US National Labs.
According to Dr. John Paffett, the Chief Executive Officer of SST-US, the use of the ISS for launch of small satellite platforms has increased in recent years, with a number of cubesat platforms being deployed.
SST-US’ agreement with NanoRacks and the development of their one-hundred-kilogram-class, ISS-optimized satellite platform will significantly expand the capability, enabling larger, higher performance missions and payloads to be deployed from the station.
www.sst-us.com/
nanoracks.com/
Peru’s First EO Satellite Finds Itself Integrated
Airbus Defence and Space has completed integration of PerúSAT-1, Peru’s first Earth observation satellite, built in less than 24 months.
PerúSAT-1 was ordered by the Peruvian government for their national space agency, CONIDA, in 2014. PerúSAT-1, based on the highly flexible, compact AstroBus-S platform, will observe Earth via a revolutionary silicon carbide optical instrument system at 70 cm resolution.
PerúSAT-1 is scheduled for take off aboard an Arianespace Vega launcher on September 16 (03:45 CEST). The 400 kg satellite will deliver images from its orbit at 694 km to be used in the areas of land management, border control, and drug trafficking enforcement.
PerúSAT-1 will observe Earth through the latest generation of a silicon carbide optical instrument, with a 70 cm resolution and may also be used to support management of humanitarian aid and evaluation of natural disasters (floods, forest fires, landslides, erosion).
PerúSAT-1 proves that a powerful and sophisticated Earth observation satellite can be built in less than two years. AIT (Assembly Integration and Test) of the instrument was completed in about eight months, with the platform construction phase, satellite construction, and technical and operational system validation taking only five months each, respectively.
This success was made possible by the creation of the “Projects Factory©”, a new and more integrated working organization in the Space System business unit.
This new way of working brings down development and construction lead times for satellites up to 500 kg and optimizes their costs and schedule delivery, without impacting quality.
The program also includes the construction of the Centro Nacional de Operaciones de Imágenes Satelitales del Perú (CNOIS) hosting the ground control segment for image reception and processing developed by Airbus Defence and Space, as well as a complete technology transfer program for the Peruvian engineers and technicians (from advanced instruction in space technologies to satellite operation and the development of appropriate imaging applications) and the supply of images from the Airbus Defence and Space fleet of optical and radar satellites.
Backing Backhaul In The UK
Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd. (NASDAQ, TASE: GILT) has reported that Avanti Communications Group plc (“Avanti”) has selected their one-platform/multiple-application X-Architecture and MEC-enabled Capricorn VSAT to support Avanti’s contract to supply EE Limited with satellite capacity for 4G cellular backhaul across the UK.

Gilat’s SkyEdge II-c Capricorn.
Gilat’s MEC-enabled SkyEdge II-c Capricorn enables Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) to deliver true LTE-over-satellite performance.
With this network, EE Limited will be able to provide dedicated voice, data and video services at high speeds using satellite backhaul.
Gilat VSATs will be deployed at fixed and portable sites throughout the UK later this year.
According to Hagay Katz, the Head of the VSAT Line of Business at Gilat, the MEC-enabled Capricorn provides the highest data and encryption rates on the market and maintains IPSec data security at unprecedented speeds without packet loss under fade conditions, bringing to play a flexible solution that will allow the company to quickly deploy a wide range of applications in the future.
Mansoor Hanif, Director of Radio Access Networks at EE Limited, added that this cellular backhaul over satellite solution will play a key part in enhancing their 4G network resilience and help the company to extend the network even further into rural areas as they continue their efforts to cover 95 percent of the UK landmass with their services.
www.gilat.com/
www.avantiplc.com/





