Kacific1 successfully launched by SpaceX with co-passenger JCSAT-18
Kacific1 was launched successfully into space aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 7:10 p.m.EST (UTC-4) on December 16, 2019, from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, USA — the satellite was placed into its target geostationary transfer orbit 33 minutes following initial ignition.
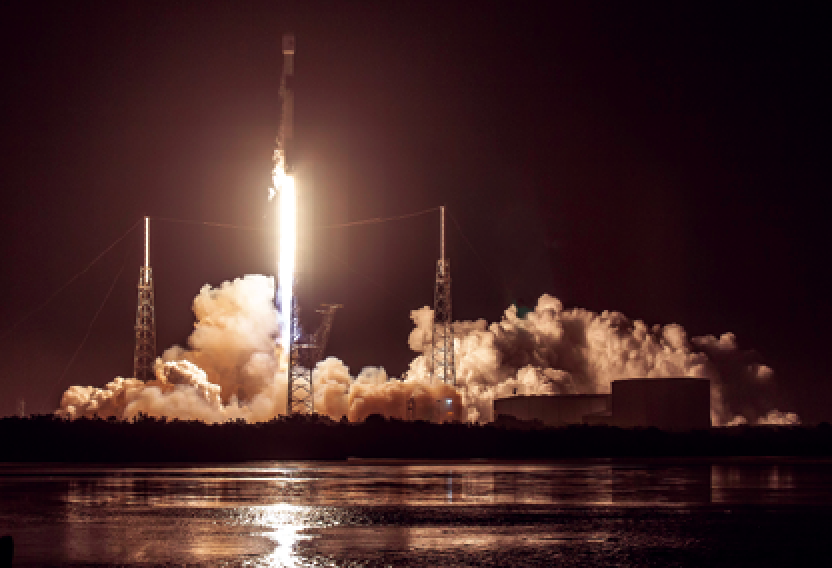

The launch of the Kacific1 and JCSAT-18
satellites via a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. Launch
photo is courtesy of SpaceX.
Owned by Kacific Broadband Satellites Group (Kacific), the Boeing-built communications satellite will stream high-speed broadband to 25 nations in South East Asia and the Pacific Islands via 56 high-throughput beams.
Kacific1 will cover Indonesia, The Philippines, Timor-Leste and South Asia with 28 spot beams, while the Pacific Islands and New Zealand will be covered with a further 28 beams.

Following a sequence of on-orbit maneuvers and tests that are expected to take approximately six weeks, Kacific1 is scheduled to begin commercial operations in the first quarter of 2020.
Christian Patouraux, Kacific founder and CEO, said Kacific1 is the newest and most powerful commercial satellite operating in the Asia-Pacific region, placing Kacific in an excellent position to grow alongside these markets. The satellites range of services, from mobile backhaul to broadband internet via VSAT terminals, will provide a catalyst for positive change in the nations it is about to serve. The company is thrilled to start seeing the social and economic impact of Kacific1.

Kacific’s first launch was celebrated in Florida by more than 160 guests from across Asia Pacific who represented telecommunication and internet service provider customers, government agencies and regulators, not-for-profit organisations, universities and Kacific investors, management and staff.
Patouraux added that celebrating this launch with Kacific’s international supporters has been an incredible and affirming experience.
A new fairing from RUAG Space ensures a quieter journey to space...
RUAG Space has successfully developed and tested a new, low shock, jettison system funded by the Future Launchers Preparatory Program (FLPP) of the European Space Agency (ESA).
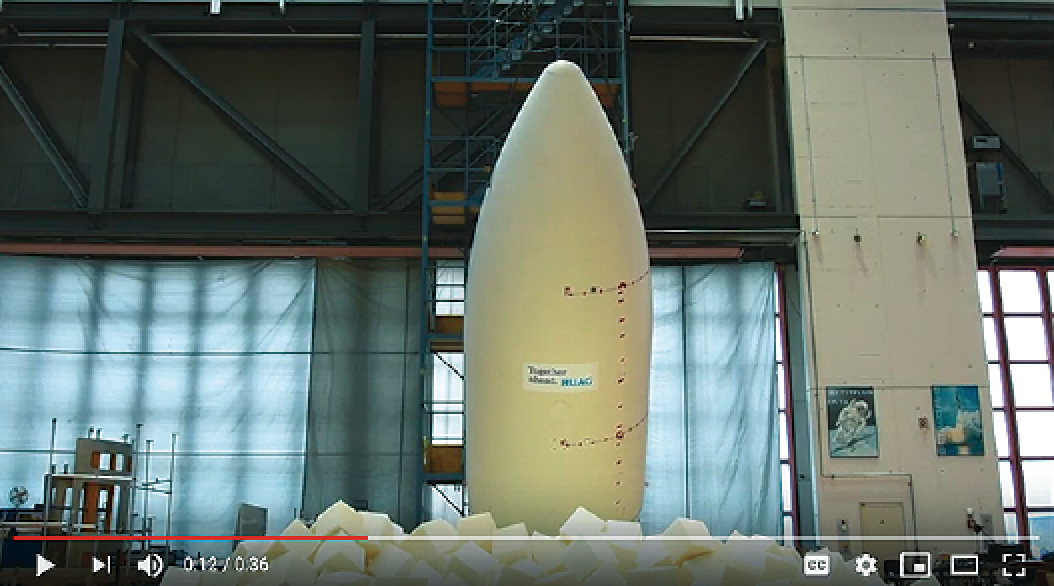

This news system enables a quieter and smoother journey to space for satellites or other payloads. The required payload fairings for the European launchers Ariane and VEGA have been produced by RUAG Space in Emmen, Switzerland, since the 1970s.
“This new solution enables a quieter journey to space,” said Peter Guggenbach, Executive Vice President RUAG Space.
More Comfort, Thanks to Low Shock Load
The payload fairing protects the satellite from aerodynamic and thermal loads during flight. After passing through dense atmospheric layer, and as soon as the satellite is no longer at risk, the payload fairing is separated from the launch vehicle.
As a rule, two pyrotechnic mechanisms are fired to open hinges, allowing the half-shells to separate safely from the payload. Pyrotechnics is a proven technology which may generate significant shock during activation and may result in excitation that needs to be considered in the design of the launcher and payload hardware.
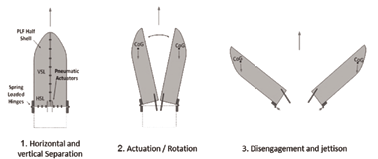
Lower Development Costs and Simpler Test Conditions
The separation and jettison system has a modular design and reduces development costs, as parts can be improved or replaced without affecting the entire system. Testing is easier and the mechanism does not require synchronization. The tests were carried out at the RUAG Space site in Emmen on Vega payload fairing.
“The new system is scalable and could also be used for, for instance, for the European launch vehicle Ariane,” explained Guggenbach.

In addition to the successful separation test, a significant noise reduction was achieved. An integrated sound-reducing perforated insulation layer within the sandwich panels of the payload fairing enables noise reduction without increasing mass and volume.
In certain frequency bands, this system could replace acoustic absorber mats currently used in payload fairings. Testing and evaluation of this new system will continue in the next phase of the project.
Satellogic acquires $50 million in new funding
Satellogic has received $50 million in funding from new and existing investors — this announcement comes on the heels of Satellogic’s $38 million Dedicated Satellite Constellation (DSC) agreement with ABDAS to deliver access to a dedicated fleet of satellites providing them with high-resolution geospatial insights that will contribute to the monitoring of agriculture over the Henan Province in China and strengthen governmental decisions.
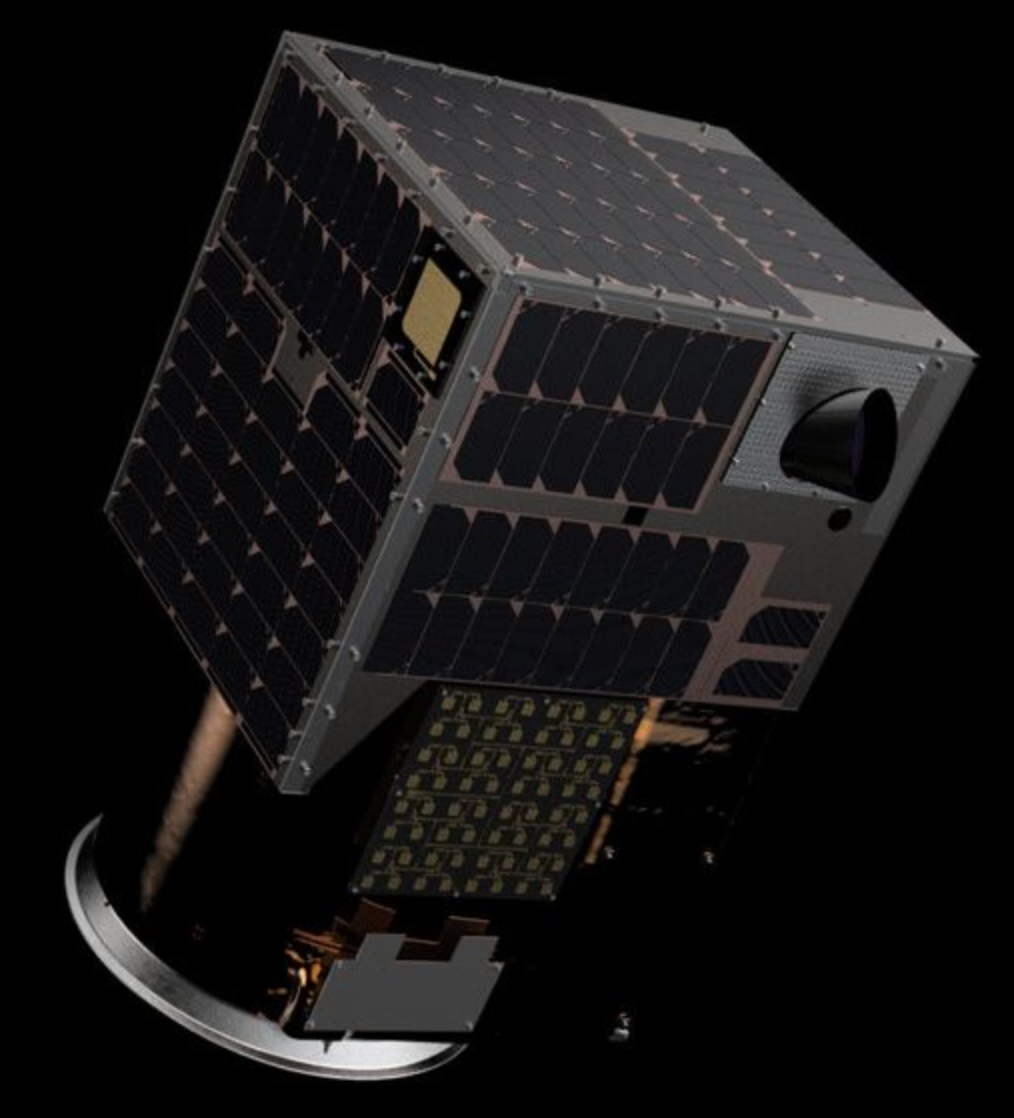

Artistic rendition of a Satellogic satellite.
Image is courtesy of the company.
Existing investors, including Tencent and Pitanga, contributed approximately 40 percent of the $50 million in newly announced funding, with some existing investors requesting more than their pro rata share. The remaining capital comes from a number of new financial and strategic investors, including the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), through IDB Lab, the innovation laboratory of the IDB Group. Pitanga, also based in the Latin American region, invests in innovative companies with high growth potential and is among the existing investors contributing to Satellogic’s newly announced funding.
Satellogic recently closed a $38 million agreement with ABDAS, a data science company established under the technical support of the Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth. The agreement gives ABDAS access to a Dedicated Satellite Constellation and geospatial analytics that will provide them with multi-spectral imagery for monthly remapping of sites they define within their departmental territory and derive insights through their in-house data science capabilities. Through the partnership, ABDAS is able to leverage their constellation to strengthen and support key policy decisions in the province, with no capital outlay and no technical or operational risks.
Today, less than one-third of the countries in the world have their own satellites orbiting the Earth, limiting their ability to capture data about their policy implementation and infrastructure. However, that landscape is changing. One recent report valued the geospatial analytics market at $19.59 billiion 2018 and predicted that it will reach a value of $29.28 billion by 2024. In this report, government interest was noted as a key driver of growth.
New investor, IDB Lab, sees an opportunity for Satellogic to have a meaningful impact in Latin America and the Caribbean in particular. IDB Lab’s financing will be specifically directed toward Satellogic’s development of user-end satellite imagery solutions in these sectors.
Tomás Lopes Teixeira, Senior Investment Officer at IDB Lab, said the company’s mission is to leverage innovation toward inclusion in Latin American and the Caribbean. The firm is excited to support Satellogic’s mission of democratizing access to geospatial analytics solutions, such as monitoring crop growth and preventing the spread of plagues in agriculture to help increase yields and livelihoods of a vast universe of small and medium-sized farmers caught in a low-productivity cycle in the region; improving the reaction time and accuracy in natural disaster response, which typically disproportionately impacts vulnerable populations; and preventing deforestation.
Fernando Reinach, Partner, Pitanga Fund, added that as an investor that has continued to support Satellogic through multiple phases of growth and development, the company is excited to see the market dynamics shift toward what our team has been building since 2010. Governments and industry alike now recognize the power of geospatial analytics and Satellogic is a proven partner. When choosing where to invest and reinvest, Pitanga seeks to fund companies that have the potential to be disruptive and capture a significant portion of large markets in a short time. In this regard, Satellogic is the perfect archetype of the Pitanga portfolio.
Satellogic Founder and CEO, Emiliano Kargieman, noted that the company is experiencing significant commercial momentum and the firm is grateful to have investors that want to fuel that growth and help Satellogic service the demand for the company’s Dedicated Satellite Constellation (DSC) and Dedicated Satellite Services (DSS) solutions. Given the commercial success with Satellogic’s DSC bookings and pipeline, in particular, the firm is fortunate to be in a position to use that cash flow to better leverage investor capital in executing the company’s business plan.
Mitsubishi Electric is the Prime for new smallsat platform
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation announced the company has been designated by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) as the prime contractor of the new satellite for Innovative Satellite Technology Demonstration-2.
Artistic rendition of the new satellite for Innovative
Satellite Technology Demonstration-2 on-orbit.
Image is courtesy of Mitsubishi Electric.
Under the program, Mitsubishi Electric aims to establish a standardized platform for designing, manufacturing and operating small 100 kg. class satellites incorporating standard parts for key functions such as attitude control and power supply.
The new platform will enable unified functions and services provided via a global constellation of smallsats.
Innovative Satellite Technology Demonstration-2 is a part of a Japanese government program aiming for the stable supply of core components to the nation’s space program.
The purpose of the new satellite developed under JAXA for this program is for in-orbit verifications and demonstrations of equipment, parts and smallsats developed by private companies, universities or other entities.
In particular, it will help to establish a standardized platform for developing small 100 kg. class satellites equipped with standard components and equipment, selected for use by JAXA through an open invitation in fiscal year of 2018.
The program requires the prime contractor to develop a platform that will facilitate the faster and less costly development of small satellites in comparison to the development of mid-sized or large satellites.
The satellite is scheduled to be launched on an Epsilon Launch Vehicle from Uchinoura Space Center in Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan in the fiscal year ending in March 2022.
Globally, smallsats are being developed for use in constellations that are comprised of dozens of small satellites that will cover the entire world.
The constellations will perform coordinated operations for a wide range of new services, such as truly globalized internet access or services based on daily photography of the entire world.
Numerous private-sector services are expected to make good use of smallsats covering the entire globe.
Going forward, Mitsubishi Electric will develop the new satellite for Innovative Satellite Technology Demonstration-2 and a standardized platform for small 100kg-class satellites, which the company will use, along with its well-established DS2000 platform for large standardized satellites, to meet a growing range of needs.
Steady growth for commercial space value chain, says Euroconsult
In its latest research titled, “The Space Economy Report 2019,” Euroconsult projects that the commercial space value chain will see steady growth over the next decade, reaching $485 billion by 2028.
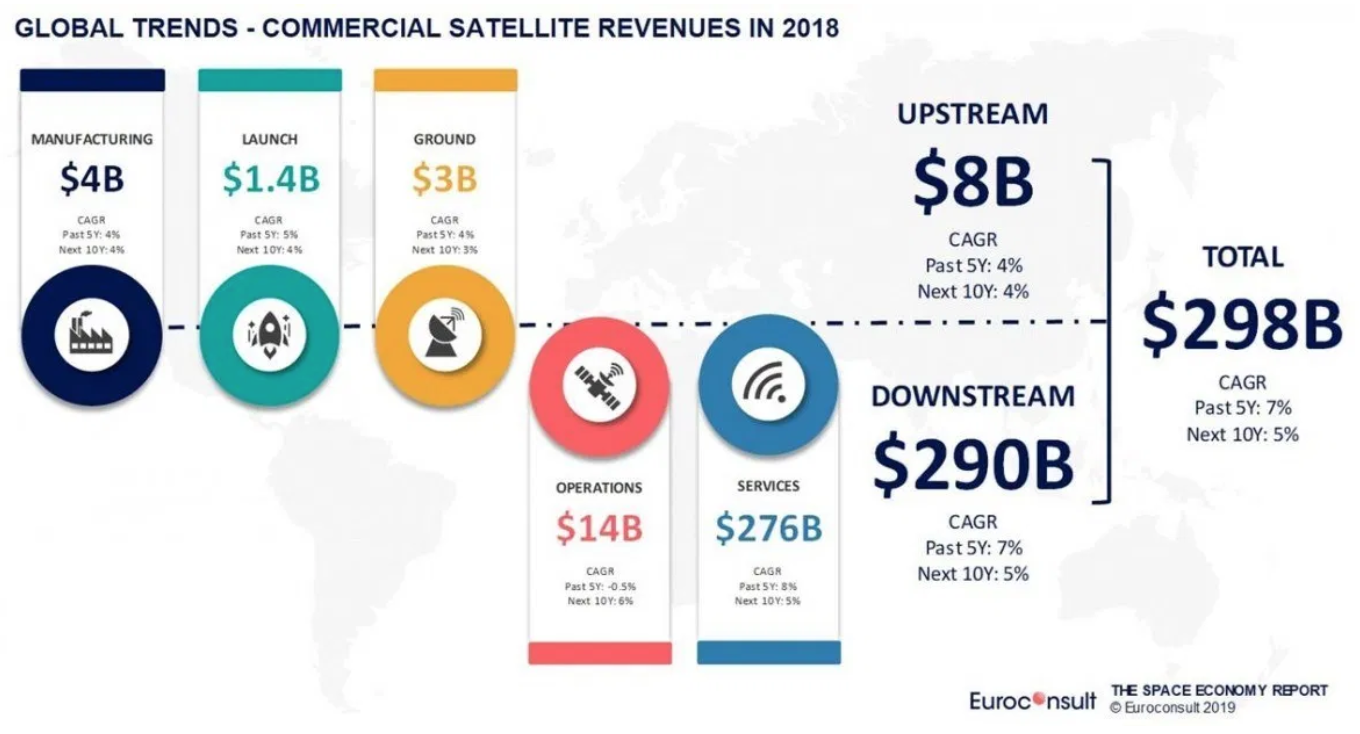
The upstream segment, which includes commercial revenues from manufacturing, launch and ground equipment is expected to increase from $8 billion in 2018 to $11 billion in 2028, a growth rate of four percent per year.
The downstream segment consisting of commercial operations and satellite services, including satellite navigation, was valued at $290 billion in 2018, projected to increase at a rate of five percent per year to reach $474 billion in 2028.
The research highlights global trends with key metrics for each of five satellite segments including manufacturing and launch, ground segment, satellite communications, Earth observation and satellite navigation. It shows that 2018 was the first year for satellite navigation to overtake satellite communications as the top commercial revenue sector.
Detailing key events from 2019 and their impact on the market, the report documents the last five years for historical trends and includes forecasts for each segment over the next ten years.
Previously called the Satellite Value Chain Report, the research has evolved to include more detail on the ground segment with an outlook on commercial ground stations and antennas for both Earth Observation and communications as well as an outlook for satcom user terminals.
“Our Space Economy Report consolidates data from across our 2019 research to provide a broad perspective on key trends and indicators and an overview of the global industry landscape,” said Steve Bochinger, Editor-in-Chief of the Research and COO of Euroconsult.


