The latest stats from the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) report that nearly half of the world’s population — more than 3.5 billion people — lacks internet access. While most of these people live in remote and rural areas, including mountains, deserts, and islands, they want to enjoy the same high-speed internet connectivity and mobile services as city-dwellers. Who will serve these unconnected markets... and how?
The growing demand for first-class cellular service in remote areas around the world is both a significant opportunity and challenge facing mobile operators going into 2020. On one hand, mobile operators have a tremendous opportunity to expand their business beyond saturated and highly competitive core urban markets. However, reaching these customers isn’t easy. Telecom infrastructure is underdeveloped and doesn’t extend into remote areas. While the deployment of microwave and satellite networks is a possibility, questions remain about whether operators can truly realize a return on investment given the traditionally high capex and opex costs involved.
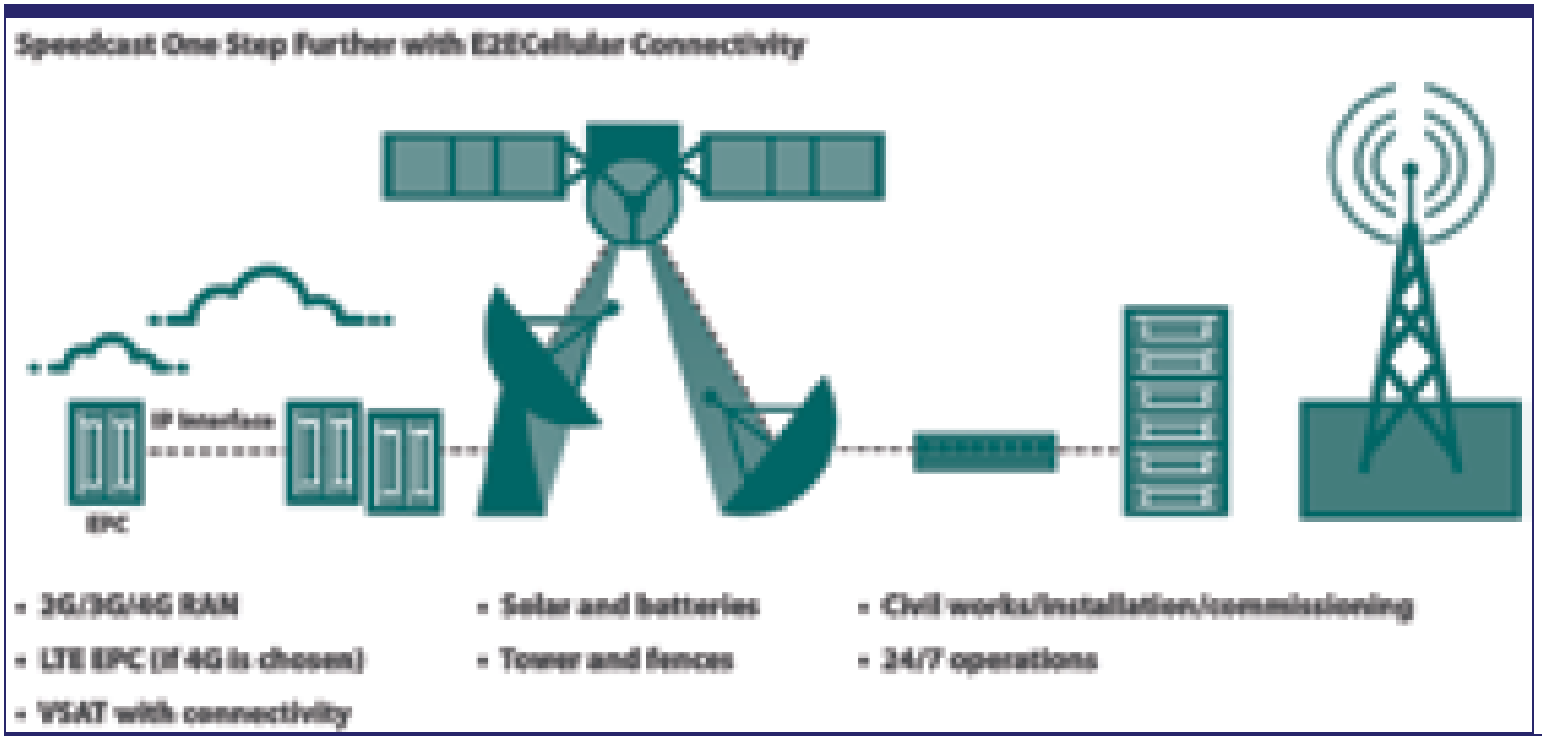
Satellite connectivity for cellular backhauling has emerged as a cost-effective, low-risk medium that enables mobile operators to connect people in remote areas to the outside world, without necessitating significant capex and opex investments.

The Business Case for Cellular Backhaul
Satellite backhaul makes smart business sense for delivering cellular services to remote areas of the world for several reasons. The first reason is cost. Today, mobile operators are looking for affordable ways to expand their cellular service into remote and rural areas.
Over recent years High Throughput Satellites (HTS) have drastically driven down the cost of satellite capacity, and satellite terminal costs have also decreased.
In addition to the costs of satellite capacity and terminals decreasing, satellite technology features unique multi-cast capabilities that are proven to lower video distribution expenses, especially when complemented by edge computing and local content caching. Given that more than 75 percent of worldwide video viewing is mobile, according to eMarketer, multicast will be critical to helping mobile operators address the rising trend of mobile video viewing.
The cost savings enabled by satellite are backed by improvements in data rate performance and operational efficiencies leveraging innovations in network optimization and virtualization technologies.
Latency is another selling point of cellular backhaul. As LEO satellites operate much closer to the Earth’s surface, they decrease the latency that has typically been a challenge with delivering high-quality mobile services to remote areas. The Washington Post reported that OneWeb, a global communications company based in London, is in the process of creating a network of about 650 LEO satellites, recording an average latency of 32 milliseconds. In today’s data-hungry world where social media and video applications are used regularly on mobile devices, low latency is proving to be essential.
The evolving requirements of subscribers living in remote areas further strengthens the business case for cellular backhaul. The expectations of remote customers are vastly different today than they were in the past, when basic voice service was sufficient. Remote users want to enjoy the same services as the rest of the world. They’re ready for 3G, 4G, and even 5G networks. Having a strong mobile service will boost local economies and improve customers’ daily quality of life, and satellite has a vital role to play in making this become a reality.
The Challenges With Choosing a Solution
The business case for satellite connectivity as an affordable option for extending coverage into remote and rural areas has been established. Next, mobile operators must determine what type of cellular backhaul solution is best. Traditionally, operators have been challenged find a financially viable solution that meets all of their diverse market requirements.
One of the main requirements is securing the correct type of satellite capacity at the optimal price. There are a broad range of satellite operators, orbits and bands to select from, as well ground infrastructure vendors. Evaluating the economics and installation elements that surround deploying infrastructure in remote areas is complex, as is configuring and managing hybrid networks.
Using advanced technologies, operators can automate network functions and scale operations while minimizing CAPEX and staff resources. There are also technologies designed to optimize the efficiency of network traffic to support higher data payloads. Yet, in most cases, knowledge of these technologies is beyond the scope of mobile operators. Outside expertise is needed to ensure that operators are delivering mobile services cost-effectively and providing a high-quality end-user experience.
Traditionally, operators have deployed their own infrastructure and maintained a dedicated staff for satellite networking. Another option that is gaining significant momentum is the managed service model for cellular backhaul.

Why Managed Services are the Future of Cellular Backhaul
Having an end-to-end managed service for cellular backhaul means that a specialized solutions provider takes care of everything for the mobile operator, including designing, purchasing, installing, configuring, managing, monitoring, analyzing and optimizing all the necessary parts of the solution.
It’s a smart investment for mobile operators, as the equipment is entirely provided, with no upfront expenses required. Operators subscribe to the satellite backhaul service on a pay-as-you-grow or pay-as-you-use basis (Mbps or MB usage), essentially with the aim of extending their network coverage. As managed services have an extremely low total cost of ownership, they eliminate the risk traditionally involved with launching new services, giving operators the freedom to expand coverage into new and remote areas, increase capacity into existing locations, and upgrade from 2G to 3G, 4G and, later, 5G.
Cost savings, minimal risk and rapid business growth are just several of the unique advantages of an end-to-end managed cellular backhaul service over satellite. Another benefit is immediate coverage without restrictions. The mobile environment is changing rapidly, and operators are looking for more than a one-size-fits-all-solution. Each mobile operator has a unique use case and technical requirements, and the backhaul service they use needs to be tailored to their needs.
For instance, some operators may need to use a backhaul service to support new 4G or 5G networks. Others have a need to deliver connectivity to preexisting networks. Cellular backhaul services over satellite can be relied upon to ensure backup connectivity for existing cell tower infrastructure during potential microwave or fiber network failures.
Backhaul services are also beneficial for offloading data to maintain quality of service when network utilization has reached its peak; downloading heavy, asymmetric data such as video covering national or international sports events; and for temporary transmission during events and disaster recovery scenarios.
With a cellular backhaul service that is fully operated and managed, operators have instant access to local support for solution design, installation, analytics, optimization and management, as well as on-demand engineering expertise to assist with network and system integration.
Conclusion
Global demand for cellular services is exploding in remote and rural locations and through private LTE/5G networks, and satellite connectivity is a tech- and business-savvy solution. It’s cost-effective, high-performance and reliable. However, installing and managing satellite infrastructure can be complex and expensive without the expertise of a managed service provider.

As the world’s leading critical communications company, Speedcast brings a high level of network capacity, expertise, and deployment experience to the cellular backhaul environment. Speedcast Atlas is the most comprehensive and flexible backhaul service available today, offering access to an extensive network of networks that includes terrestrial MPLS, LTE, 5G and the largest portfolio of satellite capacity in the world, spanning broadband and narrowband. Relying on Atlas’ network of networks, flexible pay-as-you-grow business model, and 24/7 design, installation, and engineering support, mobile operators are empowered to connect remote regions around the world and grow their revenue.
Author Stephane Palomba is the Vice President, Global Cellular Services and the Regional Vice President, Asia, for Speedcast.


